
1. Basic Usage
var recognition = new webkitSpeechRecognition();
recognition.onresult = function(event) {
console.log(event)
}
recognition.start();
The operation here will actually enable the user authorization page to turn on the microphone. If the user allows it, the user can start talking. If you stop talking, the onresult registration time will be triggered, and Will return the captured audio as a JavaScript object.
2. Response flow
You need to wait for the user to be ready for the conversation and know that the conversation is over;
var recognition = new webkitSpeechRecognition();
recognition.continuous = true;
recognition.interimResults = true;
recognition.onresult = function(event) {
console.log(event)
}
recognition.start(); 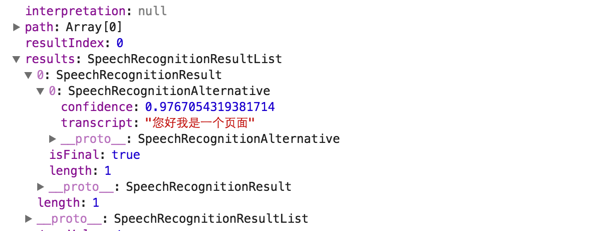
This way you can render the result in advance when the user starts to speak.
You can automatically select the recognized language, and the default is the local language.
Three, x-webkit-speech
Webkit-based browser supports voice input
<input type="text" x-webkit-speech />
It will recognize audio and convert it into text
Four. Security
Browser under http protocol The user will be reminded to confirm the voice operation every time, but the https page does not have such a troublesome operation.
JavaScript context, the entire page, can access the captured audio.




