java NIO tutorial
NIO is the abbreviation of New I/O. To understand its true connotation, you need to master a lot of knowledge. I have tried hard to outline the entire io in these notes. Paving the way for everyone’s in-depth learning.
A brief history of I/O
If you want to understand all of I/O, you must understand the I/O history of java. The I/O history of Java also reflects the development history of Java from one side.
JDK1.0-1.3
In this period of java, it can basically be said that there is no complete I/O support. Because Java I/O operations during this period are blocking, the I/O efficiency is relatively low. Basically, if you want to have a better I/O solution, you basically have to rely on yourself. During this period, Java has not been reused on the server side, which has a lot to do with poor I/O efficiency. Not only was the I/O not done well, but a series of peripheral measures were also not done well. The supported character set encodings are limited, and manual encoding work is often required. And without regular expressions, it is very difficult to process data.
JDK1.4-1.6
In java1.4 released in 2002, non-blocking I/O was added to the java language as JSR-51. At the same time, the encoding and decoding capabilities of the character set have been greatly improved. And there is a regular expression class library based on perl. At the same time, some of the underlying implementations of old I/O have also been rewritten using new I/O methods, which has improved the performance of old I/O. Finally java became popular on the server side.
At the same time, third parties have also begun to exert their efforts. Google released the Guava class library, the I/O part of which greatly simplifies some file operations and data transmission. At the same time, the nio framework netty and mina written under the leadership of Trustin Lee have also been widely circulated, which has greatly promoted the development of java nio.
JDK1.7 to present
With the launch of JSR-203, we saw NIO2 in java1.7. It provides us with more powerful asynchronous I/O operation capabilities that are non-blocking, and also provides a series of extremely convenient APIs for operating file systems and file attributes. And more powerful network I/O
I/O difference
What are the differences between blocking I/O, non-blocking I/O, and asynchronous I/O? Why does every advancement lead to a great improvement in Java I/O capabilities? Let’s take an example of a vegetable growing game.
Suppose there is a vegetable growing game (similar to the previous QQ Farm). After the player plants vegetables, he must stay on that webpage and watch the vegetables mature before he can harvest them. This is an extremely waste of time and the user experience will definitely not be good. This game was later revised. Players no longer need to stay on that web page after planting vegetables. They just need to check it again from time to time. If they find that the vegetables are mature during a certain check, they can harvest the vegetables. Of course, the user experience has been greatly improved and the time wasted by users has also been reduced. However, in order to further enhance the user experience, the game has been revised. After the player plants vegetables, he no longer needs to check whether the vegetables are ripe. When the vegetables are mature, the game will automatically send a notification to the user, telling him that the vegetables are ripe and he should come and collect them quickly. In this way, users basically no longer have to waste time.
The three game versions in the example just represent three types of I/O. Blocking I/O: The CPU cannot proceed with the next operation until the data is read and written, so the CPU has no choice but to wait there. Non-blocking I/O: The CPU can leave before the data is read or written, and it only needs to be asked every once in a while. Asynchronous I/O: Before the data is read and written, the CPU can leave without having to worry about I/O from time to time. When the data is read and written, the CPU is actively notified. The efficiency between the three types of I/O can be judged based on whether it is high or low.
New I/O
Let’s take the non-blocking I/O proposed by java1.4 as the starting point and start to understand the whole picture.
Channels
Buffers
Selectors
These three classes constitute the core API of non-blocking I/O.
Buffer is translated as buffer area, which is a piece of memory that can store data. Channel is a bit like a stream, but it can be read and written, from local I/O to network I/O. Most NIO starts from a Channel. Data can be read from the Channel into the Buffer, or written from the Buffer. to Channel.
In non-blocking I/O, the CPU can leave before the data is read or written, and it only needs to be asked every once in a while. Asking whether the data is read and written requires minimal CPU power, but if the CPU frequently switches tasks, the time required to retain the scene and restore the scene is large. So you can just use a thread to ask if the data is ready. If a thread asks whether the data is ready in multiple channels, it needs to manage multiple channels. This is
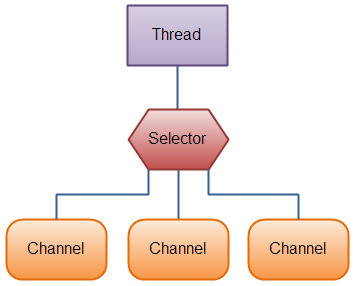
To use Selector, you must register the Channel with the Selector and then call its select() method. This method will block until a registered channel has an event ready. Once this method returns, the thread can handle these events.

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Perfect Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check Perfect number in Java?, examples with code implementation.
 Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Weka in Java. Here we discuss the Introduction, how to use weka java, the type of platform, and advantages with examples.
 Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Smith Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check smith number in Java? example with code implementation.
 Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
In this article, we have kept the most asked Java Spring Interview Questions with their detailed answers. So that you can crack the interview.
 Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8 introduces the Stream API, providing a powerful and expressive way to process data collections. However, a common question when using Stream is: How to break or return from a forEach operation? Traditional loops allow for early interruption or return, but Stream's forEach method does not directly support this method. This article will explain the reasons and explore alternative methods for implementing premature termination in Stream processing systems. Further reading: Java Stream API improvements Understand Stream forEach The forEach method is a terminal operation that performs one operation on each element in the Stream. Its design intention is
 TimeStamp to Date in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
TimeStamp to Date in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to TimeStamp to Date in Java. Here we also discuss the introduction and how to convert timestamp to date in java along with examples.
 Java Program to Find the Volume of Capsule
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Java Program to Find the Volume of Capsule
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Capsules are three-dimensional geometric figures, composed of a cylinder and a hemisphere at both ends. The volume of the capsule can be calculated by adding the volume of the cylinder and the volume of the hemisphere at both ends. This tutorial will discuss how to calculate the volume of a given capsule in Java using different methods. Capsule volume formula The formula for capsule volume is as follows: Capsule volume = Cylindrical volume Volume Two hemisphere volume in, r: The radius of the hemisphere. h: The height of the cylinder (excluding the hemisphere). Example 1 enter Radius = 5 units Height = 10 units Output Volume = 1570.8 cubic units explain Calculate volume using formula: Volume = π × r2 × h (4
 PHP vs. Python: Understanding the Differences
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:15 AM
PHP vs. Python: Understanding the Differences
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:15 AM
PHP and Python each have their own advantages, and the choice should be based on project requirements. 1.PHP is suitable for web development, with simple syntax and high execution efficiency. 2. Python is suitable for data science and machine learning, with concise syntax and rich libraries.






