Python network programming
Understand Socket
Socket is also commonly called "socket", which is used to describe IP addresses and ports. It is the handle of a communication chain. Applications usually make requests to the network or respond to network requests through "sockets".
Socket originated from Unix, and one of the basic philosophies of Unix/Linux is "everything is a file". For files, use the [Open] [Read and Write] [Close] mode to operate. Socket is an implementation of this mode. Socket is a special file. Some socket functions are operations on it (read/write IO, open, close). The difference between socket and file:
file module is for [Open] [Read and Write] [Close] a specified file
The socket module is for server-side and client-side Sockets to [Open] [Read and Write] [Close]
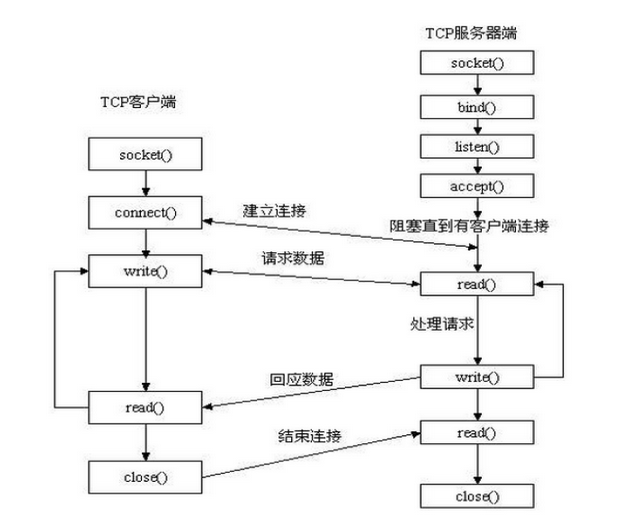
ython (version 3.5 ) To achieve the simplest socket communication
#!/usr/bin/env python # coding=utf-8 # Author:Majh import socket ip_port = ('127.0.0.1', 9999) sk = socket.socket() sk.connect(ip_port) send_data = input('>>').strip() sk.send(bytes(send_data, encoding='utf-8')) recv_data = sk.recv(1024) print(str(recv_data, encoding='utf-8')) sk.close() 客户端代码
#!/usr/bin/env python # coding=utf-8 # Author:Majh import socket sk = socket.socket() ip_port = ('127.0.0.1', 9999) sk.bind(ip_port) print('sk.bind......') sk.listen(5) print('sk.listen......') conn, addr = sk.accept() print('conn:', conn) print('addr:', addr) read_data = conn.recv(1024) print('read_data', read_data) read_data = read_data.upper() conn.send(read_data) conn.close() 服务器端代码
socket keyword parameters:
sk = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,socket.SOCK_STREAM,0)
Parameter 1: Address cluster
socket.AF_INET IPv4 (default)
socket.AF_INET6 IPv6
socket.AF_UNIX can only be used for inter-process communication in a single Unix system
Parameter 2: Type
socket.SOCK_STREAM Streaming socket, for TCP (default)
socket.SOCK_DGRAM Datagram socket , for UDP
socket.SOCK_RAW raw socket. Ordinary sockets cannot process network messages such as ICMP and IGMP, but SOCK_RAW can. Secondly, SOCK_RAW can also process special IPv4 messages. In addition, using raw sockets word, the IP header can be constructed by the user via the IP_HDRINCL socket option.
socket.SOCK_SEQPACKET Reliable continuous packet service
Parameter three: Protocol
0 (Default) The protocol related to a specific address family. If it is 0, the system will automatically select it based on the address format and socket category. A suitable protocol
sk.bind(address)
s.bind(address) binds the socket to the address. The format of address depends on the address family. Under AF_INET, the address is expressed in the form of a tuple (host, port).
sk.listen(backlog)
Start listening for incoming connections. The backlog specifies the maximum number of connections that can be pending before the connection is rejected.
Backlog equals 5, indicating that the kernel has received the connection request, but the server has not yet called accept for processing. The maximum number of connections is 5
This value cannot be infinite because the connection queue must be maintained in the kernel
sk.setblocking( bool)
Whether to block (default True), if set to False, an error will be reported if there is no data during accept and recv.
sk.accept()
Accept the connection and return (conn, address), where conn is a new socket object that can be used to receive and send data. address is the address to connect to the client.
