How much memory does a java object occupy?
Recently, I was reading "In-depth Understanding of Java Virtual Machine" and gained a better understanding of the memory layout of Java objects. So a very common question naturally came to my mind, which is how much memory does a Java object occupy?
I found a very good blog on the Internet: http://yueyemaitian.iteye.com/blog/2033046. The class provided in it is also very practical:
import java.lang.instrument.Instrumentation;
import java.lang.reflect.Array;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.Modifier;
import java.util.ArrayDeque;
import java.util.Deque;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
/**
* 对象占用字节大小工具类
*
* @author tianmai.fh
* @date 2014-03-18 11:29
*/
public class SizeOfObject {
static Instrumentation inst;
public static void premain(String args, Instrumentation instP) {
inst = instP;
}
/**
* 直接计算当前对象占用空间大小,包括当前类及超类的基本类型实例字段大小、<br></br>
* 引用类型实例字段引用大小、实例基本类型数组总占用空间、实例引用类型数组引用本身占用空间大小;<br></br>
* 但是不包括超类继承下来的和当前类声明的实例引用字段的对象本身的大小、实例引用数组引用的对象本身的大小 <br></br>
*
* @param obj
* @return
*/
public static long sizeOf(Object obj) {
return inst.getObjectSize(obj);
}
/**
* 递归计算当前对象占用空间总大小,包括当前类和超类的实例字段大小以及实例字段引用对象大小
*
* @param objP
* @return
* @throws IllegalAccessException
*/
public static long fullSizeOf(Object objP) throws IllegalAccessException {
Set<Object> visited = new HashSet<Object>();
Deque<Object> toBeQueue = new ArrayDeque<Object>();
toBeQueue.add(objP);
long size = 0L;
while (toBeQueue.size() > 0) {
Object obj = toBeQueue.poll();
//sizeOf的时候已经计基本类型和引用的长度,包括数组
size += skipObject(visited, obj) ? 0L : sizeOf(obj);
Class<?> tmpObjClass = obj.getClass();
if (tmpObjClass.isArray()) {
//[I , [F 基本类型名字长度是2
if (tmpObjClass.getName().length() > 2) {
for (int i = 0, len = Array.getLength(obj); i < len; i++) {
Object tmp = Array.get(obj, i);
if (tmp != null) {
//非基本类型需要深度遍历其对象
toBeQueue.add(Array.get(obj, i));
}
}
}
} else {
while (tmpObjClass != null) {
Field[] fields = tmpObjClass.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field : fields) {
if (Modifier.isStatic(field.getModifiers()) //静态不计
|| field.getType().isPrimitive()) { //基本类型不重复计
continue;
}
field.setAccessible(true);
Object fieldValue = field.get(obj);
if (fieldValue == null) {
continue;
}
toBeQueue.add(fieldValue);
}
tmpObjClass = tmpObjClass.getSuperclass();
}
}
}
return size;
}
/**
* String.intern的对象不计;计算过的不计,也避免死循环
*
* @param visited
* @param obj
* @return
*/
static boolean skipObject(Set<Object> visited, Object obj) {
if (obj instanceof String && obj == ((String) obj).intern()) {
return true;
}
return visited.contains(obj);
}
}You can use this code to read and verify , please note that running this program requires injecting Instrumentation through javaagent. For details, please see the original blog. Today I mainly summarize the basic rules for manually calculating the number of bytes occupied by Java objects. As a basic skill, get√ is required. I hope it can help Java novices like me.
Before the introduction, let’s briefly review the memory layout of Java objects: object header (Header), instance data (Instance Data) and alignment padding (Padding). For details, you can see my reading notes. In addition: the results may be different in different environments. My environment is a HotSpot virtual machine and 64-bit Windwos.
Now enter the text:
Object header
The object header occupies 8 bytes on 32-bit systems and 16 bytes on 64-bit systems.

Instance data
The memory usage of primitive type is as follows:
Primitive Type Memory Required(bytes)
boolean 1
byte 1
short 2
char 2
int 4
float 4
long 8
double 8
The reference type occupies 4 bytes each on 32-bit systems, and 8 bytes each on 64-bit systems.
