c# GDI+ simple drawing (2)
在上一片里已经向大家介绍了如何使用GDI+绘制简单的图像,这一片继续向大家介绍其它一些绘图知识.
1.首先我们来看下上一片中我们使用过的Pen.
Pen的属性主要有: Color(颜色),DashCap(短划线终点形状),DashStyle(虚线样式),EndCap(线尾形状), StartCap(线头形状),Width(粗细)等.
我们可以用Pen 来画虚线,带箭头的直线等
Pen p = new Pen(Color.Blue, 5);//设置笔的粗细为,颜色为蓝色
Graphics g = this.CreateGraphics();
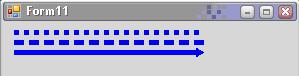
//画虚线
p.DashStyle = DashStyle.Dot;//定义虚线的样式为点
g.DrawLine(p, 10, 10, 200, 10);
//自定义虚线
p.DashPattern = new float[] { 2, 1 };//设置短划线和空白部分的数组
g.DrawLine(p, 10, 20, 200, 20);
//画箭头,只对不封闭曲线有用
p.DashStyle = DashStyle.Solid;//恢复实线
p.EndCap = LineCap.ArrowAnchor;//定义线尾的样式为箭头
g.DrawLine(p, 10, 30, 200, 30);
g.Dispose();
p.Dispose();以上代码运行结果:
2.接下来我们来看下Brush的使用
作用:我们可以用画刷填充各种图形形状,如矩形、椭圆、扇形、多边形和封闭路径等,主要有几种不同类型的画刷:
• SolidBrush:画刷最简单的形式,用纯色进行绘制
• HatchBrush:类似于 SolidBrush,但是可以利用该类从大量预设的图案中选择绘制时要使用的图案,而不是纯色
• TextureBrush:使用纹理(如图像)进行绘制
• LinearGradientBrush:使用沿渐变混合的两种颜色进行绘制
• PathGradientBrush :基于编程者定义的唯一路径,使用复杂的混合色渐变进行绘制
我们这里只是简单介绍使用其中的几种:
Graphics g = this.CreateGraphics();
Rectangle rect = new Rectangle(10, 10, 50, 50);//定义矩形,参数为起点横纵坐标以及其长和宽
//单色填充
SolidBrush b1 = new SolidBrush(Color.Blue);//定义单色画刷
g.FillRectangle(b1, rect);//填充这个矩形
//字符串
g.DrawString("字符串", new Font("宋体", 10), b1, new PointF(90, 10));
//用图片填充
TextureBrush b2 = new TextureBrush(Image.FromFile(@"e:\picture\1.jpg"));
rect.Location = new Point(10, 70);//更改这个矩形的起点坐标
rect.Width = 200;//更改这个矩形的宽来
rect.Height = 200;//更改这个矩形的高
g.FillRectangle(b2, rect);
//用渐变色填充
rect.Location = new Point(10, 290);
LinearGradientBrush b3 = new LinearGradientBrush(rect, Color.Yellow , Color.Black , LinearGradientMode.Horizontal);
g.FillRectangle(b3, rect);运行效果图:

3.坐标轴变换
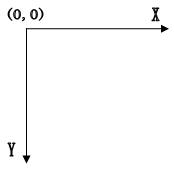
在winform中的坐标轴和我们平时接触的平面直角坐标轴不同,winform中的坐标轴方向完全相反:窗体的左上角为原点(0,0),水平向左则X增大,垂直下向则Y增大
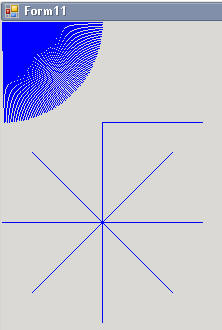
接下来,我们来实际操作下,通过旋转坐标轴的方向来画出不同角度的图案,或通过更改坐标原点的位置来平衡坐标轴的位置.
Graphics g = this.CreateGraphics();
//单色填充
//SolidBrush b1 = new SolidBrush(Color.Blue);//定义单色画刷
Pen p = new Pen(Color.Blue,1);
//转变坐标轴角度
for (int i = 0; i < 90; i++)
{
g.RotateTransform(i);//每旋转一度就画一条线
g.DrawLine(p, 0, 0, 100, 0);
g.ResetTransform();//恢复坐标轴坐标
}
//平移坐标轴
g.TranslateTransform(100, 100);
g.DrawLine(p, 0, 0, 100, 0);
g.ResetTransform();
//先平移到指定坐标,然后进行度旋转
g.TranslateTransform(100,200);
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++)
{
g.RotateTransform(45);
g.DrawLine(p, 0, 0, 100, 0);
}
g.Dispose();运行效果图:
4.最后我们来看下Graphics这个画板上我们还可以画什么
其实我们上面用到的都是在画一些简单的图形,直线,矩形,扇形,圆孤等,我们还可以用它来绘制图片,这可以用它的DrawImage方法.这里我不详细讲解,大家有兴趣可以自己去MSDN了解下.我们后面会讲到的截图就会用到这个方法.
