Principles of indexing - taking innodb as an example
1. Write in front
As the development and testing tasks come to an end, everyone is sorting out some preparations before the release of the project. One of the important tasks is to index some SQL statements written before. This high concurrency, It is very necessary in a high-traffic environment. Building a good index can greatly improve the query efficiency of SQL statements. So the question is, what is an index and how to build a good index? This article takes the mysql Innodb storage engine as an example and looks at how to build a good index based on actual projects.
2. Index definition
MySQL’s official definition of index is: Index (Index) is a data structure that helps MySQL obtain data efficiently. By extracting the backbone of the sentence, you can get the essence of the index: the index is a data structure.
We know that database query is one of the most important functions of the database, such as the following SQL statement: SELECT * FROM test_table WHERE id = 99; the data record with id 99 can be obtained from the table test_table.
We all want to query data as fast as possible, so designers of database systems will optimize from the perspective of query algorithms. The most basic query algorithm is of course linear search. It traverses the test_table and then matches row by row whether the value of id is 99. This algorithm with a complexity of O(n) is obviously bad when the amount of data is large. Good The development of computer science has provided many better search algorithms, such as binary search, binary tree search, etc. If you do a little analysis, you will find that each search algorithm can only be applied to a specific data structure. For example, binary search requires that the retrieved data be ordered, while binary tree search can only be applied to binary search trees, but the data itself The organizational structure cannot completely satisfy various data structures (for example, it is theoretically impossible to organize both columns in order at the same time), so in addition to the data, the database system also maintains data structures that satisfy specific search algorithms. Structures reference (point to) data in some way, allowing advanced search algorithms to be implemented on these data structures. This data structure is an index.
The above example is mainly used to briefly illustrate the role of indexes. Most database systems and file systems, including mysql Innodb, do not choose a binary tree structure as an index, but use B-Tree or its variant B+Tree. As an index structure, this index structure can minimize the number of disk I/O accesses during the search process. You can learn on your own about what B-Tree or B+Tree is and the reasons for choosing them as database index structures. . Below we first introduce the two B+Tree indexes of the mysql Innodb engine.
3. Mysql Innodb B+Tree index
One is the primary key index, which is the cluster index (Cluster Index). It not only has the primary key, but also has all the data to which the primary key belongs, so in Innodb, the primary key index is the data ;
One is a non-primary key index (Secondary Index) with the column value as Key and the primary key position as Value (column value, primary key position)
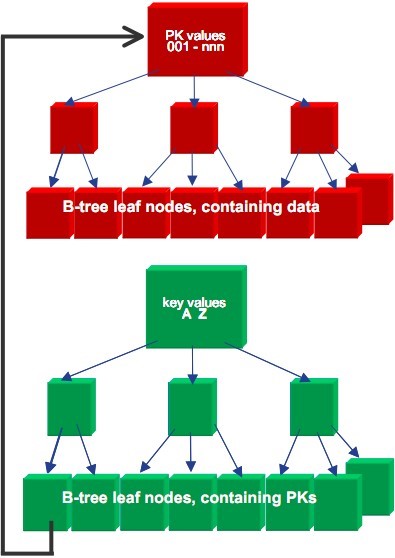

Innodb belongs to the index organized table, all All data is hung under the primary key leaf node. Therefore, if the insertion order of primary keys cannot be guaranteed, a large number of primary key node splits will occur, resulting in a large number of I/O operations. In addition, Innodb stipulates that the length of a single index field must not exceed 768 bytes, otherwise the length will be truncated and not placed in the index. Innodb's non-primary key indexes all point to the primary key index. Searching the non-primary key index cannot obtain the entire row of data. You need to find the location of its primary key index through the pointer of the leaf node to obtain the entire row of data. Therefore, the primary key index must be designed as small as possible. Otherwise the non-primary key index will be very large.
4. Principles of indexing
立 Let's take a look at the principles that need to be followed by establishing a good index and combine specific examples to explain;1. The left -handed prefix matching principle, very important principles, MySQL will always match the right match until the scope query ( >, 3 and d = 4. If you create an index in the order of (a, b, c, d), d is not used. For indexes, if you create an index of (a, b, d, c), it can be used. The order of a, b, d can be adjusted arbitrarily.