Alignment padding
HotSpot’s alignment is 8-byte alignment:
(object header + instance data + padding) % 8 equals 0 and 0 <= padding < 8
Pointer compression
Memory occupied by the object The size is affected by the VM parameter UseCompressedOops.
1) Impact on object header
Turn on (-XX:+UseCompressedOops) and the object header size is 12 bytes (64-bit machine).
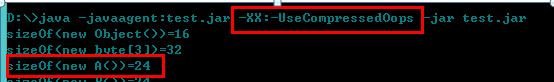
static class A {
int a;
}Memory occupied by object A:
Turn off pointer compression: 16+4=20 is not a multiple of 8, so +padding/4=24
Turn on pointer compression: 12+4=16 It is already a multiple of 8, no padding is needed.
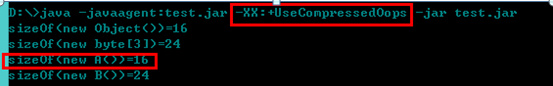
2) Impact on the reference type
The reference type occupies 8 bytes on a 64-bit machine, and occupies 4 bytes after turning on pointer compression.
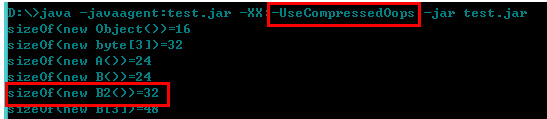
static class B2 {
int b2a;
Integer b2b;
}B2 object memory usage:
Turn off pointer compression: 16+4+8=28 is not a multiple of 8, so +padding/4=32
Turn on pointer compression: 12+4+4 =20 is not a multiple of 8, so +padding/4=24
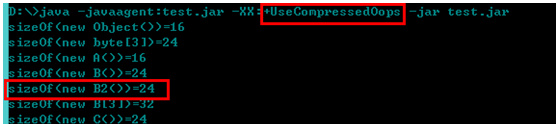
Array object
On a 64-bit machine, the object header of the array object occupies 24 bytes, and occupies 16 bytes after enabling compression. The reason why it takes up more memory than ordinary objects is that extra space is needed to store the length of the array.
First consider the memory size occupied by new Integer[0]. The length is 0, which is the size of the object header:
Without compression: 24 bytes

With compression turned on: 16 bytes

Then it’s easy to calculate new Integer[1], new Integer[2], new Integer[3] and new Integer[4]:
Compression is not turned on:
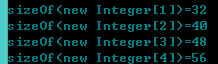
开启压缩:
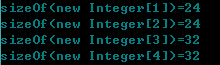
拿new Integer[3]来具体解释下:
未开启压缩:24(对象头)+8*3=48,不需要padding;
开启压缩:16(对象头)+3*4=28,+padding/4=32,其他依次类推。
自定义类的数组也是一样的,比如:
static class B3 {
int a;
Integer b;
}new B3[3]占用的内存大小:
未开启压缩:48
开启压缩后:32
复合对象
计算复合对象占用内存的大小其实就是运用上面几条规则,只是麻烦点。
1)对象本身的大小
直接计算当前对象占用空间大小,包括当前类及超类的基本类型实例字段大小、引用类型实例字段引用大小、实例基本类型数组总占用空间、实例引用类型数组引用本身占用空间大小; 但是不包括超类继承下来的和当前类声明的实例引用字段的对象本身的大小、实例引用数组引用的对象本身的大小。
static class B {
int a;
int b;
}
static class C {
int ba;
B[] as = new B[3];
C() {
for (int i = 0; i < as.length; i++) {
as[i] = new B();
}
}
}未开启压缩:16(对象头)+4(ba)+8(as引用的大小)+padding/4=32
开启压缩:12+4+4+padding/4=24
2)当前对象占用的空间总大小
递归计算当前对象占用空间总大小,包括当前类和超类的实例字段大小以及实例字段引用对象大小。
递归计算复合对象占用的内存的时候需要注意的是:对齐填充是以每个对象为单位进行的,看下面这个图就很容易明白。
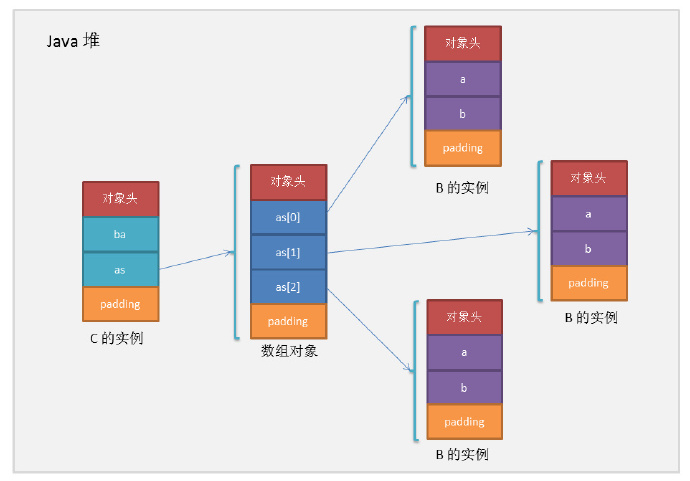
现在我们来手动计算下C对象占用的全部内存是多少,主要是三部分构成:C对象本身的大小+数组对象的大小+B对象的大小。
未开启压缩:
(16 + 4 + 8+4(padding)) + (24+ 8*3) +(16+8)*3 = 152bytes
开启压缩:
(12 + 4 + 4 +4(padding)) + (16 + 4*3 +4(数组对象padding)) + (12+8+4(B对象padding))*3= 128bytes
大家有兴趣的可以试试。
实际工作中真正需要手动计算对象大小的场景应该很少,但是个人觉得做为基础知识每个Java开发人员都应该了解,另外:对自己写的代码大概占用多少内存,内存中是怎么布局的应该有一个直觉性的认识。

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Perfect Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check Perfect number in Java?, examples with code implementation.
 Sources say Samsung Electronics and SK Hynix will commercialize stacked mobile memory after 2026
Sep 03, 2024 pm 02:15 PM
Sources say Samsung Electronics and SK Hynix will commercialize stacked mobile memory after 2026
