Implementation of commonly used caching Cache mechanism in Java
The so-called cache means that objects that are frequently called by a program or system are stored in memory so that they can be quickly called when used again without having to create new duplicate instances. Doing so can reduce system overhead and improve system efficiency.
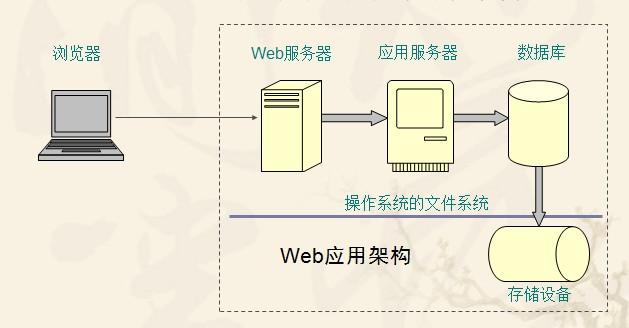
Caching can be mainly divided into two categories:
1. Through file caching, as the name implies, file caching refers to storing data on the disk, whether it is in XML format, serialized file DAT format or other File format;
2. Memory caching, that is, implementing a static Map in a class, and performing regular additions and deletions on this Map.
The code is as follows:
package lhm.hcy.guge.frameset.cache;
import java.util.*;
//Description: 管理缓存
//可扩展的功能:当chche到内存溢出时必须清除掉最早期的一些缓存对象,这就要求对每个缓存对象保存创建时间
public class CacheManager {
private static HashMap cacheMap = new HashMap();
//单实例构造方法
private CacheManager() {
super();
}
//获取布尔值的缓存
public static boolean getSimpleFlag(String key){
try{
return (Boolean) cacheMap.get(key);
}catch(NullPointerException e){
return false;
}
}
public static long getServerStartdt(String key){
try {
return (Long)cacheMap.get(key);
} catch (Exception ex) {
return 0;
}
}
//设置布尔值的缓存
public synchronized static boolean setSimpleFlag(String key,boolean flag){
if (flag && getSimpleFlag(key)) {//假如为真不允许被覆盖
return false;
}else{
cacheMap.put(key, flag);
return true;
}
}
public synchronized static boolean setSimpleFlag(String key,long serverbegrundt){
if (cacheMap.get(key) == null) {
cacheMap.put(key,serverbegrundt);
return true;
}else{
return false;
}
}
//得到缓存。同步静态方法
private synchronized static Cache getCache(String key) {
return (Cache) cacheMap.get(key);
}
//判断是否存在一个缓存
private synchronized static boolean hasCache(String key) {
return cacheMap.containsKey(key);
}
//清除所有缓存
public synchronized static void clearAll() {
cacheMap.clear();
}
//清除某一类特定缓存,通过遍历HASHMAP下的所有对象,来判断它的KEY与传入的TYPE是否匹配
public synchronized static void clearAll(String type) {
Iterator i = cacheMap.entrySet().iterator();
String key;
ArrayList arr = new ArrayList();
try {
while (i.hasNext()) {
java.util.Map.Entry entry = (java.util.Map.Entry) i.next();
key = (String) entry.getKey();
if (key.startsWith(type)) { //如果匹配则删除掉
arr.add(key);
}
}
for (int k = 0; k < arr.size(); k++) {
clearOnly(arr.get(k));
}
} catch (Exception ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
//清除指定的缓存
public synchronized static void clearOnly(String key) {
cacheMap.remove(key);
}
//载入缓存
public synchronized static void putCache(String key, Cache obj) {
cacheMap.put(key, obj);
}
//获取缓存信息
public static Cache getCacheInfo(String key) {
if (hasCache(key)) {
Cache cache = getCache(key);
if (cacheExpired(cache)) { //调用判断是否终止方法
cache.setExpired(true);
}
return cache;
}else
return null;
}
//载入缓存信息
public static void putCacheInfo(String key, Cache obj, long dt,boolean expired) {
Cache cache = new Cache();
cache.setKey(key);
cache.setTimeOut(dt + System.currentTimeMillis()); //设置多久后更新缓存
cache.setValue(obj);
cache.setExpired(expired); //缓存默认载入时,终止状态为FALSE
cacheMap.put(key, cache);
}
//重写载入缓存信息方法
public static void putCacheInfo(String key,Cache obj,long dt){
Cache cache = new Cache();
cache.setKey(key);
cache.setTimeOut(dt+System.currentTimeMillis());
cache.setValue(obj);
cache.setExpired(false);
cacheMap.put(key,cache);
}
//判断缓存是否终止
public static boolean cacheExpired(Cache cache) {
if (null == cache) { //传入的缓存不存在
return false;
}
long nowDt = System.currentTimeMillis(); //系统当前的毫秒数
long cacheDt = cache.getTimeOut(); //缓存内的过期毫秒数
if (cacheDt <= 0||cacheDt>nowDt) { //过期时间小于等于零时,或者过期时间大于当前时间时,则为FALSE
return false;
} else { //大于过期时间 即过期
return true;
}
}
//获取缓存中的大小
public static int getCacheSize() {
return cacheMap.size();
}
//获取指定的类型的大小
public static int getCacheSize(String type) {
int k = 0;
Iterator i = cacheMap.entrySet().iterator();
String key;
try {
while (i.hasNext()) {
java.util.Map.Entry entry = (java.util.Map.Entry) i.next();
key = (String) entry.getKey();
if (key.indexOf(type) != -1) { //如果匹配则删除掉
k++;
}
}
} catch (Exception ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
return k;
}
//获取缓存对象中的所有键值名称
public static ArrayList getCacheAllkey() {
ArrayList a = new ArrayList();
try {
Iterator i = cacheMap.entrySet().iterator();
while (i.hasNext()) {
java.util.Map.Entry entry = (java.util.Map.Entry) i.next();
