HibernateSummary
Hibernate provides caching and snapshot mechanisms in order to improve performance.
Its cache is divided into first-level cache and second-level cache.
Hibernate first-level cache: When a Sql statement is executed in a transaction, the returned results are stored in the Map collection in the Session (of course, there are also snapshots).
Test: (all the following codes are in try/catch blocks)
Configuration config=new Configuration().configure();//configure()方法是加载src/hibernate.cfg.xml配置文件
SessionFactory sf=config.buildSessionFactory();
Session s=sf.openSession();//Session是高一级的对Connection的封装
Transaction tran=null;
try {
tran=s.beginTransaction();
//代码在此
tran.commit();
} catch (HibernateException e) {
if(tran!=null){
tran.rollback();
}
e.printStackTrace();
} finally{
s.close();
sf.close();
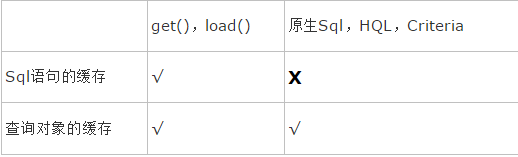
}Query: including get(), load(), native Sql, HQL, Criteria (a more object-oriented query method than HQL)
//1.get(),load()方法测试
User u=(User) s.get(User.class, 1);//第一次查询生成SQL语句,并将结果放入缓存
User u1=(User) s.get(User.class, 1);//第二次查询并无生成SQL语句,但结果取自缓存
p(u==u1);//true
//2.HQL查询
Query q=s.createQuery("from domain.User where id=1");
User u2=(User) q.uniqueResult();//第三次查询生成了SQL语句,但结果取自缓存
p(u2==u);//true
//3.原生Sql
SQLQuery q1=s.createSQLQuery("select * from User where id=1");
q1.addEntity(User.class);
User u3=(User) q1.uniqueResult();//第四次查询生成了SQL语句,但结果取自缓存
p(u3==u);//true
//4.Criteria查询
Criteria c=s.createCriteria(User.class);
c.add(Restrictions.eq("id", 1));
User u4=(User) q1.uniqueResult();//第五次查询生成了SQL语句,但结果取自缓存
p(u4==u);//trueSummary query:
Added: save(), persist()
User user = new User();//对象的瞬态
user.setName("xiaobai");
user.setAge(121);
s.save(user);//对象的持久态
s.persist(user);The difference between the two methods here is: the problem of setting the primary key before executing the method and the problem of returning the primary key after executing the method.
1, persist(), persists a transient instance, but there is no guarantee that the identifier (the attribute corresponding to the identifier primary key) will be filled in to the persistent instance immediately, and the filling in of the identifier may be delayed. When it’s time to flush.
2. save(), generates a transient instance persistence identifier in time. It returns the identifier, so it will execute Sql insert immediately.
User u = new User();
u.setName("xiaobai");
u.setAge(121);
s.save(u);//插入数据库,并将对象瞬态转为持久态,将返回对象存入缓存
User u1=(User) s.get(User.class, u.getId());//这次查询没有生成SQL语句,结果取自Session的缓存
p(u1==u);//trueDelete: delete()
User u=(User) s.get(User.class, 10);//Perform query operation
s.delete(u);//Convert the object’s persistent state to a free state
Of course, if you feel that in order to delete a piece of data, performing query operations will reduce performance, you can do this:
User u=new User();
u.setId(5);
s.delete(u);
Update: update()
User u=(User) s.get(User.class, 1);
u.setName("set");
But sometimes, we don’t need to execute s.update( Object) method, which involves a feature of the persistent state of the object (also [snapshot] plays a role in it):
When the object is persistent, when it updates data, the framework will compare it with the previous snapshot. If If they are the same, no action will be taken; if they are different, they will be automatically updated to the database.
//当然,也可以这么做
User u=new User();//对象的瞬态,不具备自动更新功能,需要我们手动update()
u.setAge(1);
u.setId(1);
u.setName("1");
s.update(u);Summary:
One point is very important: although the Sql statement is formed in the transaction, the database will only be actually operated after transaction.commit().
Hibernate needs to figure out [cache, snapshot, object three-state] and other things about database operations.
