JavaScript learning summary (1) basic part
Basic Concept
Javascript is an interpreted language, and the browser acts as an interpreter. When js is executed, it is interpreted first and then executed within the same scope. When interpreting, the variables defined by the two keywords function and var will be compiled. After the compilation is completed, it will be executed from top to bottom and assigned values to the variables.
Case Sensitive
Everything in ECMASCript (including variables, function names and operators) is case sensitive.
1. Variables
Variables are set in memory the first time they are used, making it easier to reference later in the script. Declare variables before using them. You can use the var keyword to declare variables.
var count, amount, level; // Multiple declarations declared with a single var keyword.
Variable naming
Variable names include global variables, local variables, class variables, function parameters, etc. They all belong to this category.
Variable names are composed of type prefix + meaningful words, and use camel case naming to increase the readability of variables and functions. For example: sUserName, nCount.
Prefix specification:
Each local variable needs to have a type prefix, which can be divided according to type:
s:表示字符串。例如:sName,sHtml; n:表示数字。例如:nPage,nTotal; b:表示逻辑。例如:bChecked,bHasLogin; a:表示数组。例如:aList,aGroup; r:表示正则表达式。例如:rDomain,rEmail; f:表示函数。例如:fGetHtml,fInit; o:表示以上未涉及到的其他对象,例如:oButton,oDate; g:表示全局变量,例如:gUserName,gLoginTime;
JScript is a case-sensitive language. Creating legal variable names should follow the following rules:
注意第一个字符不能是数字。 后面可以跟任意字母或数字以及下划线,但不能是空格 变量名称一定不能是 保留字。
Javascript is a weakly typed language, and JavaScript will ignore extra spaces. You can add spaces to your script to make it more readable.
var is a reserved word in JavaScript, indicating that the following is a variable description. The variable name is a user-defined identifier, and the variables are separated by commas.
If a variable is declared but no value is assigned to it, the variable exists and its value is Jscript value undefined.
Forced type conversion
In Jscript, you can perform operations on values of different types without worrying about the JScript interpreter generating exceptions. Instead, the JScript interpreter automatically changes (casts) one data type to another and then performs the operation. For example:
运算 结果 数值与字符串相加 将数值强制转换为字符串。 布尔值与字符串相加 将布尔值强制转换为字符串。 数值与布尔值相加 将布尔值强制转换为数值。
To explicitly convert a string to an integer, use the parseInt method. To explicitly convert a string to a number, use the parseFloat method.
JavaScript Variable lifetime: When you declare a variable within a function, you can only access the variable within that function. This variable will be destroyed when exiting the function. Such variables are called local variables. You can use local variables with the same name in different functions because each variable is recognized only by the function in which it is declared.
If you declare a variable outside a function, all functions on the page can access the variable. The lifetime of these variables begins after they are declared and ends when the page is closed.
js变量思维导图

2.js的数据类型
jscript 有三种->主要数据类型、两种->复合数据类型和两种->特殊数据类型。
主要(基本)数据类型
字符串 数值 布尔
复合(引用)数据类型
复合(引用)数据类型
对象
数组
特殊数据类型
Null
`Undefined`
字符串数据类型:字符串数据类型用来表示 JScript 中的文本。在js中,虽然双引号("")和单引号('')均可表示字符串,而且它们几乎没有任何区别。但只使用双引号("")来表示字符串被认为是最佳的。
一个字符串值是排在一起的一串零或零以上的 Unicode 字符(字母、数字和标点符号)。
什么是Unicode?
