Java Web simple paging display example code
This article mainly introduces the relevant information of Java Web simple paging display example code. This article achieves the paging effect by calculating the total number of pages and querying the specified page data. It is very good and has reference value. Friends in need You can refer to
This article uses two methods: (1) Calculate the total number of pages. (2) Query the specified page data to achieve a simple paging effect.
Idea: First of all, you must provide a paging query method in the DAO object. Call this method in the control layer to find the data of the specified page, and display the data of the page through EL expressions and JSTL in the presentation layer.
Let me show you the renderings first:
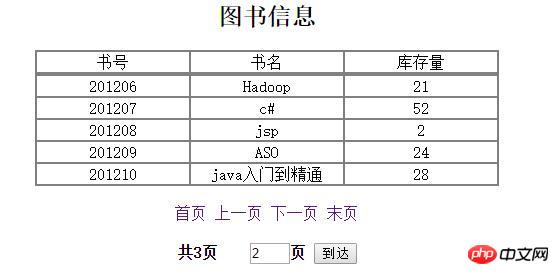
Digression: The paging display is implemented using the design idea of "presentation layer-control layer-DAO layer-database". Is there anything that needs to be improved? Let’s bring it up and learn and make progress together. Without further ado, let’s get into the topic. The detailed steps are as follows:
1. DAO layer - database
The JDBCUtils class is used to open and close the database. The core code is as follows:
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class JDBCUtils {
private Connection conn=null;
private PreparedStatement pstmt=null;
/**
* connect 连接数据库
* @return
*/
public Connection connect(){
String user="root";
String password="1234";
String driverClass = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver";
String jdbcUrl = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/book";
try {
Class.forName(driverClass);
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(jdbcUrl, user, password);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
return conn;
}
/**
* close 关闭数据库
* @param conn
* @param pstmt
* @param resu
*/
public void close(Connection conn,PreparedStatement pstmt,ResultSet result){
if(conn != null){
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
}
}
if(pstmt != null){
try {
pstmt.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(result != null){
try {
result.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}The method getPage() and the method listUser() in the UserDao class are used to calculate the total number of pages and query the data of the specified page respectively. The core code is as follows:
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import com.db.JDBCUtils;
public class UserDao {
/**
* 计算总的页数
* @return
*/
public int getPage(){
int recordCount=0,t1=0,t2=0;
PreparedStatement pstmt=null;
ResultSet result=null;
JDBCUtils jdbc=new JDBCUtils();
Connection conn=jdbc.connect();
String sql="select count(*) from books";
try {
pstmt=conn.prepareStatement(sql);
result=pstmt.executeQuery();
result.next();
recordCount=result.getInt(1);
t1=recordCount%5;
t2=recordCount/5;
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
jdbc.close(conn, pstmt, result);
}
if(t1 != 0){
t2=t2+1;
}
return t2;
}
/**
* 查询指定页的数据
* @param pageNo
* @return
*/
public List<User> listUser(int pageNo){
PreparedStatement pstmt=null;
ResultSet result=null;
List<User> list=new ArrayList<User>();
int pageSize=5;
int page=(pageNo-1)*5;
JDBCUtils jdbc=new JDBCUtils();
Connection conn=jdbc.connect();
String sql="select * from books order by id limit ?,?";
try {
pstmt=conn.prepareStatement(sql);
pstmt.setInt(1, page);
pstmt.setInt(2, pageSize);
result=pstmt.executeQuery();
while(result.next()){
User user=new User();
user.setId(result.getInt(1));
user.setName(result.getString(2));
user.setNumber(result.getString(3));
list.add(user);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
jdbc.close(conn, pstmt, result);
}
return list;
}
}The User class is used to store the queried data. The core The code is as follows:
public class User {
private int id;
private String name;
private String number;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getNumber() {
return number;
}
public void setNumber(String number) {
this.number = number;
}
}2. Control layer
ListUser class internally calls the UserDao object to query data and assign the page to display the data. The core code is as follows:
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import com.dao.User;
import com.dao.UserDao;
public class ListUser extends HttpServlet {
public ListUser() {
super();
}
public void destroy() {
super.destroy(); // Just puts "destroy" string in log
// Put your code here
}
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
doPost(request, response);
}
public void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
response.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
int pageNo = 1;
UserDao userdao=new UserDao();
List<User> lists=new ArrayList<User>();
String pageno=request.getParameter("pageNos");
if(pageno != null){
pageNo=Integer.parseInt(pageno);
}
lists=userdao.listUser(pageNo);
int recordCount=userdao.getPage();
request.setAttribute("recordCount", userdao.getPage());
request.setAttribute("listss", lists);
request.setAttribute("pageNos", pageNo);
request.getRequestDispatcher("userlist.jsp").forward(request, response);
}
public void init() throws ServletException {
// Put your code here
