 Backend Development
Backend Development
 Python Tutorial
Python Tutorial
 Implementing excel table reading and writing based on Python
Implementing excel table reading and writing based on Python
Implementing excel table reading and writing based on Python
First install the corresponding xlrd and xlwt
Open the cmd command window and enter pip install xlrd and pip install xlwt to install. Then enter pip list to check whether the configuration is successful:
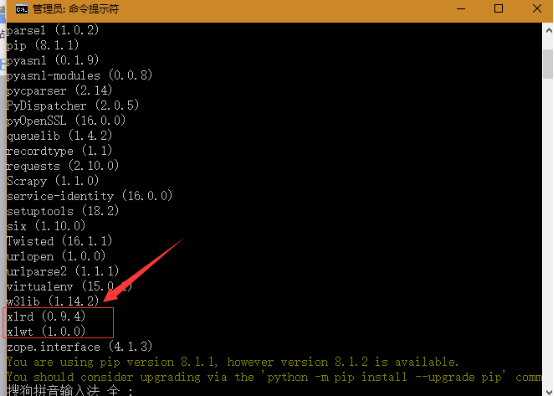
xlrd operation#
The next step is the commonly used syntax operation:
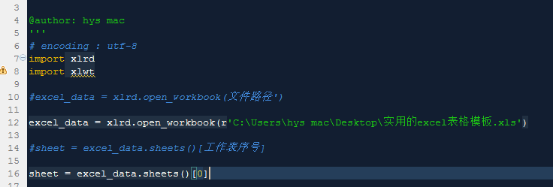
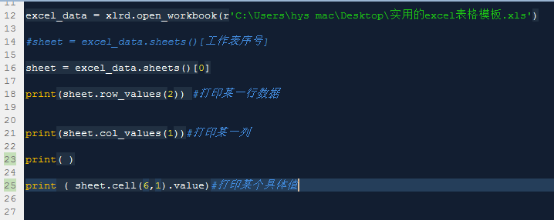
excel_data = xlrd.open_workbook(file path')#Get the corresponding worksheet
sheet = excel_data.sheets()[worksheet serial number]#Get the data of a row corresponding to a certain table in the corresponding worksheet
sheet.row_values(2)#
sheet.cell(6,1).value#corresponding For data in a certain column
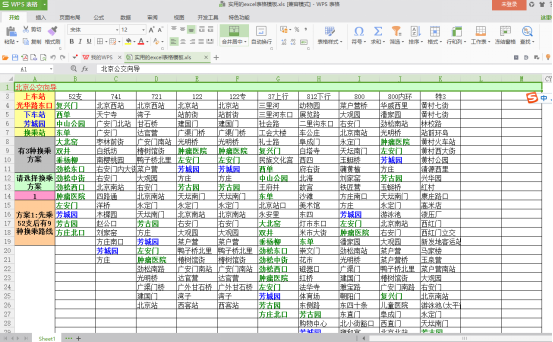
Take this table as an example and try the corresponding statement first:
First specify the corresponding table and one of the tables, otherwise an error will be prompted and the compilation will not pass. Run the above code:
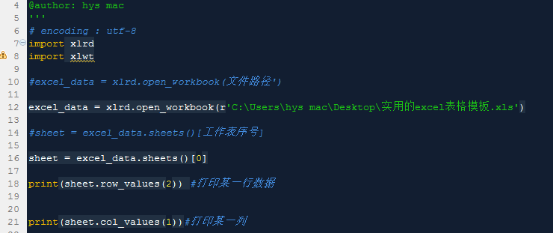
Source code as follows:
import xlrd
import xlwt
excel_data = xlrd.open_WORKBOOK (file path ')
excel_data = xlrd.open_Workbook SKTOP practical excel table template.xls')
sheet = excel_data.sheets()[worksheet serial number]
sheet = excel_data.sheets()[0]
print(sheet.row_values(2)) #Print a certain row of data
print(sheet.col_values(1))#Print a certain column
print()
print (sheet.cell(6,1).value)#Print a specific value
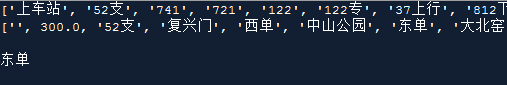
The operation results are as follows:

Comparing the tables brings something worth noting. The specified number of rows and columns starts from 0. When opening the specified table, please note that the absolute path must be included along with the file name and file suffix to successfully read the data.
