 Backend Development
Backend Development
 C#.Net Tutorial
C#.Net Tutorial
 In-depth understanding of endianness and type conversion in C/C++
In-depth understanding of endianness and type conversion in C/C++
In-depth understanding of endianness and type conversion in C/C++
If you talk about byte order and type conversion separately, everyone may think it is very simple, but they will not understand it deeply. If we combine them and discuss them, maybe we will understand them thoroughly.
If you don’t understand the basics of byte order and type conversion, you can refer to the following blog:
https://my.oschina.net/u/1783725/blog/647973 Large and small byte order
https: //my.oschina.net/u/1783725/blog/700970 Type conversion
Before getting into the topic, a quick sentence:
Different system digits correspond to different byte sizes of data types
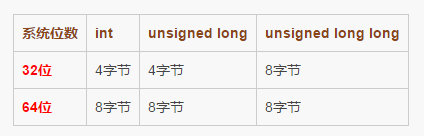
Details Introducing the connection between the two
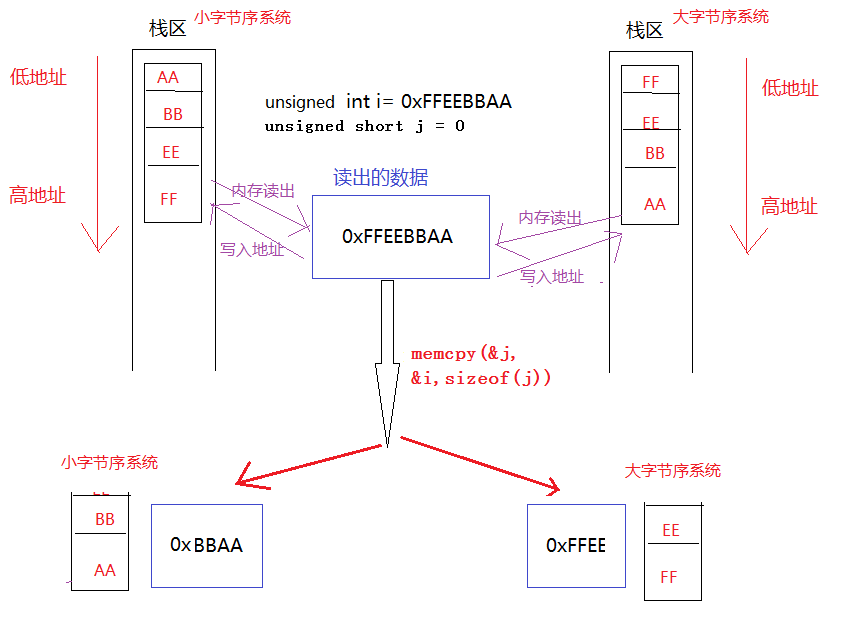
Byte order: The memory of operation is the rule for storing the data we see in memory.
Big endian: Big endian is valid, high-bit data is put into low-address memory first, and low-bit data is put into high-address memory; Little endian: little-endian is valid, low-bit data is put into low-address memory first, and then high-bit data is placed When entering high address memory
When operating memory (such as: memcpy), you need to consider the byte order
Type conversion: The operation is to read the data, which is the data to be read from the memory, according to the type of bytes Convert size.
The ones with many digits are converted into those with small digits (the high-order data will be truncated, leaving the position data), and those with small digits are converted into those with many digits (the high-order data will be filled with 0).
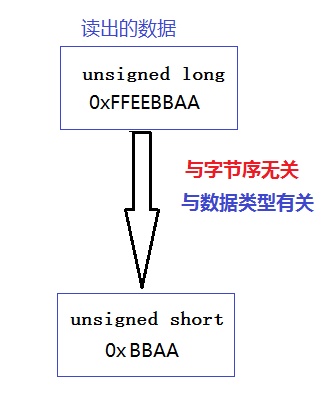
An example to understand them
1. Assignment has nothing to do with byte order. When operating memory (memcpy), you need to consider byte order
1: Assign 0xABCDEF1234 of unsigned long long type to unsigned long type Variables, regardless of byte order
2: unsigned long long type 0xABCDEF1234 variable uses memcpy to short type variable, found to be 0, related to byte order
The code is as follows:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 |
|

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1393
1393
 52
52
 1207
1207
 24
24
 What are the differences between php and c#
Jun 02, 2023 pm 01:45 PM
What are the differences between php and c#
Jun 02, 2023 pm 01:45 PM
The differences between php and c# are: 1. The language type system is different, PHP is dynamic, while C# is static type; 2. The platforms used are different, PHP can be cross-platform, while C# is exclusive to Windows; 3. The programming paradigm is different, PHP It supports object-oriented, procedural and functional programming, and C# is more inclined to object-oriented programming; 4. The execution speed is different, PHP is faster, and C# is relatively slow; 5. The application scenarios are different, PHP is used in web development, servers, etc. C# is used for Windows desktop and web applications.
