Comparison of file copying performance between io and nio in java
1. In the traditional JAVA IO system, the process of reading disk file data is as follows:
Take the FileInputStream class as an example. This class has a read(byte b[]) method. byte b[] is the data we want to store and read. Get the user space buffer. Referring to the source code of the read(byte b[]) method, we can see that it will call the readBytes(b, 0, b.length) method internally, and the readBytes(b, 0, b.length) method is a native method (i.e. Local method), and finally initiate a system call through this local method, that is, calling the read() method of the system kernel. The kernel reads data from the disk to the kernel buffer. In this process, the disk controller reads the data from the disk through DMA operation. Get the kernel buffer, this process does not depend on the CPU. The user process then copies the data from the kernel buffer to the user space buffer. The user process then reads data from the user space buffer. Because user processes cannot directly access the hardware. Therefore, the kernel needs to act as a middleman to read the file.
The whole process is shown in the figure below: 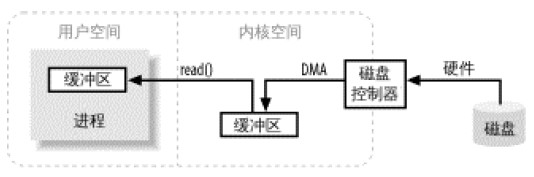
2. Since JAVA 1.4, JAVA has introduced the concept of file channel in NIO. The biggest difference from traditional IO is that traditional IO is based on Byte (byte) and Stream ( Stream), and NIO is based on Buffer (buffer) and Channel (channel). The API provides a FileChannel class and Selector (selector), which is associated with the traditional IO stream. The file channel can be obtained by FileInputStream or FileOutputStream, and we can read and write files through the channel.
3. JAVA NIO also introduces the concept of file memory mapping: most modern operating systems support virtual memory mapping, so that we can map the kernel space address and the user space virtual address to the same physical address, so that the DMA hardware (can only access physical memory address) can fill the buffer visible to both the kernel and user space processes. As shown in the figure below
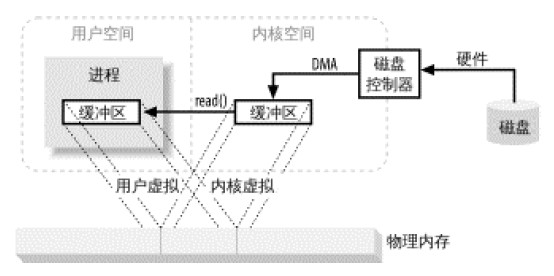
Let’s take a look at the time-consuming comparison of file copying using IO, BufferedIO and NIO: 11 MB audio file
The time-consuming file copying using the traditional IO method: 21ms
Using the NIO file channel method Time-consuming to implement file copy: 16ms
Time-consuming to implement file copy using NIO file memory mapping and file channel: 7ms
Time-consuming to implement file copy using FileUtils file copy tool class: 53ms
package com.maystar.utils;
import java.io.File ;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.nio.MappedByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel;
import org.apache.commons.io.FileUtils;
public class FileCopyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String sourcePath = "F:\glzmv.mp3";
String destPath1 = "F:\glzmvCopy1.mp3";
String destPath2 = "F:\glzmvCopy2.mp3";
String destPath3 = " ;
long t1 = System.currentTimeMillis();
traditionalCopy(sourcePath,destPath1); using using using ’s ’ s ’ using using ‐ to copy through through ‐ ‐ ‐t ‐ t2 to 1) + "ms") ;
nioCopy ( ); t3-t2) + " ms");
nioCopy2(sourcePath,destPath3);
long t4 = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("Time-consuming to implement file copy using NIO file memory mapping and file channel:" + (t 4 -t3) + "ms");
nioCopy3 ( ) nioCopy3(sourcePath, destPath4); ) + "ms");
}
private static void nioCopy3(String sourcePath, String destPath) throws Exception {
,, , , , File dest = new File(destPath);
FileUtils. copyFile(source, dest);//View source code commons-io-2.4 also uses nio operations to implement operations similar to nioCopy, but the efficiency is lower than nioCopy. The reason is that after executing doCopyFile in FileUtils.copyFile, the IOUtils tool class is closed. Stream operations call corresponding constructors according to different types of streams.
File dest = new File(destPath);
if(!dest.exists( :) (dest);
FileChannel sourceCh = getChannel(); FileChannel destCh = fos.getChannel();
MappedByteBuffer mbb = sourceCh.map(FileChannel.MapMode.READ_ONLY, 0, sourceCh.size()); sourceCh.close();
destCh .close();
.close(); File source = new File(sourcePath);
File dest = new File(destPath);
if(!dest.exists()) {
dest.createNewFile();
}
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(source);
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(dest);
byte [] buf = new byte [fis.available()];
int len = 0;
while((len = fis.read(buf)) != -1) {
fos.write(buf, 0, len);
}
fis.close();
fos.close();
}
private static void nioCopy(String sourcePath, String destPath) throws Exception{
File source = new File(sourcePath);
File dest = new File(destPath);
if(!dest.exists()) {
dest.createNewFile();
}
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(source);
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(dest);
FileChannel sourceCh = fis.getChannel();
FileChannel destCh = fos.getChannel();
destCh.transferFrom(sourceCh, 0, sourceCh.size());
sourceCh.close();
destCh.close();
}
}

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Square Root in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Square Root in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Guide to Square Root in Java. Here we discuss how Square Root works in Java with example and its code implementation respectively.
 Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Perfect Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check Perfect number in Java?, examples with code implementation.
 Random Number Generator in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:27 PM
Random Number Generator in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:27 PM
Guide to Random Number Generator in Java. Here we discuss Functions in Java with examples and two different Generators with ther examples.
 Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Weka in Java. Here we discuss the Introduction, how to use weka java, the type of platform, and advantages with examples.
 Armstrong Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Armstrong Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Guide to the Armstrong Number in Java. Here we discuss an introduction to Armstrong's number in java along with some of the code.
 Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Smith Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check smith number in Java? example with code implementation.
 Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
In this article, we have kept the most asked Java Spring Interview Questions with their detailed answers. So that you can crack the interview.
 Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8 introduces the Stream API, providing a powerful and expressive way to process data collections. However, a common question when using Stream is: How to break or return from a forEach operation? Traditional loops allow for early interruption or return, but Stream's forEach method does not directly support this method. This article will explain the reasons and explore alternative methods for implementing premature termination in Stream processing systems. Further reading: Java Stream API improvements Understand Stream forEach The forEach method is a terminal operation that performs one operation on each element in the Stream. Its design intention is