Three states of objects:
* Transient state: Not related to hibernate, no corresponding id in the database table
* Persistent state: Related to hibernate, there is a corresponding id---OID in the database table
* Free state : Not related to hibernate, there is a corresponding id in the database table

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to integrate Hibernate in SpringBoot project
May 18, 2023 am 09:49 AM
How to integrate Hibernate in SpringBoot project
May 18, 2023 am 09:49 AM
Integrating Hibernate in SpringBoot Project Preface Hibernate is a popular ORM (Object Relational Mapping) framework that can map Java objects to database tables to facilitate persistence operations. In the SpringBoot project, integrating Hibernate can help us perform database operations more easily. This article will introduce how to integrate Hibernate in the SpringBoot project and provide corresponding examples. 1.Introduce dependenciesIntroduce the following dependencies in the pom.xml file: org.springframework.bootspring-boot-starter-data-jpam
 Java Errors: Hibernate Errors, How to Handle and Avoid
Jun 25, 2023 am 09:09 AM
Java Errors: Hibernate Errors, How to Handle and Avoid
Jun 25, 2023 am 09:09 AM
Java is an object-oriented programming language that is widely used in the field of software development. Hibernate is a popular Java persistence framework that provides a simple and efficient way to manage the persistence of Java objects. However, Hibernate errors are often encountered during the development process, and these errors may cause the program to terminate abnormally or become unstable. How to handle and avoid Hibernate errors has become a skill that Java developers must master. This article will introduce some common Hib
 What are the differences between hibernate and mybatis
Jan 03, 2024 pm 03:35 PM
What are the differences between hibernate and mybatis
Jan 03, 2024 pm 03:35 PM
The differences between hibernate and mybatis: 1. Implementation method; 2. Performance; 3. Comparison of object management; 4. Caching mechanism. Detailed introduction: 1. Implementation method, Hibernate is a complete object/relational mapping solution that maps objects to database tables, while MyBatis requires developers to manually write SQL statements and ResultMap; 2. Performance, Hibernate is possible in terms of development speed Faster than MyBatis because Hibernate simplifies the DAO layer and so on.
 What is the mapping method of one-to-many and many-to-many relationships in Java Hibernate
May 27, 2023 pm 05:06 PM
What is the mapping method of one-to-many and many-to-many relationships in Java Hibernate
May 27, 2023 pm 05:06 PM
Hibernate's one-to-many and many-to-many Hibernate is an excellent ORM framework that simplifies data access between Java applications and relational databases. In Hibernate, we can use one-to-many and many-to-many relationships to handle complex data models. Hibernate's one-to-many In Hibernate, a one-to-many relationship means that one entity class corresponds to multiple other entity classes. For example, an order can correspond to multiple order items (OrderItem), and a user (User) can correspond to multiple orders (Order). To implement a one-to-many relationship in Hibernate, you need to define a collection attribute in the entity class to store
 How to perform bulk insert update operations in Hibernate?
Aug 27, 2023 pm 11:17 PM
How to perform bulk insert update operations in Hibernate?
Aug 27, 2023 pm 11:17 PM
In this article, we will see how to perform bulk insert/update in Hibernate. Whenever we execute a sql statement, we do it by making a network call to the database. Now, if we have to insert 10 entries into the database table, then we have to make 10 network calls. Instead, we can optimize network calls by using batch processing. Batch processing allows us to execute a set of SQL statements in a single network call. To understand and implement this, let us define our entity − @EntitypublicclassParent{@Id@GeneratedValue(strategy=GenerationType.AUTO)
 Introduction to Hibernate framework in Java language
Jun 10, 2023 am 11:35 AM
Introduction to Hibernate framework in Java language
Jun 10, 2023 am 11:35 AM
Hibernate is an open source ORM framework that binds the data mapping between relational databases and Java programs to each other, making it easier for developers to access data in the database. Using the Hibernate framework can greatly reduce the work of writing SQL statements and improve the development efficiency and reusability of applications. Let's introduce the Hibernate framework from the following aspects. 1. Advantages of the Hibernate framework: object-relational mapping, hiding database access details, making development
 In-depth understanding of the Java framework technology stack: explore common Java frameworks such as Spring MVC, Hibernate, MyBatis, etc.
Dec 26, 2023 pm 12:50 PM
In-depth understanding of the Java framework technology stack: explore common Java frameworks such as Spring MVC, Hibernate, MyBatis, etc.
Dec 26, 2023 pm 12:50 PM
Java framework technology stack: Introducing commonly used Java frameworks, such as SpringMVC, Hibernate, MyBatis, etc. With the continuous development of Java, more and more frameworks have been developed to simplify the development process. Among them, SpringMVC, Hibernate, MyBatis, etc. are one of the most commonly used frameworks in Java development. This article will introduce the basic concepts and usage of these frameworks to help readers better understand and apply these frameworks. First, let’s introduce Sp
 How does Hibernate second level cache work?
Sep 14, 2023 pm 07:45 PM
How does Hibernate second level cache work?
Sep 14, 2023 pm 07:45 PM
Caching helps reduce database network calls when executing queries. Level 1 cache and session linking. It is implemented implicitly. The first level cache exists until the session object exists. Once the session object is terminated/closed, there will be no cached objects. Second level cache works for multiple session objects. It is linked with the session factory. Second level cache objects are available to all sessions using a single session factory. These cache objects will be terminated when a specific session factory is closed. To implement the second level cache we need to add the following dependencies to use the second level cache. <!--https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/net.sf.ehcache/ehcache--><de