Next, the experiment reads the data of a specified cell:
sheet.cell(row, column).value
Run and get:
Compare the table and get Data:
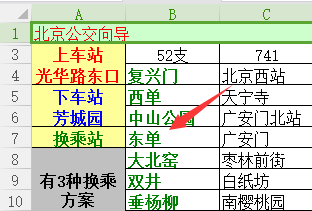
is (7, B), which is consistent with the counting from zero mentioned before.
In addition to some of the operations listed above, there are other common statements that can be viewed in relevant documents and official websites. There are relevant links at the end of the article. Next, we will experiment with another xlwt library to implement writing operations to excel tables.
xlwt operation#
The general concerns about excel tables are the following aspects:
Creating workbooks and tables
Writing into cells
Common format settings (currency text, etc.)
Creating formulas
Save
Next, try each of the functions mentioned above in turn:
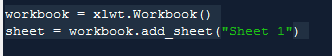
The corresponding objects of workbooks and tables are: workbook, sheet
2. Cell assignment:
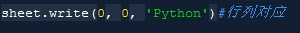
Here I tried using negative numbers

There is no problem with compilation. Save it later to check whether the result is correct.
3. Format setting:
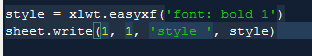
It can be seen that in addition to the row, column and value, the corresponding incoming parameters also include style, which is omitted by default. The format of the test settings here is bold. Other formats can be implemented by referring to the search document at the end of the article. Here are some other common formats:
style = easyxf(num_format_str='$#,##0.00')
# or set it directly on the style object
style = easyxf('font: bold 1')
style.num_format_str = '$#,##0.00'
sheet.write(0, 0, '100.00', style)
4. Create formula:
Excel formula can be implemented using xlwt.Formula. W Sheet.write (0, 0, xlwt.Formula ('Hyperlink ("http://yujitomita.com"; "click me"))
5. Save operation:
workbook.save ("pythonon (" pythonon ("pythonon (" pythonon ("pythonon ".
Running results:
According to the previous pit (-1,0), the trial running results are here:
# encoding: utf-8
import xlrdimport xlwt
workbook = xlwt.Workbook()
sheet = workbook. add_sheet("Sheet 1")
#Create a workbook and a worksheet
style = xlwt.easyxf('font : bold 1')
SyntaxError: (unicode error ) 'unicodeescape' codec can't decode bytes in position 2-3: truncated UXXXXXXXX escape
Encountered a file encoding problem, modified the next sentence:
workbook.save(r'C:Usershys macDesktopmr.cpython.xls')
It’s back to the pit left at the beginning. The cell assignment rules should be consistent with usage habits and cannot be negative numbers. The final modification is: import xlrdimport xlwt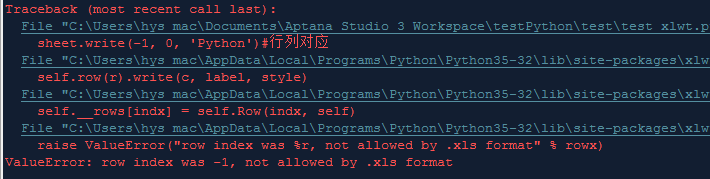
sheet = workbook.add_sheet("Sheet 1")
#Create workbook (workbook) and worksheet (sheet)
style = xlwt.easyxf('font: bold 1')

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 How to use Debian Apache logs to improve website performance
Apr 12, 2025 pm 11:36 PM
How to use Debian Apache logs to improve website performance
Apr 12, 2025 pm 11:36 PM
This article will explain how to improve website performance by analyzing Apache logs under the Debian system. 1. Log Analysis Basics Apache log records the detailed information of all HTTP requests, including IP address, timestamp, request URL, HTTP method and response code. In Debian systems, these logs are usually located in the /var/log/apache2/access.log and /var/log/apache2/error.log directories. Understanding the log structure is the first step in effective analysis. 2. Log analysis tool You can use a variety of tools to analyze Apache logs: Command line tools: grep, awk, sed and other command line tools.
