 Web Front-end
Web Front-end
 JS Tutorial
JS Tutorial
 Node.js development tutorial: Implementing file upload and verification functions based on the OnceIO framework
Node.js development tutorial: Implementing file upload and verification functions based on the OnceIO framework
Node.js development tutorial: Implementing file upload and verification functions based on the OnceIO framework
OnceIO is the underlying web framework of OnceDoc enterprise content (network disk). It can realize full caching of template files and static files. It does not require I/O operations at all to run, and supports client cache optimization, GZIP compression, etc. (only in First compression), has very good performance, saving you server costs. Its modular function allows your Web to be stored in a distributed manner, that is, an expansion package includes front-end, back-end and database definitions. You can delete functions by adding/deleting directories to achieve true Modular expansion. Here is a series of articles introducing how to use OnceIO.
In this chapter, we will demonstrate how to use OnceIO to implement the file upload function.
Build a form in a web page file
Take a simple web page file.html that only has a file upload function as an example:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <body> <form method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data" action="/file/upload"> <input type="file" name="file" /><br> <input type="submit" value="Upload" /> </form> </body> </html>
The browser display effect is like this:
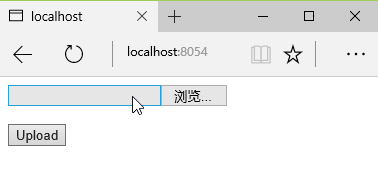
Click on the blank bar or "Browse..." The button can open the file browsing window and select the file to be uploaded:
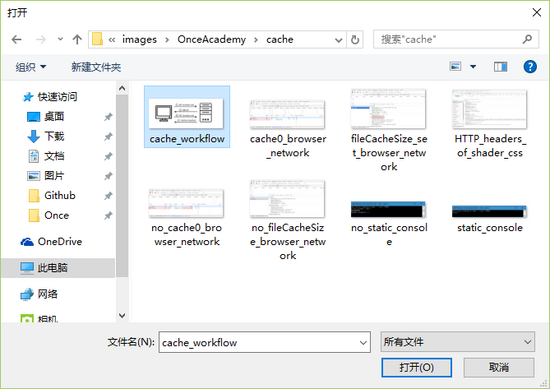
Establish the server receiving file logic
The server file websvr.js code is like this:
var fs = require('fs')
var path = require('path')
var onceio = require('../onceio/onceio')
var app = onceio()
app.get('/', function(req, res){
res.render('file.html')
})
app.file('/file/upload', function(req, res) {
var fileInfo = req.files.file || {}
fs.link(fileInfo.path, path.join('./fileStore', fileInfo.name))
res.send('File Uploaded Successfully')
}).before(function(req, res) {
var contentLength = req.headers['content-length'] || 0
if (contentLength > 1048576) {
res.send({ error: 'Error: File Size Limit (1 MB) Exceeded' })
} else {
return true
}
})
var fs = require('fs') and var path = require('path') respectively import the file system (fs) module provided by Node.js for operating files and the path module for processing file paths.
app.file(path, callback).before(callback) is equivalent to app.use(path, callback, {file: true}).before(callback) and is a middleware that processes uploaded files.
After the file is uploaded, its size, storage address, name, format and modification time will be placed in the file attribute of req.files (the name is the value of name in the input tag of type 'file') , its size information will be placed in the content-length attribute of req.headers.
before function
before is one of the main differences between OnceIO and other web frameworks. It can perform some basic verification on files before receiving them, such as size, type, etc., in order to obtain the best performance. Return true indicates that the verification is successful and the file starts to be received, otherwise the connection is closed and the upload is cancelled. In before, the req.session object is not available because the session may exist in a file or database redis, and obtaining the session is an asynchronous process that takes time. The before function needs to make an immediate judgment on the legality of the file.
In this example, the before callback function determines whether the uploaded file exceeds the size limit based on the content-length in req.headers (developers can change the upper limit of file upload size by modifying the constant in the if statement. The unit of content-length is byte. , 1024 * 1024 represents 1 MB), if it is exceeded, the file will not be uploaded, and the server will return an error message; if it is not exceeded, the function return value is true, and the server will continue to execute the callback function in app.file to transfer the file from temporary The address is transferred to the specified storage address, and the file is uploaded here.
