Nginx retry causes HTTP request to be executed repeatedly
1. Problem background
The web site uses Nginx as a reverse proxy, and two tomcats do load balancing.
The web site has a group text message module, and the administrator can fill in the sending content and mobile phone number list. Click Send, and the group text message operation will be executed in the background. After the sending is completed, the sending result will be returned.
I encountered the problem of repeated sending a long time ago. At first, I thought the administrator acted abnormally and clicked the send button repeatedly. Therefore, restrictions are placed on front-end submissions. When clicking send, set the button to disable, get the returned data after execution, and then set it to available to limit repeated submissions from the front end.
Today, a colleague suddenly used this module again and sent two batches of text messages (8000 and 1600) respectively. The front-end prompts that the operation failed, but his mobile phone received duplicate text messages.
2. Problem analysis
Firstly, we confirmed that there are no duplicates in the mobile phone number list, and also confirmed through browser debugging that the front-end did not initiate repeated requests.
By checking the logs of the two servers, it was found that repeated sending occurred, and the sending time points were not at the same time.
Through the logs, it can be estimated that the time to send a text message is 10 milliseconds.
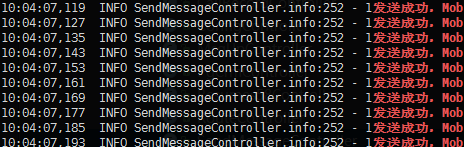
I also checked the processing timeout log through the log, and found the pattern. Repeated requests are processed on different machines and the processing intervals are consistent.
A log
10:03:05,878 INFO TIMEOUT.info:252 - time: 75701ms, concurrent: 1, url: /push/sendmessage.10:07:24,705 INFO TIMEOUT.info:252 - time: 15148ms, concurrent: 0, url: /push/sendmessage.
B log
10:03:21,599 INFO TIMEOUT.info:252 - time: 76471ms, concurrent: 1, url: /push/sendmessage.10:07:39,718 INFO TIMEOUT.info:252 - time: 15113ms, concurrent: 0, url: /push/sendmessage.
Based on the above information, we guessed, It should be that the request execution time exceeds the limit, causing the front-end prompt to fail. Duplicate submissions should be caused by the retry mechanism.
So I contacted the operation and maintenance for confirmation. Received relevant reply:
Nginx can configure the timeout, assuming it is configured to 15s, and a request takes 16s to be processed and returned. Nginx routes to server A for processing. When A executes to the 15th second, it does not return normally. Nginx will resend it to service B for processing. When B executes to the 15th second, it does not return normally. The front end waits for 30s and finally returns failure. A and B received corresponding requests respectively and processed them internally.
After confirming the reason with the operation and maintenance classmates, you can search by yourself based on the relevant information.
nginx’s retry mechanism
The article also points to a solution that can access services through IP and bypass nginx.
In addition, our website has a download function. Before optimization, the execution time of each download was also very long, but there was no timeout problem. Analyzed the possible differences between GET and POST. The following link is also given above to determine the general idea.
http://serverfault.com/questions/528653/how-can-i-stop-nginx-from-retrying-put-or-post-requests-on-upstream-server-timeo
3. Summary of questions
Through online information reference, Nginx can set different timeout strategies for file upload, download, GET and POST requests.
In addition, for the SMS bulk sending business, there is actually a separate module that manages configuration through rules and performs offline task execution. The existing mass sending module is only for small-scale business.

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to allow external network access to tomcat server
Apr 21, 2024 am 07:22 AM
How to allow external network access to tomcat server
Apr 21, 2024 am 07:22 AM
To allow the Tomcat server to access the external network, you need to: modify the Tomcat configuration file to allow external connections. Add a firewall rule to allow access to the Tomcat server port. Create a DNS record pointing the domain name to the Tomcat server public IP. Optional: Use a reverse proxy to improve security and performance. Optional: Set up HTTPS for increased security.
 How to run thinkphp
Apr 09, 2024 pm 05:39 PM
How to run thinkphp
Apr 09, 2024 pm 05:39 PM
Steps to run ThinkPHP Framework locally: Download and unzip ThinkPHP Framework to a local directory. Create a virtual host (optional) pointing to the ThinkPHP root directory. Configure database connection parameters. Start the web server. Initialize the ThinkPHP application. Access the ThinkPHP application URL and run it.
 Welcome to nginx!How to solve it?
Apr 17, 2024 am 05:12 AM
Welcome to nginx!How to solve it?
Apr 17, 2024 am 05:12 AM
To solve the "Welcome to nginx!" error, you need to check the virtual host configuration, enable the virtual host, reload Nginx, if the virtual host configuration file cannot be found, create a default page and reload Nginx, then the error message will disappear and the website will be normal show.
 How to communicate between docker containers
Apr 07, 2024 pm 06:24 PM
How to communicate between docker containers
Apr 07, 2024 pm 06:24 PM
There are five methods for container communication in the Docker environment: shared network, Docker Compose, network proxy, shared volume, and message queue. Depending on your isolation and security needs, choose the most appropriate communication method, such as leveraging Docker Compose to simplify connections or using a network proxy to increase isolation.
 How to deploy nodejs project to server
Apr 21, 2024 am 04:40 AM
How to deploy nodejs project to server
Apr 21, 2024 am 04:40 AM
Server deployment steps for a Node.js project: Prepare the deployment environment: obtain server access, install Node.js, set up a Git repository. Build the application: Use npm run build to generate deployable code and dependencies. Upload code to the server: via Git or File Transfer Protocol. Install dependencies: SSH into the server and use npm install to install application dependencies. Start the application: Use a command such as node index.js to start the application, or use a process manager such as pm2. Configure a reverse proxy (optional): Use a reverse proxy such as Nginx or Apache to route traffic to your application
 How to register phpmyadmin
Apr 07, 2024 pm 02:45 PM
How to register phpmyadmin
Apr 07, 2024 pm 02:45 PM
To register for phpMyAdmin, you need to first create a MySQL user and grant permissions to it, then download, install and configure phpMyAdmin, and finally log in to phpMyAdmin to manage the database.
 How to generate URL from html file
Apr 21, 2024 pm 12:57 PM
How to generate URL from html file
Apr 21, 2024 pm 12:57 PM
Converting an HTML file to a URL requires a web server, which involves the following steps: Obtain a web server. Set up a web server. Upload HTML file. Create a domain name. Route the request.
 What to do if the installation of phpmyadmin fails
Apr 07, 2024 pm 03:15 PM
What to do if the installation of phpmyadmin fails
Apr 07, 2024 pm 03:15 PM
Troubleshooting steps for failed phpMyAdmin installation: Check system requirements (PHP version, MySQL version, web server); enable PHP extensions (mysqli, pdo_mysql, mbstring, token_get_all); check configuration file settings (host, port, username, password); Check file permissions (directory ownership, file permissions); check firewall settings (whitelist web server ports); view error logs (/var/log/apache2/error.log or /var/log/nginx/error.log); seek Technical support (phpMyAdmin






