
HTTP request format
1) Request information: For example, "Get /index.php HTTP/1.1", request the index.php file
2) Header: For example, "Host: localhost", indicating the server address
3) Blank lines
4) Information text
Both "request information" and "header" must be ended with a newline character (CRLF). Blank lines can only contain newlines and no other spaces.
The following example sends an HTTP request to the server www.yhsafe.com
GET /index.php HTTP/1.1↙ //Request information
Host:www.yhsafe.com↙ //Header
↙ //Space line The
↙
↙ symbol represents the Enter key. After the blank line, you must press a space to send the HTTP request. Among the headers of the HTTP request, only the Host header is necessary, and the rest of the HTTP headers are Depends on the content of the HTTP request.
HTTP request method
1) GET: Request response
2) HEAD: The same response as GET, only the response header is required
3) POST: Send data to the server for processing, the data is included in the HTTP information In the text
4) PUT: Upload files
5) DELETE: Delete files
6) TRACE: Track received requests
7) OPTIONS: Return the HTTP request method supported by the server
8) CONNECT: Convert the HTTP request connection into a transparent TCP/IP channel
HTTP response format
After the server processes the HTTP request made by the client, it will send the following response.
1) The first line is the status code
2) The second line starts with other information
The status code contains a number that identifies the status and a word that describes the status. For example:
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
200 is a number that identifies the status, and OK is a word that describes the status. This status code indicates that the request is successful.
Examples of HTTP requests and responses
Open cmd and enter telnet, enter open www.00aq.com 80
Open the connection and enter
GET /index.php HTTP/1.1↙
Host:www.00aq.com↙
↙
↙
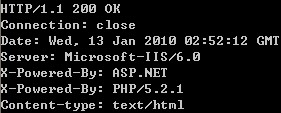
Return the header of the HTTP response
The returned homepage content
Use PHP to send HTTP requests
The header function can be used to send the headers of HTTP requests and responses
Function prototype
void header(string string [, bool replace [, int http_response_code]])
string is the string of HTTP header
If replace is TRUE, it means to replace the previous similar table with the current header header; if replace is FALSE, it means to use multiple similar headers, the default value is TRUE
http_response_code is used to force the HTTP response code to use the value of http_response_code
Example:
//Open Internet socket connection
$fp = fsockopen(www.00aq.com, 80);
// Write HTTP request header
fputs($fp, "GET / HTTP/1.1rn");
fputs($fp, "Host: www.00aq.comrnrn ");
// HTTP response string
$http_response = "";
while (!feof($fp))
{
// Read 256-bit HTTP response string
$http_response .= fgets($ fp,);
}
// Turn off the internet socket connection
fclose ($ fp);
// display http response information
Echo NL2BR (HTMLENTIES ($ http_response));
? Splitting attack 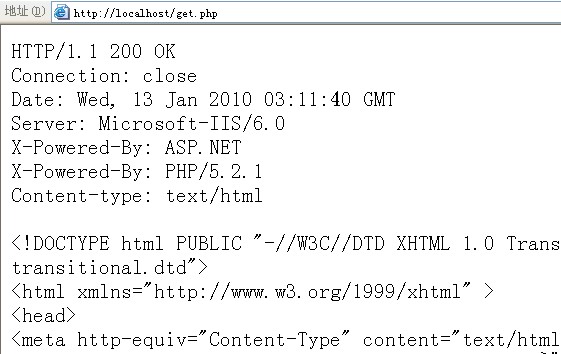 HTTP response splitting is because the attacker carefully designs the use of emails or links to allow the target user to use one request to generate two responses. The former response is the server's response, and the latter is the response designed by the attacker. This attack occurs because the WEB program places user data in the HTTP response header, and these user data are carefully designed by the attacker.
HTTP response splitting is because the attacker carefully designs the use of emails or links to allow the target user to use one request to generate two responses. The former response is the server's response, and the latter is the response designed by the attacker. This attack occurs because the WEB program places user data in the HTTP response header, and these user data are carefully designed by the attacker.
header("Location: " . $_GET['page' ]);
?> 1.1 302 FoundDate: Wed, 13 Jan 2010 03:44:24 GMT
Server: Apache/2.2.8 (Win32) PHP/5.2.6
X-Powered-By: PHP/5.2.6
Location: http: //www.00aq.com
Content-Length: 0
Keep-Alive: timeout=5, max=100
Connection: Keep-Alive
Content-Type: text/html
Visit the link below, A login window will appear directly
http://localhost/location.php?page=%0d%0aContent-Type:%20text/html%0d%0aHTTP/1.1%20200%20OK%0d%0aContent-Type:%20text /html%0d%0aContent-Length:%20158%0d%0a%0d%0aAccount%20Password%20
converted into a readable string:
Content-Type: text/html
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Type: text/html
Content-Length: 158
Account
Password
One HTTP request generated two responses
Prevention method:
1) Replace CRLF newline character
header("Location: " . strtr($_GET['page'], array("r"=>"", "n"=>"")));
?>
2) Use the latest version of PHP. In the latest version of PHP, newline characters are no longer allowed in the HTTP header. Off
php in php.ini, option expose_php = Off
The above is the complete solution to PHP vulnerabilities (8) - HTTP response splitting. For more related content, please pay attention to the PHP Chinese website (www.php.cn)!