Solving the problem of duplicate file names
Our current server program cannot solve the problem of duplicate file names. If the user uploads a file with the same name, the server will return an error that the file already exists. In order to solve this problem, we can add a timestamp between the main file name and the extension name of the file. The function code for this processing is as follows:
var timestampName = function(fileName){
// get filename extension
var extName = path.extname(fileName)
// get base name of the file
var baseName = path.basename(fileName, extName)
// insert timestamp between base name and filename extension
// the plus sign ('+') before new Date() converts it into a number
return baseName + +new Date() + extName
}
Then replace fileInfo.name in the fs.link statement with timestampName(fileInfo.name):
fs.link(fileInfo.path, path.join('./fileStore', timestampName(fileInfo.name)))
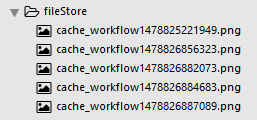
The improved server program can allow users to upload files with the same name. Take uploading a file named 'cache_workflow.png' 5 times as an example. The file storage address of the server There will be 5 files with names starting with 'cache_workflow' but with different timestamps:
OnceIO address: https://github.com/OnceDoc/onceio
Sample source code: https://github.com /OnceDoc/OnceAcademy/tree/master/Lesson14
The above is the Node.js development tutorial introduced by the editor to implement file upload and verification based on the OnceIO framework. I hope it will be helpful to you. If you have any questions, please Leave me a message and I will reply to you in time. I would also like to thank you all for your support of the PHP Chinese website!
For more Node.js development tutorials on implementing file upload and verification functions based on the OnceIO framework, please pay attention to the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1376
1376
 52
52
 How do I create and publish my own JavaScript libraries?
Mar 18, 2025 pm 03:12 PM
How do I create and publish my own JavaScript libraries?
Mar 18, 2025 pm 03:12 PM
Article discusses creating, publishing, and maintaining JavaScript libraries, focusing on planning, development, testing, documentation, and promotion strategies.
 How do I optimize JavaScript code for performance in the browser?
Mar 18, 2025 pm 03:14 PM
How do I optimize JavaScript code for performance in the browser?
Mar 18, 2025 pm 03:14 PM
The article discusses strategies for optimizing JavaScript performance in browsers, focusing on reducing execution time and minimizing impact on page load speed.
 What should I do if I encounter garbled code printing for front-end thermal paper receipts?
Apr 04, 2025 pm 02:42 PM
What should I do if I encounter garbled code printing for front-end thermal paper receipts?
Apr 04, 2025 pm 02:42 PM
Frequently Asked Questions and Solutions for Front-end Thermal Paper Ticket Printing In Front-end Development, Ticket Printing is a common requirement. However, many developers are implementing...
 How do I debug JavaScript code effectively using browser developer tools?
Mar 18, 2025 pm 03:16 PM
How do I debug JavaScript code effectively using browser developer tools?
Mar 18, 2025 pm 03:16 PM
The article discusses effective JavaScript debugging using browser developer tools, focusing on setting breakpoints, using the console, and analyzing performance.
 How do I use source maps to debug minified JavaScript code?
Mar 18, 2025 pm 03:17 PM
How do I use source maps to debug minified JavaScript code?
Mar 18, 2025 pm 03:17 PM
The article explains how to use source maps to debug minified JavaScript by mapping it back to the original code. It discusses enabling source maps, setting breakpoints, and using tools like Chrome DevTools and Webpack.
 How do I use Java's collections framework effectively?
Mar 13, 2025 pm 12:28 PM
How do I use Java's collections framework effectively?
Mar 13, 2025 pm 12:28 PM
This article explores effective use of Java's Collections Framework. It emphasizes choosing appropriate collections (List, Set, Map, Queue) based on data structure, performance needs, and thread safety. Optimizing collection usage through efficient
 TypeScript for Beginners, Part 2: Basic Data Types
Mar 19, 2025 am 09:10 AM
TypeScript for Beginners, Part 2: Basic Data Types
Mar 19, 2025 am 09:10 AM
Once you have mastered the entry-level TypeScript tutorial, you should be able to write your own code in an IDE that supports TypeScript and compile it into JavaScript. This tutorial will dive into various data types in TypeScript. JavaScript has seven data types: Null, Undefined, Boolean, Number, String, Symbol (introduced by ES6) and Object. TypeScript defines more types on this basis, and this tutorial will cover all of them in detail. Null data type Like JavaScript, null in TypeScript
 Getting Started With Chart.js: Pie, Doughnut, and Bubble Charts
Mar 15, 2025 am 09:19 AM
Getting Started With Chart.js: Pie, Doughnut, and Bubble Charts
Mar 15, 2025 am 09:19 AM
This tutorial will explain how to create pie, ring, and bubble charts using Chart.js. Previously, we have learned four chart types of Chart.js: line chart and bar chart (tutorial 2), as well as radar chart and polar region chart (tutorial 3). Create pie and ring charts Pie charts and ring charts are ideal for showing the proportions of a whole that is divided into different parts. For example, a pie chart can be used to show the percentage of male lions, female lions and young lions in a safari, or the percentage of votes that different candidates receive in the election. Pie charts are only suitable for comparing single parameters or datasets. It should be noted that the pie chart cannot draw entities with zero value because the angle of the fan in the pie chart depends on the numerical size of the data point. This means any entity with zero proportion



