Introduction and use of xml files
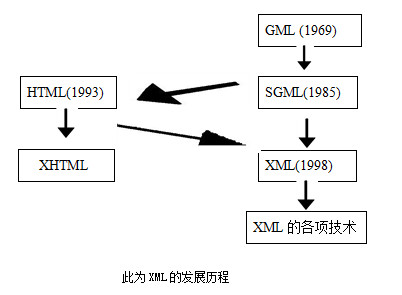
We often see xml files, but rarely use them. As the name suggests, xml is an extensible markup language. Its development is shown in the figure below:
Comparison of xml and html:
| Comparison Content | HTML | XML |
| Extensibility | Does not allow users to define their own extension tags | Allows users to define their own extension tags |
| Structure description | Does not support deep nested expressions | Supports deep nested expressions, suitable for representing document data with complex structures |
| Readability and maintainability | Difficult to read and maintain | Clear structure, easy to read and maintain |
| Data and display Relationship | Content description and presentation form are integrated | Content description and presentation form are separated |
xml is more powerful than html, but its use is more standardized and strict:
(1). XML is case-sensitive;
(2). The starting and ending tags of all elements must appear in pairs and be correct Nesting;
(3). If an XML description is used, it must be the first line of the XML document:
(4). Element attributes must be in quotes Quotes can be single or double quotes, but they must appear in pairs. Such as:
(5). XML naming rules:
①.XML names start with an underscore or letter;
②.XML names can contain letters, numbers, periods, underscores and colons;
③.XML names cannot contain spaces;
④.XML names cannot start with numbers, but can contain numbers;
⑤.XML names are size-sensitive Write.
(6). Retain markup characters. If you want to display tags like
<: represents the character>
> ;: Represents >character
&: Represents & character
&apos: Represents 'character
": Represents "character
We can also use ENTITY custom entities:
In this way we can call it with &linux;.
(7). The spaces in the XML document content are meaningful and will be retained after conversion.
(8). Elements start with , such as
Look at a simple xml code:
Understand the concepts of elements, attributes and entities:
Element It is a tag such as the classes element; the attribute is additional information such as the englishname attribute of the name element; the entity is used to replace the string in xml, such as When using www.phpddt.com You can use the &website cross-border method!
DTD's "Document Type Definition" introduction:
standardizes the format of XML files, such as:
DTD is actually one or several files written in XML.

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1389
1389
 52
52
 Is the conversion speed fast when converting XML to PDF on mobile phone?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:09 PM
Is the conversion speed fast when converting XML to PDF on mobile phone?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:09 PM
The speed of mobile XML to PDF depends on the following factors: the complexity of XML structure. Mobile hardware configuration conversion method (library, algorithm) code quality optimization methods (select efficient libraries, optimize algorithms, cache data, and utilize multi-threading). Overall, there is no absolute answer and it needs to be optimized according to the specific situation.
 How to convert XML files to PDF on your phone?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
How to convert XML files to PDF on your phone?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
It is impossible to complete XML to PDF conversion directly on your phone with a single application. It is necessary to use cloud services, which can be achieved through two steps: 1. Convert XML to PDF in the cloud, 2. Access or download the converted PDF file on the mobile phone.
 How to convert XML to PDF on your phone?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
How to convert XML to PDF on your phone?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
It is not easy to convert XML to PDF directly on your phone, but it can be achieved with the help of cloud services. It is recommended to use a lightweight mobile app to upload XML files and receive generated PDFs, and convert them with cloud APIs. Cloud APIs use serverless computing services, and choosing the right platform is crucial. Complexity, error handling, security, and optimization strategies need to be considered when handling XML parsing and PDF generation. The entire process requires the front-end app and the back-end API to work together, and it requires some understanding of a variety of technologies.
 Recommended XML formatting tool
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:03 PM
Recommended XML formatting tool
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:03 PM
XML formatting tools can type code according to rules to improve readability and understanding. When selecting a tool, pay attention to customization capabilities, handling of special circumstances, performance and ease of use. Commonly used tool types include online tools, IDE plug-ins, and command-line tools.
 Is there any mobile app that can convert XML into PDF?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 08:54 PM
Is there any mobile app that can convert XML into PDF?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 08:54 PM
An application that converts XML directly to PDF cannot be found because they are two fundamentally different formats. XML is used to store data, while PDF is used to display documents. To complete the transformation, you can use programming languages and libraries such as Python and ReportLab to parse XML data and generate PDF documents.
 How to open web.xml
Apr 03, 2025 am 06:51 AM
How to open web.xml
Apr 03, 2025 am 06:51 AM
To open a web.xml file, you can use the following methods: Use a text editor (such as Notepad or TextEdit) to edit commands using an integrated development environment (such as Eclipse or NetBeans) (Windows: notepad web.xml; Mac/Linux: open -a TextEdit web.xml)
 How to open xml format
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:00 PM
How to open xml format
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:00 PM
Use most text editors to open XML files; if you need a more intuitive tree display, you can use an XML editor, such as Oxygen XML Editor or XMLSpy; if you process XML data in a program, you need to use a programming language (such as Python) and XML libraries (such as xml.etree.ElementTree) to parse.
 xml online formatting
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
xml online formatting
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
XML Online Format Tools automatically organizes messy XML code into easy-to-read and maintain formats. By parsing the syntax tree of XML and applying formatting rules, these tools optimize the structure of the code, enhancing its maintainability and teamwork efficiency.