2. = and in can be out of order, such as a = 1 and b = 2 and c = 3. The (a, b, c) index can be established in any order. MySQL's query optimizer will help you optimize it into a form that the index can recognize. .
3. Try to choose columns with high distinction as indexes. The formula for distinction is count(distinct col)/count(*), which represents the proportion of fields that are not repeated. The greater the proportion, the fewer records we scan, and the unique key The distinction is 1, while some status and gender fields may have a distinction of 0 in the face of big data. Then someone may ask, does this ratio have any empirical value? The usage scenarios are different, and this value is also difficult to determine. Generally, we require fields that need to be joined to be above 0.1, that is, an average of 10 records will be scanned
4. Index columns cannot participate in calculations, so keep the columns "clean", such as from_unixtime(create_time ) = '2015-08-14', the index cannot be used. The reason is very simple. The b+ tree stores field values in the data table. However, when retrieving, you need to apply functions to all elements to compare. Obviously, the cost Too big. So the statement should be written as create_time = unix_timestamp(‘2015-08-14’).
5. Expand the index as much as possible, do not create a new index. For example, there is already an index for a in the table, and now you want to add an index for (a, b), then you only need to modify the original index.
6. In the order by or group by clause, if you want to sort by index, the order of the index columns must be consistent with the order of the order by or group by clause, and the sorting direction of all columns (reverse order or forward order) order) are the same; if the query is associated with multiple tables, only when the fields referenced by the order by clause are all from the first table, the index can be used to sort; the order by or group by statement has the same restrictions as the query statement : It is necessary to satisfy the leftmost prefix principle of the index; otherwise mysql will perform a sorting operation and cannot use the index to sort; (There is a situation where the order by or group by clause does not need to satisfy the leftmost prefix principle, that is, when its leader is a constant , if where or join specifies constants for these columns, it can make up for the lack of indexes).

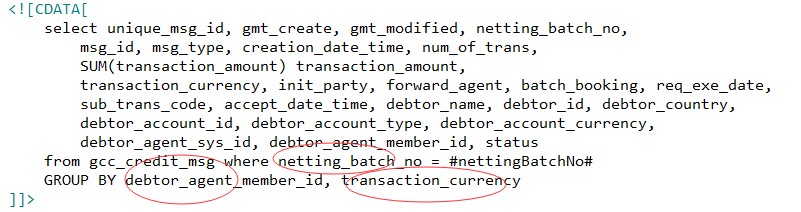
For statement 1 Create (status, netting_batch_no, debtor_agent_member_id);
Create (netting_batch_no, debtor_agent_member_id, transaction_currency) for statement 2;
If you consider it all, one index is enough, that is (netting_batch_no, debtor_agent_member_id). There is no need to add status or The transaction_currency field is placed in the index because the distinction between the two fields is too poor;
According to the indexing principle 2, statement 1 can go to this index;
According to the indexing principle 1, statement 2 can also go This index;
The more indexes, the better. Creating too many indexes will increase the consumption of database memory or disk, and will affect the performance of operations such as insertion and deletion. When establishing an index, you must follow the principles of index creation. , consider everything;

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 what is mysql innodb
Apr 14, 2023 am 10:19 AM
what is mysql innodb
Apr 14, 2023 am 10:19 AM
InnoDB is one of the database engines of MySQL. It is now the default storage engine of MySQL and one of the standards for binary releases by MySQL AB. InnoDB adopts a dual-track authorization system, one is GPL authorization and the other is proprietary software authorization. InnoDB is the preferred engine for transactional databases and supports transaction security tables (ACID); InnoDB supports row-level locks, which can support concurrency to the greatest extent. Row-level locks are implemented by the storage engine layer.