a.add((String) entry.getKey());
}
} catch (Exception ex) {} finally {
return a;
}
}
//获取缓存对象中指定类型 的键值名称
public static ArrayList getCacheListkey(String type) {
ArrayList a = new ArrayList();
String key;
try {
Iterator i = cacheMap.entrySet().iterator();
while (i.hasNext()) {
java.util.Map.Entry entry = (java.util.Map.Entry) i.next();
key = (String) entry.getKey();
if (key.indexOf(type) != -1) {
a.add(key);
}
}
} catch (Exception ex) {} finally {
return a;
}
}
}
package lhm.hcy.guge.frameset.cache;
public class Cache {
private String key;//缓存ID
private Object value;//缓存数据
private long timeOut;//更新时间
private boolean expired; //是否终止
public Cache() {
super();
}
public Cache(String key, Object value, long timeOut, boolean expired) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.timeOut = timeOut;
this.expired = expired;
}
public String getKey() {
return key;
}
public long getTimeOut() {
return timeOut;
}
public Object getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setKey(String string) {
key = string;
}
public void setTimeOut(long l) {
timeOut = l;
}
public void setValue(Object object) {
value = object;
}
public boolean isExpired() {
return expired;
}
public void setExpired(boolean b) {
expired = b;
}
}
//测试类,
class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(CacheManager.getSimpleFlag("alksd"));
// CacheManager.putCache("abc", new Cache());
// CacheManager.putCache("def", new Cache());
// CacheManager.putCache("ccc", new Cache());
// CacheManager.clearOnly("");
// Cache c = new Cache();
// for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
// CacheManager.putCache("" + i, c);
// }
// CacheManager.putCache("aaaaaaaa", c);
// CacheManager.putCache("abchcy;alskd", c);
// CacheManager.putCache("cccccccc", c);
// CacheManager.putCache("abcoqiwhcy", c);
// System.out.println("删除前的大小:"+CacheManager.getCacheSize());
// CacheManager.getCacheAllkey();
// CacheManager.clearAll("aaaa");
// System.out.println("删除后的大小:"+CacheManager.getCacheSize());
// CacheManager.getCacheAllkey();
}
}
Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1376
1376
 52
52
 Square Root in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Square Root in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Guide to Square Root in Java. Here we discuss how Square Root works in Java with example and its code implementation respectively.
 Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Perfect Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check Perfect number in Java?, examples with code implementation.
 Random Number Generator in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:27 PM
Random Number Generator in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:27 PM
Guide to Random Number Generator in Java. Here we discuss Functions in Java with examples and two different Generators with ther examples.
 Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Weka in Java. Here we discuss the Introduction, how to use weka java, the type of platform, and advantages with examples.
 Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Smith Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check smith number in Java? example with code implementation.
 Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
In this article, we have kept the most asked Java Spring Interview Questions with their detailed answers. So that you can crack the interview.
 Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8 introduces the Stream API, providing a powerful and expressive way to process data collections. However, a common question when using Stream is: How to break or return from a forEach operation? Traditional loops allow for early interruption or return, but Stream's forEach method does not directly support this method. This article will explain the reasons and explore alternative methods for implementing premature termination in Stream processing systems. Further reading: Java Stream API improvements Understand Stream forEach The forEach method is a terminal operation that performs one operation on each element in the Stream. Its design intention is
 TimeStamp to Date in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
TimeStamp to Date in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to TimeStamp to Date in Java. Here we also discuss the introduction and how to convert timestamp to date in java along with examples.




