Linux--Terminal, job control, and daemons
1. The concepts of process group, job, and session
1. Process group: It is a collection of one or more processes. Typically, associated with the same job, various signals from the same terminal can be received. Each process has a unique process group ID. Each process group can have a leader process. The identity of the group leader process is that its process group ID is equal to its process ID. The group leader process can create a process group, create the processes in the group, and then terminate. As long as there is a process in a process group, the process group exists, regardless of whether the group leader process terminates.
2. Job: Shell is divided into front and backends to control not the process but the job (job) or process group. A foreground job can be composed of multiple processes, and a background job can also be composed of multiple processes. The shell can run a foreground job and any number of background jobs, which is called job control.
The difference between a job and a process group: If a process in the job creates a child process, the child process does not belong to the job.
Once the job ends, the Shell will bring itself to the foreground. If the original foreground process still exists (if the child process has not been terminated), it will automatically become a background process group.
3. Session: It is a collection of one or more process groups. A session can have one controlling terminal. The session first process that establishes a connection with the controlling terminal is called the controlling process. Several process groups in a session can be divided into a foreground process group and one or more background process groups. Therefore, a session should include the control process (the first process of the session), a foreground process group and any background process group.
**************** (The process group is equivalent to a class, and the group leader is equivalent to the squad leader. The conversation is equivalent to a grade. Each grade has an Academic Affairs Office .(control terminal)).
2. Terminal
1. The concept of terminal: After the user logs in to the system through the terminal, he gets a Shell process. This terminal is called the control terminal of the Shell process.
Each process can pass a special device file /dev/tty accesses its controlling terminal. In fact, each terminal device
corresponds to a different device file. /dev/tty provides a universal interface. A process can access its control terminal through /dev/tty or through the terminal device. Corresponding device file to access. The ttyname function can find out the corresponding file name from the file descriptor. The file descriptor must point to a terminal device and not any file.
******************Check the device file names corresponding to various terminals.
1 #include<stdio.h>
2 #include<unistd.h>
3 int main()
4 {
5 printf("fd: %d -> %s\n",0,ttyname(0));
6 printf("fd: %d -> %s\n",1,ttyname(1));
7 printf("fd: %d -> %s\n",2,ttyname(2));
8 }2. Terminal login process:
A PC usually only has one set of keyboard and monitor, that is, only one set of terminal equipment, but it can be switched to 6 by Ctrl-Alt-F1~Ctrl-Alt-F6 Character terminals are equivalent to 6 sets of virtual terminal devices. They share the same set of physical terminal devices. The corresponding device files are /dev/tty1~/dev/tty6, so they are called virtual terminals. The device file /dev/tty0 represents the current virtual terminal. For example, when switching to the character terminal of Ctrl-Alt-F1, /dev/tty0 represents /dev/tty1. When switching to the character terminal of Ctrl-Alt-F2, /dev/tty0 represents Represents /dev/tty2, which is a universal interface just like /dev/tty, but it cannot represent the terminal corresponding to the graphical terminal window.
a. When the system starts, the init process determines which terminals need to be opened based on the configuration file /etc/inittab.
b. getty opens the terminal device as its control terminal according to the command line parameters, points the file descriptors 0, 1, and 2 to the control
terminal, and then prompts the user to enter an account. After the user enters the account, getty's task is completed, and it executes the login program:
execle("/bin/login", "login", "-p", username, NULL, envp);
c . The login program prompts the user to enter a password (turn off the terminal's echo during password input), and then verifies the correctness of the account password. If the password is incorrect, the login process is terminated, and init will re-fork/exec a getty process. If the password is correct, the login program sets some environment variables, sets the current working directory to the user's home directory, and then executes Shell:
execl("/bin/bash", "-bash", NULL);
三, Daemon process
1. The daemon process, also called the daemon process, is a special process running in the background. It is independent of the control terminal and periodically performs some task or waits for some event to occur.
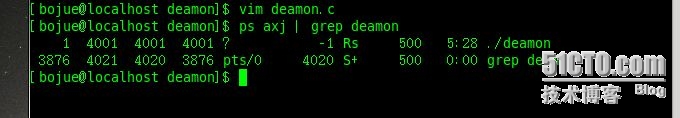
2. Use ps axj | grep -E 'd$' to view the daemon process
Parameter a indicates that not only the processes of the current user are listed, but also the processes of all other users, and parameter x indicates that not only the processes of the control terminal are listed Process also lists all processes without control terminals. Parameter j indicates listing information related to job control.
3. Create a daemon process
Call the setsid function to create a new Session and become the Session Leader (session first process). The newly created Session id will be returned if the call is successful, and -1 will be returned on error;
a. Call umask to set the file mode creation mask to 0.
b. Call fork and the parent process exits (exit). Reasons:
1) If the daemon is started as a simple shell command, then the parent process termination causes the shell to think that the command has been executed.
2) Ensure that the child process is not the leader process of a process group.
c. Call setsid to create a new session. setsid will cause:
1) The calling process becomes the first process of the new session.
2) The calling process becomes the leader process of a process group.
3) The calling process does not have a controlling terminal. (Fork again to ensure that the daemon process will not open the tty device afterwards)
d. Change the current working directory to the root directory.
e. Close file descriptors that are no longer needed.
f, Others: Ignore the SIGCHLD signal.
#include<stdio.h>
2 #include<stdlib.h>
3 #include<unistd.h>
4 void mydeamon(void)
5 {
6 pid_t id=fork();
7 umask(0);//将文件模式创建屏蔽字设置为0.