 How MySQL sees InnoDB row format from binary content
Jun 03, 2023 am 09:55 AM
How MySQL sees InnoDB row format from binary content
Jun 03, 2023 am 09:55 AM
InnoDB is a storage engine that stores data in tables on disk, so our data will still exist even after shutdown and restart. The actual process of processing data occurs in memory, so the data in the disk needs to be loaded into the memory. If it is processing a write or modification request, the contents in the memory also need to be refreshed to the disk. And we know that the speed of reading and writing to disk is very slow, which is several orders of magnitude different from reading and writing in memory. So when we want to get certain records from the table, does the InnoDB storage engine need to read the records from the disk one by one? The method adopted by InnoDB is to divide the data into several pages, and use pages as the basic unit of interaction between disk and memory. The size of a page in InnoDB is generally 16
 How to handle mysql innodb exception
Apr 17, 2023 pm 09:01 PM
How to handle mysql innodb exception
Apr 17, 2023 pm 09:01 PM
1. Roll back and reinstall mysql. In order to avoid the trouble of importing this data from other places, first make a backup of the database file of the current library (/var/lib/mysql/location). Next, I uninstalled the Perconaserver 5.7 package, reinstalled the original 5.1.71 package, started the mysql service, and it prompted Unknown/unsupportedtabletype:innodb and could not start normally. 11050912:04:27InnoDB:Initializingbufferpool,size=384.0M11050912:04:27InnoDB:Complete
 MySQL storage engine selection comparison: InnoDB, MyISAM and Memory performance index evaluation
Jul 26, 2023 am 11:25 AM
MySQL storage engine selection comparison: InnoDB, MyISAM and Memory performance index evaluation
Jul 26, 2023 am 11:25 AM
MySQL storage engine selection comparison: InnoDB, MyISAM and Memory performance index evaluation Introduction: In the MySQL database, the choice of storage engine plays a vital role in system performance and data integrity. MySQL provides a variety of storage engines, the most commonly used engines include InnoDB, MyISAM and Memory. This article will evaluate the performance indicators of these three storage engines and compare them through code examples. 1. InnoDB engine InnoDB is My
 How to solve phantom reading in innoDB in Mysql
May 27, 2023 pm 03:34 PM
How to solve phantom reading in innoDB in Mysql
May 27, 2023 pm 03:34 PM
1. Mysql transaction isolation level These four isolation levels, when there are multiple transaction concurrency conflicts, some problems of dirty reading, non-repeatable reading, and phantom reading may occur, and innoDB solves them in the repeatable read isolation level mode. A problem of phantom reading, 2. What is phantom reading? Phantom reading means that in the same transaction, the results obtained when querying the same range twice before and after are inconsistent as shown in the figure. In the first transaction, we execute a range query. At this time, there is only one piece of data that meets the conditions. In the second transaction, it inserts a row of data and submits it. When the first transaction queries again, the result obtained is one more than the result of the first query. Data, note that the first and second queries of the first transaction are both in the same
 Explain InnoDB Full-Text Search capabilities.
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:09 PM
Explain InnoDB Full-Text Search capabilities.
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:09 PM
InnoDB's full-text search capabilities are very powerful, which can significantly improve database query efficiency and ability to process large amounts of text data. 1) InnoDB implements full-text search through inverted indexing, supporting basic and advanced search queries. 2) Use MATCH and AGAINST keywords to search, support Boolean mode and phrase search. 3) Optimization methods include using word segmentation technology, periodic rebuilding of indexes and adjusting cache size to improve performance and accuracy.
 How to use MyISAM and InnoDB storage engines to optimize MySQL performance
May 11, 2023 pm 06:51 PM
How to use MyISAM and InnoDB storage engines to optimize MySQL performance
May 11, 2023 pm 06:51 PM
MySQL is a widely used database management system, and different storage engines have different impacts on database performance. MyISAM and InnoDB are the two most commonly used storage engines in MySQL. They have different characteristics and improper use may affect the performance of the database. This article will introduce how to use these two storage engines to optimize MySQL performance. 1. MyISAM storage engine MyISAM is the most commonly used storage engine for MySQL. Its advantages are fast speed and small storage space. MyISA
 Tips and Strategies to Improve MySQL Storage Engine Read Performance: Comparative Analysis of MyISAM and InnoDB
Jul 26, 2023 am 10:01 AM
Tips and Strategies to Improve MySQL Storage Engine Read Performance: Comparative Analysis of MyISAM and InnoDB
Jul 26, 2023 am 10:01 AM
Tips and strategies to improve the read performance of MySQL storage engine: Comparative analysis of MyISAM and InnoDB Introduction: MySQL is one of the most commonly used open source relational database management systems, mainly used to store and manage large amounts of structured data. In applications, the read performance of the database is often very important, because read operations are the main type of operations in most applications. This article will focus on how to improve the read performance of the MySQL storage engine, focusing on a comparative analysis of MyISAM and InnoDB, two commonly used storage engines.