}
} 3. The presentation layer
outputs the page userlist.jsp, using EL and JSTL to output query results. The core code is as follows:
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<%@ taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" %>
<%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/fmt" prefix="fmt"%>
<%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/functions" prefix="fn"%>
<%
String path = request.getContextPath();
String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path+"/";
%>
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN">
<html>
<head>
<base href="<%=basePath%>">
<title>My JSP 'userlist.jsp' starting page</title>
<meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="expires" content="0">
<meta http-equiv="keywords" content="keyword1,keyword2,keyword3">
<meta http-equiv="description" content="This is my page">
<!--
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="styles.css">
-->
<style type="text/css">
th,td{width: 150px;border: 2px solid gray;text-align: center;}
body{text-align: center;}
a{text-decoration: none;}
table {border-collapse: collapse;}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h2 align="center">图书信息</h2>
<table align="center">
<tr><td>书号</td><td>书名</td><td>库存量</td></tr>
</table>
<table align="center">
<c:forEach items="${listss}" var="person">
<tr>
<td class="hidden-480">${person.id}</td>
<td class="hidden-480">${person.name }</td>
<td class="hidden-480">${person.number }</td>
</tr>
</c:forEach>
</table>
<br>
<c:if test="${pageNos>1 }">
<a href="ListUser?pageNos=1" >首页</a>
<a href="ListUser?pageNos=${pageNos-1 }">上一页</a>
</c:if>
<c:if test="${pageNos <recordCount }">
<a href="ListUser?pageNos=${pageNos+1 }">下一页</a>
<a href="ListUser?pageNos=${recordCount }">末页</a>
</c:if>
<form action="ListUser">
<h4 align="center">共${recordCount}页  
<input type="text" value="${pageNos}" name="pageNos" size="1">页
<input type="submit" value="到达">
</h4>
</form>
</body>
</html>The above is the simple paging display example code of Java Web introduced by the editor. , I hope it will be helpful to you. If you have any questions, please leave me a message and the editor will reply to you in time. I would also like to thank you all for your support of the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Perfect Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check Perfect number in Java?, examples with code implementation.
 Random Number Generator in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:27 PM
Random Number Generator in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:27 PM
Guide to Random Number Generator in Java. Here we discuss Functions in Java with examples and two different Generators with ther examples.
 Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Weka in Java. Here we discuss the Introduction, how to use weka java, the type of platform, and advantages with examples.
 Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Smith Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check smith number in Java? example with code implementation.
 Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
In this article, we have kept the most asked Java Spring Interview Questions with their detailed answers. So that you can crack the interview.
 Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8 introduces the Stream API, providing a powerful and expressive way to process data collections. However, a common question when using Stream is: How to break or return from a forEach operation? Traditional loops allow for early interruption or return, but Stream's forEach method does not directly support this method. This article will explain the reasons and explore alternative methods for implementing premature termination in Stream processing systems. Further reading: Java Stream API improvements Understand Stream forEach The forEach method is a terminal operation that performs one operation on each element in the Stream. Its design intention is
 TimeStamp to Date in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
TimeStamp to Date in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to TimeStamp to Date in Java. Here we also discuss the introduction and how to convert timestamp to date in java along with examples.
 Java Program to Find the Volume of Capsule
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Java Program to Find the Volume of Capsule
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Capsules are three-dimensional geometric figures, composed of a cylinder and a hemisphere at both ends. The volume of the capsule can be calculated by adding the volume of the cylinder and the volume of the hemisphere at both ends. This tutorial will discuss how to calculate the volume of a given capsule in Java using different methods. Capsule volume formula The formula for capsule volume is as follows: Capsule volume = Cylindrical volume Volume Two hemisphere volume in, r: The radius of the hemisphere. h: The height of the cylinder (excluding the hemisphere). Example 1 enter Radius = 5 units Height = 10 units Output Volume = 1570.8 cubic units explain Calculate volume using formula: Volume = π × r2 × h (4