Unicode为每个字符都提供了唯一的数值,不管是什么平台、什么程序或什么语言。开发unicode是为了给处理世界上存在的所有字符提供统一的编码。
数值数据类型
我们需要明白一点,JScript 内部将所有的数值表示为浮点值,因此,在 Jscript 中整数和浮点值没有差别。
Boolean数据类型
布尔(逻辑)只能有两个值:true 或 false。
js数组和对象
详情看我这篇文章->javascript学习总结— —数组和对象部分
Null 数据类型:可以通过给一个变量赋 null 值来清除变量的内容。
Jscript中 typeof 运算符将报告 null 值为 Object 类型,而非类型 null。
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" xml:lang="en"><head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html;charset=UTF-8" />
<title></title>
<script type="text/javascript">
alert(typeof null); </script></head><body></body></html>null用来表示尚未存在的对象,常用来表示函数企图返回一个不存在的对象。
Undefined 数据类型:
如下情况将返回 undefined 值:
对象属性不存在, 声明了变量但从未赋值。
null和undefined的区别
alert(typeof undefined); //output "undefined" alert(typeof null); //output "object" alert(null == undefined); //output "true"
ECMAScript认为undefined是从null派生出来的,所以把它们定义为相等的。
alert(null === undefined); //output "false" alert(typeof null == typeof undefined); //output "false"
null与undefined的类型是不一样的,所以输出"false"。而===代表绝对等于,在这里null === undefined输出false
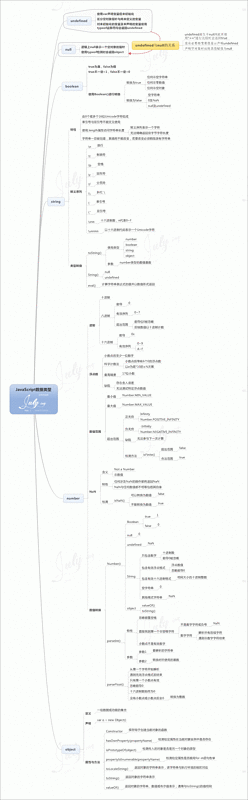
另外,这里介绍一种比较重要的数据类型——引用数据类型
引用数据类型
javascript引用数据类型是保存在堆内存中的对象,JavaScript不允许直接访问堆内存空间中的位置和操作堆内存空间,只能通过操作对象在栈内存中的引用地址。所以引用类型的数据,在栈内存中保存的实际上是对象在堆内存中的引用地址。通过这个引用地址可以快速查找到保存在堆内存中的对象。
下面我们来演示这个引用数据类型赋值过程
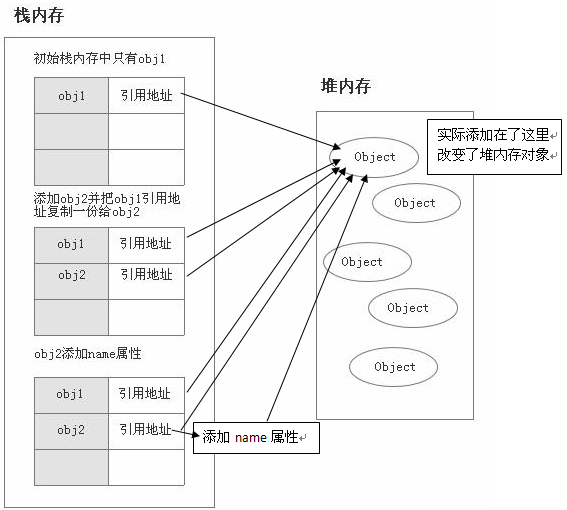
自然,给obj2添加name属性,实际上是给堆内存中的对象添加了name属性,obj2和obj1在栈内存中保存的只是堆内存对象的引用地址,虽然也是拷贝了一份,但指向的对象却是同一个。故而改变obj2引起了obj1的改变。
基本类型值指的是那些保存在栈内存中的简单数据段,即这种值完全保存在内存中的一个位置。
而引用类型值则是指那些保存在堆内存中的对象,即变量中保存的实际上只是一个指针,这个指针指向内存中的另一个位置,该位置保存对象。
简而言之,堆内存存放引用值,栈内存存放固定类型值。
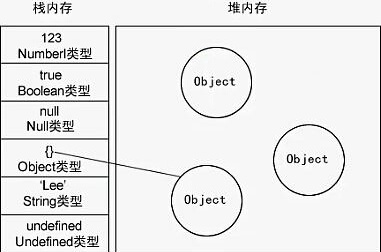
在 ECMAScript 中,变量可以存在两种类型的值,即原始值和引用值。
原始值存储在栈(stack)中的简单数据段,也就是说,它们的值直接存储在变量访问的位置。引用值存储在堆(heap)中的对象,也就是说,存储在变量处的值是一个指针(point),指向存储对象的内存处
<script type="text/javascript”> var box = new Object(); //创建一个引用类型 var box = "lee"; //基本类型值是字符串 box.age = 23; //基本类型值添加属性很怪异,因为只有对象才可以添加属性。 alert(box.age); //不是引用类型,无法输出; </script>
3.JScript 的运算符
优先级:指运算符的运算顺序,通俗的说就是先计算哪一部分。结合性:同一优先级运算符的计算顺序,通俗的说就是从哪个方向算起,是左到右还是右到左。
数据类型转换和基本包装类型
String() 转换为字符串类型
Number() 转换为数字类型
Boolean() 转换为布尔类型
parseInt:将字符串转换为整数。从字符串的开头开始解析,在第一个非整数的位置停止解析,并返回前面读到所有的整数。如果字符串不是以整数开头的,将返回NaN。如:parseInt(“150 hi”)返回的值是:150,parseInt("hi")返回的值是:NaN。
parseFloat:将字符串转换为浮点数。 从字符串的开头开始解析,在第一个非整数的位置停止解析,并返回前面读到所有的整数。如果字符串不是以整数开头的,将返回NaN。如:parseFloat("15.5 hi") 返回的值是:15.5,parseFloat("hi 15.5")返回的值是:NaN。
eval:将字符串作为javascript表达式进行计算,并返回执行结果,如果没有结果则返回undefined。
基本包装类型
每当读取一个基本类型值的时候,后台就会创建一个对应的基本包装类型的对象,从而能调用一些方法来操作这些数据。基本包装类型包括Boolean、Number和String
var box = 'trigkit4'; //字面量box.name = 'mike'; //无效属性box.age = function () { //无效方法
return 22;
};
//new运算符写法var box = new String('trigkit4');//new 运算符box.name = 'mike'; //有效属性box.age = function () { //有效方法
return 22;
};String类型包含了三个属性和大量的可用内置方法
属性 描述length :返回字符串的字符长度 Constructor : 返回创建String对象的函数prototype : 通过添加属性和方法扩展字符串定义
4.js流程控制
对于js流程控制语句,这里只讲几个比较难懂的。其他不赘述。等下附上一张思维导图。1.for...in 语句对应于一个对象的每个,或一个数组的每个元素,执行一个或多个语句。
for (variable in [object | array]) statements
参数:
variable:必选项。一个变量,它可以是 object 的任一属性或 array 的任一元素。
object, array:可选项。要在其上遍历的对象或数组。
statement:可选项。相对于 object 的每个属性或 array 的每个元素,都要被执行的一个或多个语句。可以是复合语句。
虽然条件控制语句(如if语句)只在执行多条语句的情况下才要求使用代码块(左花括号"{"开头,右花括号"}"结尾),但最佳实践是始终使用代码块。
if(args)
alert(args);//容易出错
if(args){
alert(args);//推荐使用}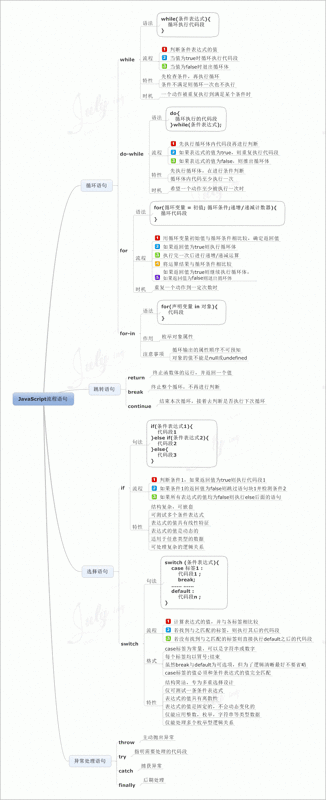 s流程控制语句思维导图
s流程控制语句思维导图
5.js函数
函数是由事件驱动的或者当它被调用时执行的可重复使用的代码块。
Jscript 支持两种函数:一类是语言内部的函数,另一类是自己创建的。
JavaScript 函数允许没有参数(但包含参数的小括号不能省略),也可以向函数传递参数供函数使用。
更多关于函数的知识请访问我的另一篇文章:javascript学习大总结(四)function函数部分
对象的组成
方法——函数:过程、动态的 属性——变量:状态、静态的
最后,再附上一张前辈总结的思维导图:

以上就是JavaScript学习总结(一)基础部分的内容,更多相关内容请关注PHP中文网(www.php.cn)!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1376
1376
 52
52
 How to implement an online speech recognition system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 pm 02:54 PM
How to implement an online speech recognition system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 pm 02:54 PM
How to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online speech recognition system Introduction: With the continuous development of technology, speech recognition technology has become an important part of the field of artificial intelligence. The online speech recognition system based on WebSocket and JavaScript has the characteristics of low latency, real-time and cross-platform, and has become a widely used solution. This article will introduce how to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online speech recognition system.
 WebSocket and JavaScript: key technologies for implementing real-time monitoring systems
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:30 PM
WebSocket and JavaScript: key technologies for implementing real-time monitoring systems
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:30 PM
WebSocket and JavaScript: Key technologies for realizing real-time monitoring systems Introduction: With the rapid development of Internet technology, real-time monitoring systems have been widely used in various fields. One of the key technologies to achieve real-time monitoring is the combination of WebSocket and JavaScript. This article will introduce the application of WebSocket and JavaScript in real-time monitoring systems, give code examples, and explain their implementation principles in detail. 1. WebSocket technology
 How to implement an online reservation system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 am 09:39 AM
How to implement an online reservation system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 am 09:39 AM
How to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online reservation system. In today's digital era, more and more businesses and services need to provide online reservation functions. It is crucial to implement an efficient and real-time online reservation system. This article will introduce how to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online reservation system, and provide specific code examples. 1. What is WebSocket? WebSocket is a full-duplex method on a single TCP connection.
 How to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 12:09 PM
How to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 12:09 PM
Introduction to how to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system: With the popularity of the Internet and the advancement of technology, more and more restaurants have begun to provide online ordering services. In order to implement a real-time online ordering system, we can use JavaScript and WebSocket technology. WebSocket is a full-duplex communication protocol based on the TCP protocol, which can realize real-time two-way communication between the client and the server. In the real-time online ordering system, when the user selects dishes and places an order
 JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecasting system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecasting system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecast system Introduction: Today, the accuracy of weather forecasts is of great significance to daily life and decision-making. As technology develops, we can provide more accurate and reliable weather forecasts by obtaining weather data in real time. In this article, we will learn how to use JavaScript and WebSocket technology to build an efficient real-time weather forecast system. This article will demonstrate the implementation process through specific code examples. We
 Simple JavaScript Tutorial: How to Get HTTP Status Code
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
Simple JavaScript Tutorial: How to Get HTTP Status Code
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
JavaScript tutorial: How to get HTTP status code, specific code examples are required. Preface: In web development, data interaction with the server is often involved. When communicating with the server, we often need to obtain the returned HTTP status code to determine whether the operation is successful, and perform corresponding processing based on different status codes. This article will teach you how to use JavaScript to obtain HTTP status codes and provide some practical code examples. Using XMLHttpRequest
 How to use insertBefore in javascript
Nov 24, 2023 am 11:56 AM
How to use insertBefore in javascript
Nov 24, 2023 am 11:56 AM
Usage: In JavaScript, the insertBefore() method is used to insert a new node in the DOM tree. This method requires two parameters: the new node to be inserted and the reference node (that is, the node where the new node will be inserted).
 How to get HTTP status code in JavaScript the easy way
Jan 05, 2024 pm 01:37 PM
How to get HTTP status code in JavaScript the easy way
Jan 05, 2024 pm 01:37 PM
Introduction to the method of obtaining HTTP status code in JavaScript: In front-end development, we often need to deal with the interaction with the back-end interface, and HTTP status code is a very important part of it. Understanding and obtaining HTTP status codes helps us better handle the data returned by the interface. This article will introduce how to use JavaScript to obtain HTTP status codes and provide specific code examples. 1. What is HTTP status code? HTTP status code means that when the browser initiates a request to the server, the service