Receive the connection from the TCP client (blocking) and wait for the connection to arrive
sk.connect(address)
Connect to the socket at address. Generally, the format of address is a tuple (hostname, port). If a connection error occurs, a socket.error error is returned.
sk.connect_ex(address)
Same as above, except there will be a return value, 0 is returned when the connection is successful, and the code is returned when the connection fails, for example: 10061
sk.close()
Close the socket
sk .recv(bufsize[,flag])
Accepts socket data. The data is returned as a string, and bufsize specifies the maximum number that can be received. flag provides additional information about the message and can usually be ignored.
sk.recvfrom(bufsize[.flag])
Similar to recv(), but the return value is (data, address). Where data is a string containing the received data, and address is the socket address to which the data is sent.
sk.send(string[,flag])
Send the data in string to the connected socket. The return value is the number of bytes to send, which may be less than the string's byte size. That is: all specified content may not be sent.
sk.sendall(string[,flag])
Sends the data in string to the connected socket, but attempts to send all data before returning. Returns None on success, throws an exception on failure.
Internally, all content is sent out by calling send recursively.
sk.sendto(string[,flag],address)
Send data to the socket, address is a tuple in the form of (ipaddr, port), specifying the remote address. The return value is the number of bytes sent. This function is mainly used for UDP protocol.
sk.settimeout(timeout)
Set the timeout period for socket operations. timeout is a floating point number in seconds. A value of None means there is no timeout period. Generally, the timeout period should be set when the socket is first created, because they may be used for connection operations (such as client connections waiting up to 5s)
sk.getpeername()
Returns the remote address of the connected socket. The return value is usually a tuple (ipaddr, port).
sk.getsockname()
Returns the socket’s own address. Usually a tuple (ipaddr,port)

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 The 2-Hour Python Plan: A Realistic Approach
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:04 AM
The 2-Hour Python Plan: A Realistic Approach
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:04 AM
You can learn basic programming concepts and skills of Python within 2 hours. 1. Learn variables and data types, 2. Master control flow (conditional statements and loops), 3. Understand the definition and use of functions, 4. Quickly get started with Python programming through simple examples and code snippets.
 Python: Exploring Its Primary Applications
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:41 AM
Python: Exploring Its Primary Applications
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:41 AM
Python is widely used in the fields of web development, data science, machine learning, automation and scripting. 1) In web development, Django and Flask frameworks simplify the development process. 2) In the fields of data science and machine learning, NumPy, Pandas, Scikit-learn and TensorFlow libraries provide strong support. 3) In terms of automation and scripting, Python is suitable for tasks such as automated testing and system management.
 How to use AWS Glue crawler with Amazon Athena
Apr 09, 2025 pm 03:09 PM
How to use AWS Glue crawler with Amazon Athena
Apr 09, 2025 pm 03:09 PM
As a data professional, you need to process large amounts of data from various sources. This can pose challenges to data management and analysis. Fortunately, two AWS services can help: AWS Glue and Amazon Athena.
 How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
To read a queue from Redis, you need to get the queue name, read the elements using the LPOP command, and process the empty queue. The specific steps are as follows: Get the queue name: name it with the prefix of "queue:" such as "queue:my-queue". Use the LPOP command: Eject the element from the head of the queue and return its value, such as LPOP queue:my-queue. Processing empty queues: If the queue is empty, LPOP returns nil, and you can check whether the queue exists before reading the element.
 How to view server version of Redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 01:27 PM
How to view server version of Redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 01:27 PM
Question: How to view the Redis server version? Use the command line tool redis-cli --version to view the version of the connected server. Use the INFO server command to view the server's internal version and need to parse and return information. In a cluster environment, check the version consistency of each node and can be automatically checked using scripts. Use scripts to automate viewing versions, such as connecting with Python scripts and printing version information.
 How to start the server with redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:12 PM
How to start the server with redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:12 PM
The steps to start a Redis server include: Install Redis according to the operating system. Start the Redis service via redis-server (Linux/macOS) or redis-server.exe (Windows). Use the redis-cli ping (Linux/macOS) or redis-cli.exe ping (Windows) command to check the service status. Use a Redis client, such as redis-cli, Python, or Node.js, to access the server.
 How to set the Redis memory size according to business needs?
Apr 10, 2025 pm 02:18 PM
How to set the Redis memory size according to business needs?
Apr 10, 2025 pm 02:18 PM
Redis memory size setting needs to consider the following factors: data volume and growth trend: Estimate the size and growth rate of stored data. Data type: Different types (such as lists, hashes) occupy different memory. Caching policy: Full cache, partial cache, and phasing policies affect memory usage. Business Peak: Leave enough memory to deal with traffic peaks.
 What is the impact of Redis persistence on memory?
Apr 10, 2025 pm 02:15 PM
What is the impact of Redis persistence on memory?
Apr 10, 2025 pm 02:15 PM
Redis persistence will take up extra memory, RDB temporarily increases memory usage when generating snapshots, and AOF continues to take up memory when appending logs. Influencing factors include data volume, persistence policy and Redis configuration. To mitigate the impact, you can reasonably configure RDB snapshot policies, optimize AOF configuration, upgrade hardware and monitor memory usage. Furthermore, it is crucial to find a balance between performance and data security.