Sep 03, 2024 pm 02:15 PM
According to news from this website on September 3, Korean media etnews reported yesterday (local time) that Samsung Electronics and SK Hynix’s “HBM-like” stacked structure mobile memory products will be commercialized after 2026. Sources said that the two Korean memory giants regard stacked mobile memory as an important source of future revenue and plan to expand "HBM-like memory" to smartphones, tablets and laptops to provide power for end-side AI. According to previous reports on this site, Samsung Electronics’ product is called LPWide I/O memory, and SK Hynix calls this technology VFO. The two companies have used roughly the same technical route, which is to combine fan-out packaging and vertical channels. Samsung Electronics’ LPWide I/O memory has a bit width of 512
 Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Weka in Java. Here we discuss the Introduction, how to use weka java, the type of platform, and advantages with examples.
 Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Smith Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check smith number in Java? example with code implementation.
 Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
In this article, we have kept the most asked Java Spring Interview Questions with their detailed answers. So that you can crack the interview.
 Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8 introduces the Stream API, providing a powerful and expressive way to process data collections. However, a common question when using Stream is: How to break or return from a forEach operation? Traditional loops allow for early interruption or return, but Stream's forEach method does not directly support this method. This article will explain the reasons and explore alternative methods for implementing premature termination in Stream processing systems. Further reading: Java Stream API improvements Understand Stream forEach The forEach method is a terminal operation that performs one operation on each element in the Stream. Its design intention is
 TimeStamp to Date in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
TimeStamp to Date in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to TimeStamp to Date in Java. Here we also discuss the introduction and how to convert timestamp to date in java along with examples.
 Java Program to Find the Volume of Capsule
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Java Program to Find the Volume of Capsule
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Capsules are three-dimensional geometric figures, composed of a cylinder and a hemisphere at both ends. The volume of the capsule can be calculated by adding the volume of the cylinder and the volume of the hemisphere at both ends. This tutorial will discuss how to calculate the volume of a given capsule in Java using different methods. Capsule volume formula The formula for capsule volume is as follows: Capsule volume = Cylindrical volume Volume Two hemisphere volume in, r: The radius of the hemisphere. h: The height of the cylinder (excluding the hemisphere). Example 1 enter Radius = 5 units Height = 10 units Output Volume = 1570.8 cubic units explain Calculate volume using formula: Volume = π × r2 × h (4