8 if(id>0)
9 {
10 exit(0);//调用fork,父进程退出(exit)
11 }
12 setsid();//调用setsid创建一个新会话
13 chdir("/");//将当前工作目录更改为根目录。
14 close(0);//关闭不在需要的文件描述符。
15 close(1);
16 close(2);
17 }
18 int main()
19 {
20 mydeamon();
21 while(1);
22 return 0;
23 }Use ps axj |grep "file name" to view the daemon process just created
The above is Linux--terminal, job control, and daemon process For more related content, please pay attention to the PHP Chinese website (www.php.cn)!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1387
1387
 52
52
 What should I do if the Ubuntu terminal cannot be opened? How to fix the problem that Ubuntu cannot open the terminal
Feb 29, 2024 pm 05:30 PM
What should I do if the Ubuntu terminal cannot be opened? How to fix the problem that Ubuntu cannot open the terminal
Feb 29, 2024 pm 05:30 PM
It is a very common problem these days that Ubuntu does not allow its users to open the terminal. If you receive a similar issue and don’t know what to do next, learn about five fixes on how to resolve this “Ubuntu cannot open terminal” issue on your Linux device. Without further ado, let’s dive into what causes it and the solutions available to it. Why can't Ubuntu open the terminal on it? This mainly happens when you install some defective software or modify the terminal configuration. In addition to this, new applications or games that interact with locales and corrupt them can cause similar problems. Some users reported a fix for this issue when searching for Terminal in Ubuntu's activity menu. This shows that
 How to open win7 hyper terminal
Jul 14, 2023 pm 12:17 PM
How to open win7 hyper terminal
Jul 14, 2023 pm 12:17 PM
The win7 system has a built-in communication function called Hyper Terminal, and users can use this function to connect to other computers. So how to open the win7 Hyper Terminal? You first open the control panel, find the phone and modem, then set the location information, then open the hypertrm.exe program, enter the name in the pop-up page, if there are multiple connections, you can continue to add them by creating a new one, and finally enter The IP address will allow you to connect. How to open Win7 HyperTerminal: 1. First set it in the control panel, Start→Control Panel→Phone and Modem 2. Open location information→Select country, area code, phone and other related information→OK 3. Double-click to open hypertrm.exe program, there will be a default
 Common commands and shortcuts in Linux systems
Jun 18, 2023 am 08:46 AM
Common commands and shortcuts in Linux systems
Jun 18, 2023 am 08:46 AM
With the widespread application of the Linux operating system, more and more people are beginning to need to learn and understand the basic commands and shortcuts in the Linux system. In this article, we will introduce some commonly used Linux commands and shortcuts to help beginners understand the Linux system and improve work efficiency. Commonly used commands 1.1ls command The ls command is one of the most commonly used commands in Linux. It is mainly used to list files and subdirectories in the current directory. Commonly used options are: -l: Display file information in long format, including file type
 How to deal with garbled characters in Linux terminal
Mar 20, 2024 pm 03:12 PM
How to deal with garbled characters in Linux terminal
Mar 20, 2024 pm 03:12 PM
How to deal with the problem of garbled characters in the Linux terminal. When using the Linux system, sometimes the text displayed in the terminal will be garbled. This brings inconvenience to us when using the terminal and needs to be dealt with in time. This article will introduce how to deal with some common Linux terminal garbled problems, and provide specific code examples. Problem 1: Garbled Chinese characters on the terminal. Garbled Chinese characters on the terminal are usually caused by incorrect character encoding settings on the terminal. We can solve this problem by modifying the terminal's character encoding settings. #View the current terminal
 Python server programming: how daemons are implemented
Jun 18, 2023 pm 08:04 PM
Python server programming: how daemons are implemented
Jun 18, 2023 pm 08:04 PM
Python is a very popular programming language, especially widely used in network programming. Server-side programming is also one of them. In server-side programming, daemon processes are a common concept. This article introduces how to implement daemon processes in Python server programming. What is a daemon process? When the server-side program is running, in order to ensure the long-term stable operation of the program, we need to convert it into a daemon process. A daemon is a process that runs continuously in the background and does not occupy a console or login
 How to open the terminal window in vscode
Mar 25, 2024 pm 03:48 PM
How to open the terminal window in vscode
Mar 25, 2024 pm 03:48 PM
Steps to open the terminal window in vscode: 1. Open the terminal window through shortcut keys; 2. Open the terminal window through the menu bar; 3. Open the terminal window through the command panel; 4. Modify the default terminal; 5. Use the terminal window.
 Microsoft updates Visual Studio Code 1.80
Jul 10, 2023 pm 08:13 PM
Microsoft updates Visual Studio Code 1.80
Jul 10, 2023 pm 08:13 PM
Microsoft recently launched Visual Studio Code 1.80. Although this update was released in July, the official still calls it the June update. After users install this update, the built-in terminal can directly display images, and auxiliary functions have also been optimized. In the previously released preview version of Visual Studio Code, support for images in the terminal has been supported, and it is enabled by default in the new 1.80 version. In order to be able to display the image in the terminal, the image pixel data is converted into text through a special escape sequence and finally written to the terminal. If you want to pipe typical PNG, GIF or JPEG files to the terminal, you need to install the imgcatpython package and then run imgc in the terminal
 Where is the linux terminal?
Mar 24, 2023 am 10:29 AM
Where is the linux terminal?
Mar 24, 2023 am 10:29 AM
The Linux terminal is in the "/bin" directory by default. The methods to open the Linux terminal are: 1. Use "Ctrl+alt+T" on the Linux homepage to open the terminal; 2. Search through the "search your computer" function and enter "ter "Open the terminal and then close the terminal with "Ctrl+d".




