How to implement geocoding with Python
Taking the logistics industry as an example, this paper analyzes the application methods of PostgreSQL and Greenplum in the logistics industry in terms of geographical location information processing, optimal path algorithms, and machine learning. It mentioned the problem of converting addresses into coordinates. A more professional term should be "geocoding", that is, knowing an address, such as No. 10, Shangdi 10th Street, Haidian District, Beijing, how to obtain the corresponding longitude and latitude location information ( 40,116), or vice versa.
Geocoding concept
Many map-related vendors provide related APIs, and we can directly use these APIs to obtain this information. For example, Baidu's Geocoding API.
Geocoding API is a type of interface used to provide conversion services from addresses to longitude and latitude coordinates or from longitude and latitude coordinates to addresses. Users can use development languages such as C#, C++, and Java to send requests and receive return data in JSON and XML. Geocoding API includes address parsing and reverse geocoding functions:

Borrowing a more intuitive picture from the ESRI document
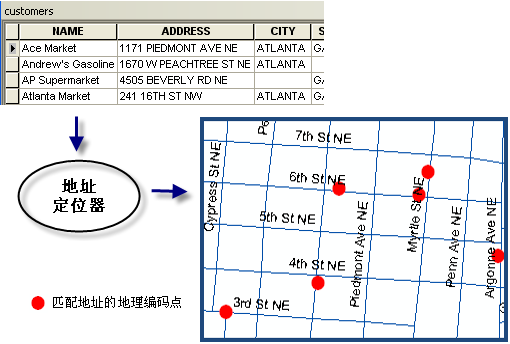
Geocoding: that is, address parsing, obtaining Baidu longitude and latitude information from structured addresses as detailed as streets , for example: the result of address resolution of "No. 27, Zhongguancun South Street, Haidian District, Beijing" is "lng:116.31985,lat:39.959836". At the same time, geocoding also supports direct parsing of the names of places of interest and landmark buildings to return Baidu latitude and longitude. For example, the result of address parsing of "Baidu Building" is "lng:116.30815,lat:40.056885".
Reverse geocoding: that is, reverse geocoding, which obtains structured address information from Baidu longitude and latitude information. For example: "lat:31.325152,lng:120.558957" The result of reverse geocoding is "318 Tayuan Road, Huqiu District, Suzhou City, Jiangsu Province Number".
However, one thing that needs to be explained is that if you want to use Baidu’s API, you need to have a Baidu account and apply for the corresponding Key. In fact, in addition to Baidu, Google, ESRI, Microsoft's Bing, etc. all have similar geocoding services. However, most of these services do not have libraries specifically for Python and their Json structures are inconsistent with each other. Therefore, the Python master who specializes in dealing with dissatisfaction made a special geocoding tool geocoder to integrate and unify the services of these different manufacturers.
Geocoder
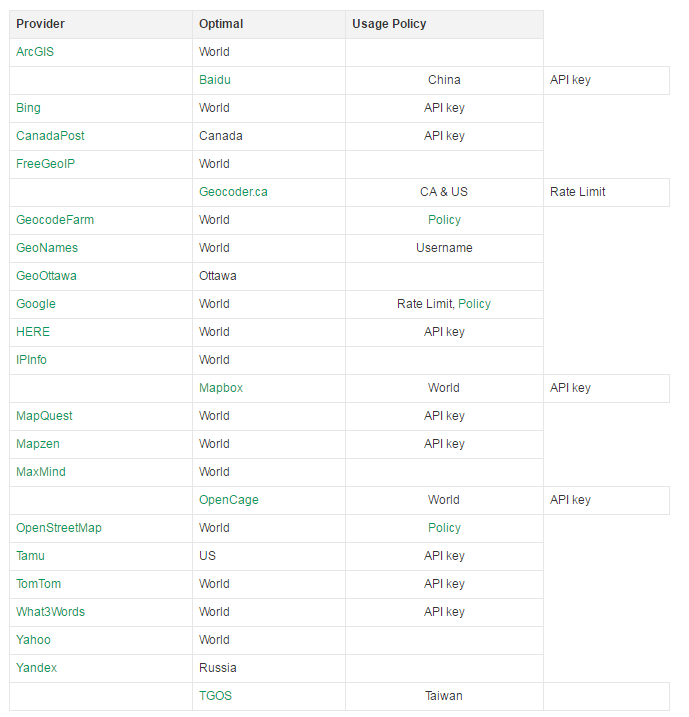
First take a look at which companies' geocoding services it supports:
Installation
pip install geocoder
Geocoding
import geocoder
g = geocoder.google("1403 Washington Ave, New Orleans, LA 70130")
g = geocoder.arcgis(u"北京市海淀区上地十街10号")
g.latlngThe output is
[29.9287839, -90.08421849999999]
You can also view the complete geojson
g.geojson
output For
{'bbox': [-90.0855674802915,
29.9274349197085,
-90.0828695197085,
29.9301328802915],
'geometry': {'coordinates': [-90.08421849999999, 29.9287839],
'type': 'Point'},
'properties': {'accuracy': u'ROOFTOP',
'address': u'1403 Washington Ave, New Orleans, LA 70130, USA',
'bbox': [-90.0855674802915,
29.9274349197085,
-90.0828695197085,
29.9301328802915],
'city': u'New Orleans',
'confidence': 9,
'country': u'US',
'county': u'Orleans Parish',
'encoding': 'utf-8',
'housenumber': u'1403',
'lat': 29.9287839,
'lng': -90.08421849999999,
'location': '1403 Washington Ave, New Orleans, LA 70130',
'neighborhood': u'Garden District',
'ok': True,
'place': u'ChIJGyFHWc2lIIYRYSoneaXAUiw',
'postal': u'70130',
'provider': 'google',
'quality': u'street_address',
'state': u'LA',
'status': 'OK',
'status_code': 200,
'street': u'Washington Ave'},
'type': 'Feature'}, when trying to query the Chinese address directly using Google, it failed
g = geocoder.google(u"北京市海淀区上地十街10号") g.ok
The output is
False
It should be fine using Baidu, but I did not apply for the corresponding key. Switch to arcgis and be able to successfully encode
g = geocoder.arcgis(u"北京市海淀区上地十街10号") g.latlng
The output is
[40.050934, 116.30079]
Reverse geocoding
g = geocoder.google([29.9287839, -90.08421849999999], method='reverse') print g.address print g.city print g.state print g.country
The output is
1403 Washington Ave, New Orleans, LA 70115, USA New Orleans LA US
Change to the Chinese address
g = geocoder.google([40.050934, 116.30079], method='reverse') print g.address print g.city print g.state print g.country
The output is
Bai Du Da Sha, Haidian Qu, Beijing Shi, China, 100193 Beijing Beijing Shi CN
Try using the arcgis service
g = geocoder.arcgis([40.050934, 116.30079], method='reverse') print g.address print g.city print g.state print g.country
The output is
None 北京市 北京市 CHN
Google converts it into English, but the address is relatively complete. Although arcgis is in Chinese, the detailed address is actually output as None, which is useful.