 Why in C/C++, the sizeof of the structure is not equal to the sum of the sizeof of each member?
Aug 26, 2023 am 09:29 AM
Why in C/C++, the sizeof of the structure is not equal to the sum of the sizeof of each member?
Aug 26, 2023 am 09:29 AM
The size of the structure type elements obtained by sizeof() is not always equal to the size of each individual member. Sometimes the compiler adds some padding to avoid alignment problems. So dimensions may change. Padding is added when a structure member is followed by a member of larger size or is at the end of the structure. Different compilers have different types of alignment constraints. In the C standard, total alignment structures are implementation dependent. Case 1 In this case, the double z is 8 bytes long, which is larger than x (4 bytes)). So another 4 bytes of padding are added. Additionally, the short type data y has 2 bytes of space in memory, so an extra 6 bytes are added as padding. Sample code #include<stdio.h>structmyS
 Create a C/C++ code formatting tool using Clang tool
Aug 26, 2023 pm 01:09 PM
Create a C/C++ code formatting tool using Clang tool
Aug 26, 2023 pm 01:09 PM
In this tutorial, we willdiscussingaprogramtocreateaC/C++codeformattingtoolwiththehelpofclangtools.SETUPsudoaptinstallpythonsudoaptinstallclang-format-3.5 We will then create a Python file in a location where the current user has read and write permissions. Example importoscpp_extensions=(".cxx",".cpp&
![One article explains in detail vscode configuration C/C++ running environment [nanny-level teaching]](https://img.php.cn/upload/article/000/000/024/63fc94eb8852a975.jpg?x-oss-process=image/resize,m_fill,h_207,w_330) One article explains in detail vscode configuration C/C++ running environment [nanny-level teaching]
Feb 27, 2023 pm 07:33 PM
One article explains in detail vscode configuration C/C++ running environment [nanny-level teaching]
Feb 27, 2023 pm 07:33 PM
How to develop C/C++ in VScode? How to configure the C/C++ environment? The following article will share with you the VScode configuration C/C++ running environment tutorial (nanny-level teaching). I hope it will be helpful to you!
 In C/C++, there are two operations: pre-increment and post-increment.
Aug 25, 2023 pm 02:25 PM
In C/C++, there are two operations: pre-increment and post-increment.
Aug 25, 2023 pm 02:25 PM
Here we take a look at what are pre-increment and post-increment in C or C++. Both pre-increment and post-increment are increment operators. But there is little difference between them. The pre-increment operator first increments the value of a variable and then assigns it to other variables, but in the case of post-increment operator, it first assigns to a variable and then increments the value. Example #include<iostream>usingnamespacestd;main(){ intx,y,z; x=10; y=10;&nb
 In C/C++, the strcpy() function is a function used to copy one string to another string
Sep 09, 2023 am 08:49 AM
In C/C++, the strcpy() function is a function used to copy one string to another string
Sep 09, 2023 am 08:49 AM
The function strcpy() is a standard library function. It is used to copy one string to another string. In C language, it is declared in the "string.h" header file, while in C++ language, it is declared in the cstring header file. It returns a pointer to the destination. This is the syntax of strcpy() in C language, char*strcpy(char*dest,constchar*src); some key points of strcpy(). It copies the entire string into the target string. It replaces the entire string instead of appending it. It does not change the source string. The following is an example of strcpy() in C language: Example Online Demo#in
 C/C++ program to calculate the number of trailing zeros in the factorial of a number
Aug 29, 2023 pm 12:29 PM
C/C++ program to calculate the number of trailing zeros in the factorial of a number
Aug 29, 2023 pm 12:29 PM
Here we will see how to calculate the number of trailing zeros in the factorial result of any number. Therefore, if n=5, then 5! =120. There is only one trailing 0. For 20!, it would be 4 zeros as 20!=2432902008176640000. The simplest way is to calculate the factorial and count 0. But for larger values of n, this approach fails. So we're going to take another approach. If the prime factors are 2 and 5, then trailing zeros will appear. If we calculate 2 and 5, we can get the result. To do this we will follow this rule. Trailing 0 = Counting algorithm for 5 in factorial (n) prime factors countTrailingZeros(n)begin &
 In C/C++, the putwchar() function is a function used to output a wide character
Sep 11, 2023 pm 05:57 PM
In C/C++, the putwchar() function is a function used to output a wide character
Sep 11, 2023 pm 05:57 PM
In this article, we will discuss the working principle, syntax and examples of putwchar() function in C++STL. What is putwchar()? The putwchar() function is a built-in function in C++STL, which is defined in the <cwchar> header file. The putwchar() function is used to write wide characters on the standard output device. This function takes the wide character from the argument and writes it to the system's stdout or standard output. This function is the wide character version of putchar(), which is defined in the <cstdio> header file. Syntax putwchar(wchar_twidec); Parameters This function accepts the following parameters



