Factory Method Pattern
When it comes to factories and assembly lines, the work is repeated over and over again. It is really harder than us coders.
The factory pattern is also used very frequently. Its official explanation is: define an interface for creating objects and let the subclass decide which class to instantiate. The factory pattern defers instantiation of a class to its subclasses.
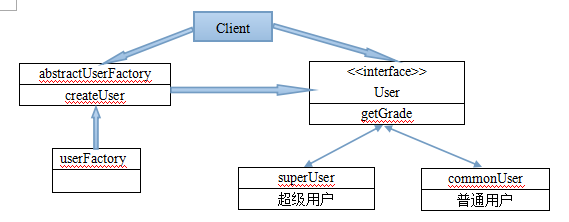
As shown in the figure, there are two types of super users and ordinary users in the system. Define a public interface User class and define a public abstract factory class abstractUserFactory. The userFactory class implements the method createUser to create the User class by inheriting the abstractUserFactory class. , thereby realizing the factory mode, the implementation code is as follows:
Php code
<?php
abstract class abstractUserFactory {
public abstract function createUser();
}
class userFactory extends <span style="font-size: 1em; line-height: 1.5;">abstractUserFactory </span><span style="font-size: 1em; line-height: 1.5;">{</span>
Php代码
public function createUser( $className ) {
try{
if(class_exists($className))
return new $className();
else{
$error = "no class";
throw new Exception($error);
}
}catch( Exception $e ) {
echo 'Caught exception: ', $e->getMessage(), "\n";
}
}
}
interface User{
public function getGrade();
}
class superUser implements User{
public function getGrade() {
echo 1;
}
}
class commonUser implements User{
public function getGrade() {
echo 0;
}
}
$userFactory = new userFactory();
$userFactory->createUser( 'superUser' )->getGrade();
$userFactory->createUser( 'commonUser' )->getGrade();
运行结果:10Caught exception: no class
Advantages of the factory mode:
1. Good encapsulation and clear code structure. The creation of an object is conditionally constrained. For example, if a caller needs a specific product object, he only needs to know the class name (or constraint string) of the product. There is no need to know the arduous process of creating an object, which reduces the coupling between modules. .
2. Very good scalability. In the case of adding product categories, "embracing change" can be completed by appropriately modifying the specific factory class or extending a factory class. For example, in the above example, if you need to add a blue diamond user, you only need to add a blueUser class. The factory class can complete system expansion without modifying tasks.
3. Shielding product categories. This feature is very important. The caller does not need to care about how the implementation of the product class changes. It only needs to care about the interface of the product. As long as the interface remains unchanged, the upper modules in the system should not change.
4. Typical decoupling framework. The high-level module value needs to know the abstract class of the product, and other implementation classes do not need to be concerned. It is in line with Dimit's law. I don't need to communicate if I don't need it. It is also in line with the dependency inversion principle. It only relies on the abstraction of the product class. Of course, it is also in line with According to the substitution principle, use product subclasses to replace product parent classes, no problem!
Usage scenarios of factory pattern:
1. Factory pattern is a replacement for new object, so it can be used wherever objects need to be generated, but you need to carefully consider whether to add a factory class for management and add code complexity.
2. When you need a flexible and extensible framework, you can consider using the factory pattern. Everything is an object, and everything is a product.
3. Factory pattern can be used in heterogeneous projects.
4. You can use the test-driven development framework. For example, to test a class A, you need to generate class B that is related to class A at the same time. We can use the factory pattern to virtualize class B to avoid the coupling between class A and class B. (Currently, Java has jmock and easymock, and this scenario has been weakened).
Extensions of factory pattern:
1. Simple factory pattern (commonly used in PHP)
A module only needs a factory class, there is no need to generate it, just use a static method. According to this Requirements, we modify the abstractUserFactory in the above example, as shown in the figure:
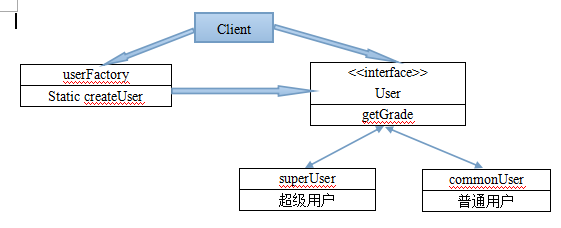
Remove the abstractUserFactory abstract class, and set createUser to a static class, which simplifies the class creation process. Its disadvantage is that it is difficult to extend the factory class and does not comply with the opening and closing principle, but it is still a very practical design pattern.
2. Upgrade to multiple factory classes (one-to-one between products and factories)
Each product class corresponds to a creation class. The advantage is that the responsibilities of the creation class are clear and the structure is simple, but it provides scalability and Maintainability has a certain impact. If you want to extend a product class, you need to create a corresponding factory class, which increases the difficulty of expansion. Because the number of factory classes and products is the same, the relationship between the two objects needs to be considered during maintenance.