Others
geocoder’s functions don’t stop there, it can also check IPs (including your own).
g = geocoder.ip('199.7.157.0') print g.latlng print g.city g = geocoder.ip('me') print g.latlng print g.city
The output is
[43.6934, -79.4857] Toronto [51.05, 13.75] Dresden
Querying the spatial bounding box of a city
g = geocoder.arcgis(u"山东") g.bbox
The output is
{'northeast': [38.976997, 121.976998], 'southwest': [33.022997, 116.022998]}Summary
Spatial information can be described by text information such as administrative divisions and natural geographical areas, or it can be identified by coordinate systems and numbers (zip codes, etc.). Geocoding technology can be used to associate geolocation elements of spatial information with corresponding text information. This article mainly introduces the geocoder geocoding tool, which can conveniently and quickly use the geocoding services provided by maps and other related manufacturers to convert the location described in text into longitude and latitude on the map, or obtain the corresponding coordinates through a certain location on the map. Text description of the location information.

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 HadiDB: A lightweight, horizontally scalable database in Python
Apr 08, 2025 pm 06:12 PM
HadiDB: A lightweight, horizontally scalable database in Python
Apr 08, 2025 pm 06:12 PM
HadiDB: A lightweight, high-level scalable Python database HadiDB (hadidb) is a lightweight database written in Python, with a high level of scalability. Install HadiDB using pip installation: pipinstallhadidb User Management Create user: createuser() method to create a new user. The authentication() method authenticates the user's identity. fromhadidb.operationimportuseruser_obj=user("admin","admin")user_obj.
 Python: Exploring Its Primary Applications
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:41 AM
Python: Exploring Its Primary Applications
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:41 AM
Python is widely used in the fields of web development, data science, machine learning, automation and scripting. 1) In web development, Django and Flask frameworks simplify the development process. 2) In the fields of data science and machine learning, NumPy, Pandas, Scikit-learn and TensorFlow libraries provide strong support. 3) In terms of automation and scripting, Python is suitable for tasks such as automated testing and system management.
 The 2-Hour Python Plan: A Realistic Approach
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:04 AM
The 2-Hour Python Plan: A Realistic Approach
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:04 AM
You can learn basic programming concepts and skills of Python within 2 hours. 1. Learn variables and data types, 2. Master control flow (conditional statements and loops), 3. Understand the definition and use of functions, 4. Quickly get started with Python programming through simple examples and code snippets.
 Navicat's method to view MongoDB database password
Apr 08, 2025 pm 09:39 PM
Navicat's method to view MongoDB database password
Apr 08, 2025 pm 09:39 PM
It is impossible to view MongoDB password directly through Navicat because it is stored as hash values. How to retrieve lost passwords: 1. Reset passwords; 2. Check configuration files (may contain hash values); 3. Check codes (may hardcode passwords).
 How to use AWS Glue crawler with Amazon Athena
Apr 09, 2025 pm 03:09 PM
How to use AWS Glue crawler with Amazon Athena
Apr 09, 2025 pm 03:09 PM
As a data professional, you need to process large amounts of data from various sources. This can pose challenges to data management and analysis. Fortunately, two AWS services can help: AWS Glue and Amazon Athena.
 How to start the server with redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:12 PM
How to start the server with redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:12 PM
The steps to start a Redis server include: Install Redis according to the operating system. Start the Redis service via redis-server (Linux/macOS) or redis-server.exe (Windows). Use the redis-cli ping (Linux/macOS) or redis-cli.exe ping (Windows) command to check the service status. Use a Redis client, such as redis-cli, Python, or Node.js, to access the server.
 How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
To read a queue from Redis, you need to get the queue name, read the elements using the LPOP command, and process the empty queue. The specific steps are as follows: Get the queue name: name it with the prefix of "queue:" such as "queue:my-queue". Use the LPOP command: Eject the element from the head of the queue and return its value, such as LPOP queue:my-queue. Processing empty queues: If the queue is empty, LPOP returns nil, and you can check whether the queue exists before reading the element.
 How to view server version of Redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 01:27 PM
How to view server version of Redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 01:27 PM
Question: How to view the Redis server version? Use the command line tool redis-cli --version to view the version of the connected server. Use the INFO server command to view the server's internal version and need to parse and return information. In a cluster environment, check the version consistency of each node and can be automatically checked using scripts. Use scripts to automate viewing versions, such as connecting with Python scripts and printing version information.




