PHP design pattern iterator pattern
Concept
Iterator mode (Iterator), also called Cursor (Cursor) mode. Provides a way to sequentially access the various elements in an aggregate object without exposing the object's internal representation.
When you need to access an aggregate object and need to traverse it no matter what these objects are, you should consider using the iterator pattern. In addition, when you need to traverse a collection in multiple ways, you can consider using the iterator pattern. The iterator pattern provides a unified interface for traversing different collection structures, such as the start, next, whether to end, and the current item.
Applicable scenarios
Access the contents of an aggregate object without exposing its internal representation
Supports multiple traversals of aggregate objects
Provides a unified interface for traversing different aggregate structures
UML diagram
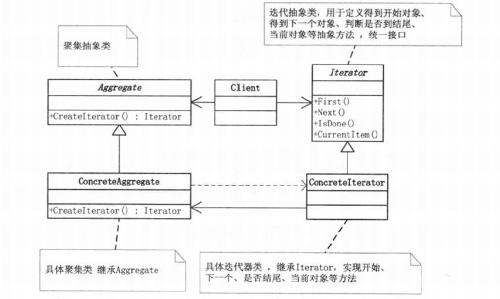
Role
Iterator (iterator): Iterator defines the interface for accessing and traversing elements
ConcreteIterator (concrete iterator): A specific iterator implements the iterator interface and tracks the current position when traversing the aggregate
Aggregate (aggregation) : Aggregation defines the interface that creates the corresponding iterator object
ConcreteAggregate (concrete aggregation): The concrete aggregate implements the interface that creates the corresponding iterator. This operation returns an appropriate instance of ConcreteIterator
Code
The code is as follows:
PHP SPL The iterator interface Iterator and the container interface IteatorAggragate have been provided. The source code is as follows:
/**
* Interface to detect if a class is traversable using &foreach;.
* @link http://php.net/manual/en/class.traversable.php
*/
interface Traversable {
}
/**
* Interface to create an external Iterator.
* @link http://php.net/manual/en/class.iteratoraggregate.php
*/
interface IteratorAggregate extends Traversable {
/**
* Retrieve an external iterator
* @link http://php.net/manual/en/iteratoraggregate.getiterator.php
* @return Traversable An instance of an object implementing <b>Iterator</b> or
* <b>Traversable</b>
* @since 5.0.0
*/
public function getIterator();
}
/**
* Interface for external iterators or objects that can be iterated
* themselves internally.
* @link http://php.net/manual/en/class.iterator.php
*/
interface Iterator extends Traversable {
/**
* Return the current element
* @link http://php.net/manual/en/iterator.current.php
* @return mixed Can return any type.
* @since 5.0.0
*/
public function current();
/**
* Move forward to next element
* @link http://php.net/manual/en/iterator.next.php
* @return void Any returned value is ignored.
* @since 5.0.0
*/
public function next();
/**
* Return the key of the current element
* @link http://php.net/manual/en/iterator.key.php
* @return mixed scalar on success, or null on failure.
* @since 5.0.0
*/
public function key();
/**
* Checks if current position is valid
* @link http://php.net/manual/en/iterator.valid.php
* @return boolean The return value will be casted to boolean and then evaluated.
* Returns true on success or false on failure.
* @since 5.0.0
*/
public function valid();
/**
* Rewind the Iterator to the first element
* @link http://php.net/manual/en/iterator.rewind.php
* @return void Any returned value is ignored.
* @since 5.0.0
*/
public function rewind();
}Here we directly implement the above two interfaces, please see the following code:
<?php
header('Content-type:text/html;charset=utf-8');
/**
* 迭代器模式
*/
/**
* Class ConcreteIterator 具体的迭代器
*/
class ConcreteIterator implements Iterator
{
private $position = 0;
private $array = array();
public function __construct($array) {
$this->array = $array;
$this->position = 0;
}
function rewind() {
$this->position = 0;
}
function current() {
return $this->array[$this->position];
}
function key() {
return $this->position;
}
function next() {
++$this->position;
}
function valid() {
return isset($this->array[$this->position]);
}
}
/**
* Class MyAggregate 聚合容器
*/
class ConcreteAggregate implements IteratorAggregate
{
public $property;
/**
* 添加属性
*
* @param $property
*/
public function addProperty($property)
{
$this->property[] = $property;
}
public function getIterator()
{
return new ConcreteIterator($this->property);
}
}
/**
* Class Client 客户端测试
*/
class Client
{
public static function test()
{
//创建一个容器
$concreteAggregate = new ConcreteAggregate();
// 添加属性
$concreteAggregate->addProperty('属性1');
// 添加属性
$concreteAggregate->addProperty('属性2');
//给容器创建迭代器
$iterator = $concreteAggregate->getIterator();
//遍历
while($iterator->valid())
{
$key = $iterator->key();
$value = $iterator->current();
echo '键: '.$key.' 值: '.$value.'<hr>';
$iterator->next();
}
}
}
Client:: test();Running result:
Key: 0 Value: Attribute 1
Key: 1 Value: Attribute 2

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 CakePHP Project Configuration
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:25 PM
CakePHP Project Configuration
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:25 PM
In this chapter, we will understand the Environment Variables, General Configuration, Database Configuration and Email Configuration in CakePHP.
 PHP 8.4 Installation and Upgrade guide for Ubuntu and Debian
Dec 24, 2024 pm 04:42 PM
PHP 8.4 Installation and Upgrade guide for Ubuntu and Debian
Dec 24, 2024 pm 04:42 PM
PHP 8.4 brings several new features, security improvements, and performance improvements with healthy amounts of feature deprecations and removals. This guide explains how to install PHP 8.4 or upgrade to PHP 8.4 on Ubuntu, Debian, or their derivati
 CakePHP Date and Time
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:27 PM
CakePHP Date and Time
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:27 PM
To work with date and time in cakephp4, we are going to make use of the available FrozenTime class.
 CakePHP File upload
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:27 PM
CakePHP File upload
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:27 PM
To work on file upload we are going to use the form helper. Here, is an example for file upload.
 CakePHP Routing
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:25 PM
CakePHP Routing
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:25 PM
In this chapter, we are going to learn the following topics related to routing ?
 Discuss CakePHP
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:28 PM
Discuss CakePHP
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:28 PM
CakePHP is an open-source framework for PHP. It is intended to make developing, deploying and maintaining applications much easier. CakePHP is based on a MVC-like architecture that is both powerful and easy to grasp. Models, Views, and Controllers gu
 CakePHP Creating Validators
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:26 PM
CakePHP Creating Validators
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:26 PM
Validator can be created by adding the following two lines in the controller.
 CakePHP Working with Database
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:25 PM
CakePHP Working with Database
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:25 PM
Working with database in CakePHP is very easy. We will understand the CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) operations in this chapter.