更多c# GDI+简单绘图(二)相关文章请关注PHP中文网!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1385
1385
 52
52
 How to handle special characters in C language
Apr 03, 2025 pm 03:18 PM
How to handle special characters in C language
Apr 03, 2025 pm 03:18 PM
In C language, special characters are processed through escape sequences, such as: \n represents line breaks. \t means tab character. Use escape sequences or character constants to represent special characters, such as char c = '\n'. Note that the backslash needs to be escaped twice. Different platforms and compilers may have different escape sequences, please consult the documentation.
 What is the role of char in C strings
Apr 03, 2025 pm 03:15 PM
What is the role of char in C strings
Apr 03, 2025 pm 03:15 PM
In C, the char type is used in strings: 1. Store a single character; 2. Use an array to represent a string and end with a null terminator; 3. Operate through a string operation function; 4. Read or output a string from the keyboard.
 The difference between char and wchar_t in C language
Apr 03, 2025 pm 03:09 PM
The difference between char and wchar_t in C language
Apr 03, 2025 pm 03:09 PM
In C language, the main difference between char and wchar_t is character encoding: char uses ASCII or extends ASCII, wchar_t uses Unicode; char takes up 1-2 bytes, wchar_t takes up 2-4 bytes; char is suitable for English text, wchar_t is suitable for multilingual text; char is widely supported, wchar_t depends on whether the compiler and operating system support Unicode; char is limited in character range, wchar_t has a larger character range, and special functions are used for arithmetic operations.
 How to use various symbols in C language
Apr 03, 2025 pm 04:48 PM
How to use various symbols in C language
Apr 03, 2025 pm 04:48 PM
The usage methods of symbols in C language cover arithmetic, assignment, conditions, logic, bit operators, etc. Arithmetic operators are used for basic mathematical operations, assignment operators are used for assignment and addition, subtraction, multiplication and division assignment, condition operators are used for different operations according to conditions, logical operators are used for logical operations, bit operators are used for bit-level operations, and special constants are used to represent null pointers, end-of-file markers, and non-numeric values.
 The difference between multithreading and asynchronous c#
Apr 03, 2025 pm 02:57 PM
The difference between multithreading and asynchronous c#
Apr 03, 2025 pm 02:57 PM
The difference between multithreading and asynchronous is that multithreading executes multiple threads at the same time, while asynchronously performs operations without blocking the current thread. Multithreading is used for compute-intensive tasks, while asynchronously is used for user interaction. The advantage of multi-threading is to improve computing performance, while the advantage of asynchronous is to not block UI threads. Choosing multithreading or asynchronous depends on the nature of the task: Computation-intensive tasks use multithreading, tasks that interact with external resources and need to keep UI responsiveness use asynchronous.
 How to convert char in C language
Apr 03, 2025 pm 03:21 PM
How to convert char in C language
Apr 03, 2025 pm 03:21 PM
In C language, char type conversion can be directly converted to another type by: casting: using casting characters. Automatic type conversion: When one type of data can accommodate another type of value, the compiler automatically converts it.
 What is the function of C language sum?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 02:21 PM
What is the function of C language sum?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 02:21 PM
There is no built-in sum function in C language, so it needs to be written by yourself. Sum can be achieved by traversing the array and accumulating elements: Loop version: Sum is calculated using for loop and array length. Pointer version: Use pointers to point to array elements, and efficient summing is achieved through self-increment pointers. Dynamically allocate array version: Dynamically allocate arrays and manage memory yourself, ensuring that allocated memory is freed to prevent memory leaks.
 How to use char array in C language
Apr 03, 2025 pm 03:24 PM
How to use char array in C language
Apr 03, 2025 pm 03:24 PM
The char array stores character sequences in C language and is declared as char array_name[size]. The access element is passed through the subscript operator, and the element ends with the null terminator '\0', which represents the end point of the string. The C language provides a variety of string manipulation functions, such as strlen(), strcpy(), strcat() and strcmp().