 Python: Games, GUIs, and More
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:14 AM
Python: Games, GUIs, and More
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:14 AM
Python excels in gaming and GUI development. 1) Game development uses Pygame, providing drawing, audio and other functions, which are suitable for creating 2D games. 2) GUI development can choose Tkinter or PyQt. Tkinter is simple and easy to use, PyQt has rich functions and is suitable for professional development.
 PHP and Python: Comparing Two Popular Programming Languages
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:13 AM
PHP and Python: Comparing Two Popular Programming Languages
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:13 AM
PHP and Python each have their own advantages, and choose according to project requirements. 1.PHP is suitable for web development, especially for rapid development and maintenance of websites. 2. Python is suitable for data science, machine learning and artificial intelligence, with concise syntax and suitable for beginners.
 How debian readdir integrates with other tools
Apr 13, 2025 am 09:42 AM
How debian readdir integrates with other tools
Apr 13, 2025 am 09:42 AM
The readdir function in the Debian system is a system call used to read directory contents and is often used in C programming. This article will explain how to integrate readdir with other tools to enhance its functionality. Method 1: Combining C language program and pipeline First, write a C program to call the readdir function and output the result: #include#include#include#includeintmain(intargc,char*argv[]){DIR*dir;structdirent*entry;if(argc!=2){
 The role of Debian Sniffer in DDoS attack detection
Apr 12, 2025 pm 10:42 PM
The role of Debian Sniffer in DDoS attack detection
Apr 12, 2025 pm 10:42 PM
This article discusses the DDoS attack detection method. Although no direct application case of "DebianSniffer" was found, the following methods can be used for DDoS attack detection: Effective DDoS attack detection technology: Detection based on traffic analysis: identifying DDoS attacks by monitoring abnormal patterns of network traffic, such as sudden traffic growth, surge in connections on specific ports, etc. This can be achieved using a variety of tools, including but not limited to professional network monitoring systems and custom scripts. For example, Python scripts combined with pyshark and colorama libraries can monitor network traffic in real time and issue alerts. Detection based on statistical analysis: By analyzing statistical characteristics of network traffic, such as data
 Python and Time: Making the Most of Your Study Time
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:02 AM
Python and Time: Making the Most of Your Study Time
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:02 AM
To maximize the efficiency of learning Python in a limited time, you can use Python's datetime, time, and schedule modules. 1. The datetime module is used to record and plan learning time. 2. The time module helps to set study and rest time. 3. The schedule module automatically arranges weekly learning tasks.
 Nginx SSL Certificate Update Debian Tutorial
Apr 13, 2025 am 07:21 AM
Nginx SSL Certificate Update Debian Tutorial
Apr 13, 2025 am 07:21 AM
This article will guide you on how to update your NginxSSL certificate on your Debian system. Step 1: Install Certbot First, make sure your system has certbot and python3-certbot-nginx packages installed. If not installed, please execute the following command: sudoapt-getupdatesudoapt-getinstallcertbotpython3-certbot-nginx Step 2: Obtain and configure the certificate Use the certbot command to obtain the Let'sEncrypt certificate and configure Nginx: sudocertbot--nginx Follow the prompts to select
 How to configure HTTPS server in Debian OpenSSL
Apr 13, 2025 am 11:03 AM
How to configure HTTPS server in Debian OpenSSL
Apr 13, 2025 am 11:03 AM
Configuring an HTTPS server on a Debian system involves several steps, including installing the necessary software, generating an SSL certificate, and configuring a web server (such as Apache or Nginx) to use an SSL certificate. Here is a basic guide, assuming you are using an ApacheWeb server. 1. Install the necessary software First, make sure your system is up to date and install Apache and OpenSSL: sudoaptupdatesudoaptupgradesudoaptinsta



