How to unit test Angular.js Controller
1. Write a simple Angular App
Before starting to write the test, we first write a simple calculation App, which will calculate the sum of two numbers.
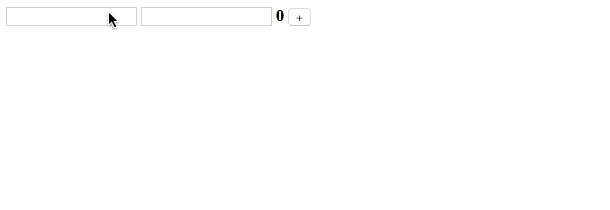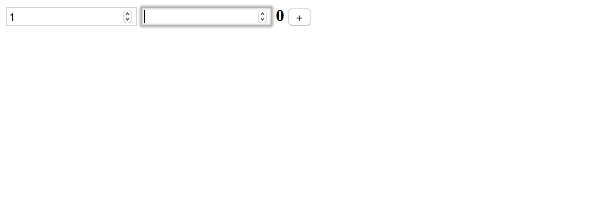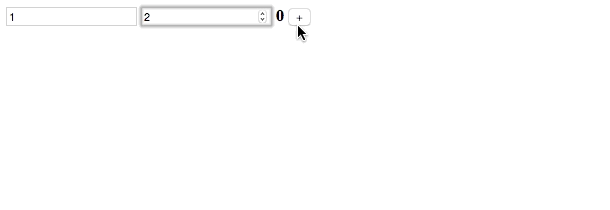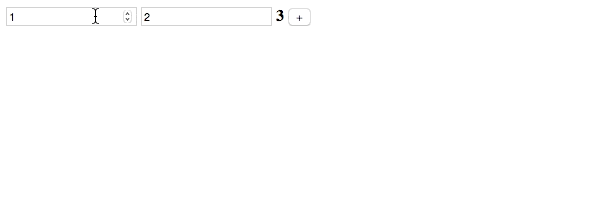
The code is as follows:
<html>
<head>
<script type="text/javascript" src="https://code.angularjs.org/1.4.0-rc.2/angular.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<!-- This div element corresponds to the CalculatorController we created via the JavaScript-->
<div ng-controller="CalculatorController">
<input ng-model="x" type="number">
<input ng-model="y" type="number">
<strong>{{z}}</strong>
<!-- the value for ngClick maps to the sum function within the controller body -->
<input type="button" ng-click="sum()" value="+">
</div>
</body>
<script type="text/javascript">
// Creates a new module called 'calculatorApp'
angular.module('calculatorApp', []);
// Registers a controller to our module 'calculatorApp'.
angular.module('calculatorApp').controller('CalculatorController', function CalculatorController($scope) {
$scope.z = 0;
$scope.sum = function() {
$scope.z = $scope.x + $scope.y;
};
});
// load the app
angular.element(document).ready(function() {
angular.bootstrap(document, ['calculatorApp']);
});
</script>
</html>
Second, briefly talk about some basic concepts involved:
Create a module
What is angular.module? It is a place for creating and recycling modules. We create a new module called calculatorApp and we add the component to this module.
angular.module('calculatorApp', []);
About the second parameter? The second parameter is required and indicates that we are creating a new module. If our application needs other dependencies, we can pass them ['ngResource', 'ngCookies']. The presence of the second parameter indicates that this is an instance of the module returned by the request.
Conceptually, it is meant to mean something like the following:
* angular.module.createInstance(name, requires); * angular.module.getInstance(name)
However, actually we write it like this:
* angular.module('calculatorApp', []); // i.e. createInstance
* angular.module('calculatorApp'); // i.e. getInstance
More information about module https://docs.angularjs .org/api/ng/function/angular.module
2. Add a controller to the module
Then we add a controller to the angular module example
angular.module('calculatorApp').controller('CalculatorController', function CalculatorController($scope) {
$scope.z = 0;
$scope.sum = function() {
$scope.z = $scope.x + $scope.y;
};
});
The controller is mainly responsible for business logic and view binding , $scope is the direct messenger to the view's controller.
3. Connect elements in the view
In the HTML below, we need to calculate the value in the input, and these are contained in the div of this controller.
<div ng-controller="CalculatorController">
<input ng-model="x" type="number">
<input ng-model="y" type="number">
<strong>{{z}}</strong>
<!-- the value for ngClick maps to the sum function within the controller body -->
<input type="button" ng-click="sum()" value="+">
</div>
Input The value bound to ng-model is the same as that defined on $scope, such as $scope.x. We also bound the $scope.sum method to the button element using ng-click.
