When I first came into contact with the web, I was in college. The first web page I wrote was a login page. At that time, it used a table layout, which was quite satisfactory. After coming into contact with CSS, I always use div+css for layout, which achieves the separation of performance and structure and is very flexible. Although I have been exposed to the layout method of CSS for a long time, I don't use it often, so many things have been forgotten. Recently, I have been tinkering with the layout of CSS, so I wanted to record it here as my own study notes.
The css box model is a relatively core concept in css. In a web page, we can think of all web page elements as a box. A box consists of four parts: margins, borders, inner margins, and content, as shown below.
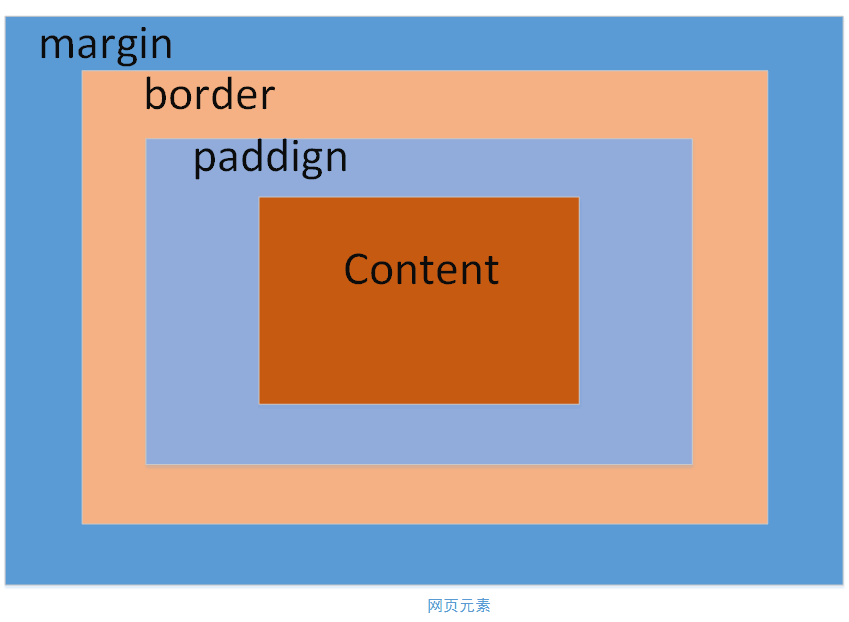
The following explains the functions of these four parts in order from outside to inside.
margin (margin): represents the margin between this element and other elements. It should be noted that if two adjacent elements have a margin value set, the largest value shall prevail. For example, for two adjacent divs, if the upper div is set to margin: 30px and the lower div is set to margin: 50px, then the final distance between the two elements will not be 30+20=50px, but will be 30px.
border (border): represents the border of this web page element. The border can set the size, background (color or picture), style (implementation or dotted line, etc.).
padding (padding): represents the distance between the element content and the border. You can call it the white space of the element.
content (content): represents the content area of the element, such as the size of the text.
Among them, margins, borders, and padding can be applied to the top, bottom, left, and right sides of the element, or to each individual side. In particular, the margins can also be set to negative values. In some special occasions, negative values for the margins are needed.
Generally, we set the width and height of an element, usually the width and height of the padding+content area, excluding margin and border.
When I set the background color of an element, the background will only be applied to the area within the border of the element, that is, padding+content, and the background color of the margin and border areas will not be changed.
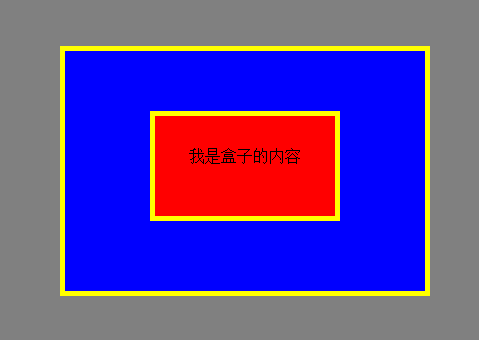
An example will be demonstrated below. The code is as follows:
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<style type="text/css">
body{
background:gray;
}
div{
height: 240px;
width: 360px;
border: 5px solid yellow;
background: blue;
margin: 50px auto;
}
span{
display:block;
margin:60px auto;
border:5px solid yellow;
width:180px;
height:100px;
text-align:center;
line-height:80px;
vertical-align: middle;
background-color:red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<span>
我是盒子的内容 </span>
</div>
</body>
</html>The effect is as follows: