1. Export data external
1) mysql connection + output the query results to a file. Execute in the command line (cmd command line of windows, terminal of mac)
mysql -hxx -uxx -pxx -e "query statement" db > file
-h: followed by the linked host (host)
-u: What follows is the username
-p: What follows is the password
db: The database you want to query
File: The file you want to write, absolute path
For example:
The following is the query result of the sql statement select * from edu_iclass_areas The output is output to the file /Users/zhengcanrui/WORK/test/test.xls.
mysql -h127.0.0.1 -uroot -p123 -e "select * from edu_iclass_areas" test > /Users/zhengcanrui/WORK/test/test.xls
2) Mysql connection and output of query results to the database are executed separately
mysql -hxxx -uxx -pxx select * from table into outfile 'xxx.txt';
The contents of the -h/-u/-p parameters are the same as above. xxx.txt is the file path and name to be output.
Such as:
-- 登录mysql mysql -h127.0.0.1 -uroot -p123 -- 将查询结果输出到文件中 select * from edu_iclass_areas into outfile /Users/zhengcanrui/WORK/test/test.xls
The above two execution effects are equivalent.
2. Problems encountered
1. Mac starts the mysql command in the terminal
1) After installing the MySQL service ( For installation steps, please refer to series of experience 1). Open "System Preferences" and click the "MySQL" icon at the bottom.
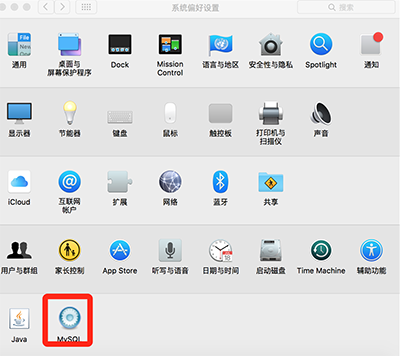
2) In the "MySQL" dialog box, click the "Start MySQL Service" button
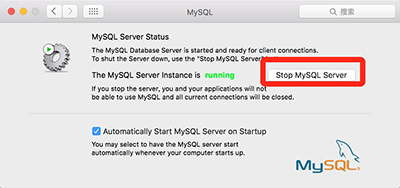
3) Click Applications in Finder's sidebar, and then in Utilities, double-click to launch the Terminal command.
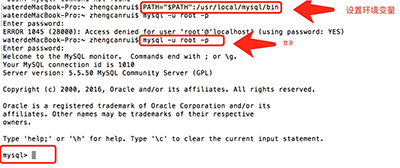
4) Enter the command to add the MySQL path in the terminal:
PATH="$PATH":/usr/local/mysql/bin
5) The command to log in to MySQL in the terminal is as follows:
mysql -u root -p
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* TO 'myuser'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY 'mypassword' WITH GRANT OPTION; flush privileges;
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* TO 'myuser'@'192.168.1.3' IDENTIFIED BY 'mypassword' WITH GRANT OPTION; flush privileges;