3. Add tests
Next we finally get to our topic, add some unit tests to the controller. We ignore the html part of the code and focus mainly on the controller code.
angular.module('calculatorApp').controller('CalculatorController', function CalculatorController($scope) {
$scope.z = 0;
$scope.sum = function() {
$scope.z = $scope.x + $scope.y;
};
});
In order to test the controller, we need to mention the following points? + How to create a controller instance + How to get/set the properties of an object + How to call functions in $scope
describe('calculator', function () {
beforeEach(angular.mock.module('calculatorApp'));
var $controller;
beforeEach(angular.mock.inject(function(_$controller_){
$controller = _$controller_;
}));
describe('sum', function () {
it('1 + 1 should equal 2', function () {
var $scope = {};
var controller = $controller('CalculatorController', { $scope: $scope });
$scope.x = 1;
$scope.y = 2;
$scope.sum();
expect($scope.z).toBe(3);
});
});
});
Before we start, we need to introduce ngMock. We add angular.mock
, ngMock to the test code Modules provide a mechanism for unit testing of virtual services.
4. How to get the controller instance
Using ngMock we can register a calculator app instance.
beforeEach(angular.mock.module('calculatorApp'));
Once the calculatorApp is initialized, we can use the inject function, which can solve the controller reference problem.
beforeEach(angular.mock.inject(function(_$controller_) {
$controller = _$controller_;
}));
Once the app is loaded, we use the inject function, and the $controller service can obtain an instance of CalculatorController.
var controller = $controller('CalculatorController', { $scope: $scope });
5. How to get/set the attributes of an object
In the previous code, we can already get an instance of a controller. The second parameter in the brackets is actually the controller itself. Our controller only has A parameter $scope object
function CalculatorController($scope) { ... }
In our test $scope represents a simple JavaScript object.
var $scope = {};
var controller = $controller('CalculatorController', { $scope: $scope });
// set some properties on the scope object
$scope.x = 1;
$scope.y = 2;
We set the values of x and y to simulate what is shown in the gif just now. We agree that we can also read the properties in the object, just like the assertion in the following test:
expect($scope.z).toBe(3);
6. How to call the functions in $scope
The last thing is how we simulate the user’s click , just like what we use in most JS, it is actually just a simple call to the function,
$scope.sum();


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Angular learning talks about standalone components (Standalone Component)
Dec 19, 2022 pm 07:24 PM
Angular learning talks about standalone components (Standalone Component)
Dec 19, 2022 pm 07:24 PM
This article will take you to continue learning angular and briefly understand the standalone component (Standalone Component) in Angular. I hope it will be helpful to you!
 Detailed explanation of angular learning state manager NgRx
May 25, 2022 am 11:01 AM
Detailed explanation of angular learning state manager NgRx
May 25, 2022 am 11:01 AM
This article will give you an in-depth understanding of Angular's state manager NgRx and introduce how to use NgRx. I hope it will be helpful to you!
 What should I do if the project is too big? How to split Angular projects reasonably?
Jul 26, 2022 pm 07:18 PM
What should I do if the project is too big? How to split Angular projects reasonably?
Jul 26, 2022 pm 07:18 PM
The Angular project is too large, how to split it reasonably? The following article will introduce to you how to reasonably split Angular projects. I hope it will be helpful to you!
 Let's talk about how to customize the angular-datetime-picker format
Sep 08, 2022 pm 08:29 PM
Let's talk about how to customize the angular-datetime-picker format
Sep 08, 2022 pm 08:29 PM
How to customize the angular-datetime-picker format? The following article talks about how to customize the format. I hope it will be helpful to everyone!
 A brief analysis of independent components in Angular and see how to use them
Jun 23, 2022 pm 03:49 PM
A brief analysis of independent components in Angular and see how to use them
Jun 23, 2022 pm 03:49 PM
This article will take you through the independent components in Angular, how to create an independent component in Angular, and how to import existing modules into the independent component. I hope it will be helpful to you!
 A step-by-step guide to understanding dependency injection in Angular
Dec 02, 2022 pm 09:14 PM
A step-by-step guide to understanding dependency injection in Angular
Dec 02, 2022 pm 09:14 PM
This article will take you through dependency injection, introduce the problems that dependency injection solves and its native writing method, and talk about Angular's dependency injection framework. I hope it will be helpful to you!
 Angular's :host, :host-context, ::ng-deep selectors
May 31, 2022 am 11:08 AM
Angular's :host, :host-context, ::ng-deep selectors
May 31, 2022 am 11:08 AM
This article will give you an in-depth understanding of several special selectors in Angular: host, :host-context, ::ng-deep. I hope it will be helpful to you!
 Deep understanding of @Component decorator in angular
May 27, 2022 pm 08:13 PM
Deep understanding of @Component decorator in angular
May 27, 2022 pm 08:13 PM
Component is a subclass of Directive, which is a decorator used to mark a class as an Angular component. The following article will give you an in-depth understanding of the @Component decorator in angular. I hope it will be helpful to you.