Of course, in complex applications, the multi-factory method is generally used, and then a coordination class is added to prevent the caller from communicating with each sub-factory. The function of the coordination class is to encapsulate the sub-factory classes and provide a unified access interface to high-level modules. .
3. Alternative to singleton mode
This mode is implemented by instantiating a class that defines a private no-argument constructor through reflection. Visual inspection is not possible with PHP, so I will skip it here.
4. Delayed initialization
After an object is consumed, it is not released immediately. The factory class maintains its initial state, waiting to be used again. For the PHP interpreted language, it can be extended to lazy loading, that is, the corresponding class file is loaded only when the factory class is ready to create a new object, instead of loading possible classes every time the script is executed.

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 The difference between design patterns and architectural patterns in Java framework
Jun 02, 2024 pm 12:59 PM
The difference between design patterns and architectural patterns in Java framework
Jun 02, 2024 pm 12:59 PM
In the Java framework, the difference between design patterns and architectural patterns is that design patterns define abstract solutions to common problems in software design, focusing on the interaction between classes and objects, such as factory patterns. Architectural patterns define the relationship between system structures and modules, focusing on the organization and interaction of system components, such as layered architecture.
 Analysis of the Decorator Pattern in Java Design Patterns
May 09, 2024 pm 03:12 PM
Analysis of the Decorator Pattern in Java Design Patterns
May 09, 2024 pm 03:12 PM
The decorator pattern is a structural design pattern that allows dynamic addition of object functionality without modifying the original class. It is implemented through the collaboration of abstract components, concrete components, abstract decorators and concrete decorators, and can flexibly expand class functions to meet changing needs. In this example, milk and mocha decorators are added to Espresso for a total price of $2.29, demonstrating the power of the decorator pattern in dynamically modifying the behavior of objects.
 PHP design pattern practical case analysis
May 08, 2024 am 08:09 AM
PHP design pattern practical case analysis
May 08, 2024 am 08:09 AM
1. Factory pattern: Separate object creation and business logic, and create objects of specified types through factory classes. 2. Observer pattern: allows subject objects to notify observer objects of their state changes, achieving loose coupling and observer pattern.
 How design patterns deal with code maintenance challenges
May 09, 2024 pm 12:45 PM
How design patterns deal with code maintenance challenges
May 09, 2024 pm 12:45 PM
Design patterns solve code maintenance challenges by providing reusable and extensible solutions: Observer Pattern: Allows objects to subscribe to events and receive notifications when they occur. Factory Pattern: Provides a centralized way to create objects without relying on concrete classes. Singleton pattern: ensures that a class has only one instance, which is used to create globally accessible objects.
 The wonderful use of the adapter pattern in Java design patterns
May 09, 2024 pm 12:54 PM
The wonderful use of the adapter pattern in Java design patterns
May 09, 2024 pm 12:54 PM
The Adapter pattern is a structural design pattern that allows incompatible objects to work together. It converts one interface into another so that the objects can interact smoothly. The object adapter implements the adapter pattern by creating an adapter object containing the adapted object and implementing the target interface. In a practical case, through the adapter mode, the client (such as MediaPlayer) can play advanced format media (such as VLC), although it itself only supports ordinary media formats (such as MP3).
 PHP Design Patterns: Test Driven Development in Practice
Jun 03, 2024 pm 02:14 PM
PHP Design Patterns: Test Driven Development in Practice
Jun 03, 2024 pm 02:14 PM
TDD is used to write high-quality PHP code. The steps include: writing test cases, describing the expected functionality and making them fail. Write code so that only the test cases pass without excessive optimization or detailed design. After the test cases pass, optimize and refactor the code to improve readability, maintainability, and scalability.
 Application of design patterns in Guice framework
Jun 02, 2024 pm 10:49 PM
Application of design patterns in Guice framework
Jun 02, 2024 pm 10:49 PM
The Guice framework applies a number of design patterns, including: Singleton pattern: ensuring that a class has only one instance through the @Singleton annotation. Factory method pattern: Create a factory method through the @Provides annotation and obtain the object instance during dependency injection. Strategy mode: Encapsulate the algorithm into different strategy classes and specify the specific strategy through the @Named annotation.
 What are the advantages and disadvantages of using design patterns in java framework?
Jun 01, 2024 pm 02:13 PM
What are the advantages and disadvantages of using design patterns in java framework?
Jun 01, 2024 pm 02:13 PM
The advantages of using design patterns in Java frameworks include: enhanced code readability, maintainability, and scalability. Disadvantages include complexity, performance overhead, and steep learning curve due to overuse. Practical case: Proxy mode is used to lazy load objects. Use design patterns wisely to take advantage of their advantages and minimize their disadvantages.






