 Java
Java
 javaTutorial
javaTutorial
 Examples of using chain of responsibility pattern in Java design pattern programming
Examples of using chain of responsibility pattern in Java design pattern programming
Examples of using chain of responsibility pattern in Java design pattern programming
Chain of responsibility mode: Multiple objects are connected into a chain by the references of their corresponding objects, and the request is passed on this chain until a receiving object on the chain handles the request. Because the requesting client does not know who will ultimately handle the request in the chain, the system can dynamically reorganize and allocate responsibilities without affecting the client, thus avoiding the coupling between the request sender and the request handler. .
There are three roles involved in the chain of responsibility:
1, abstract processor role
2, concrete processor role
3, request sender
Small example: Suppose you want to buy a house, Buying a house requires bargaining. Depending on the position of the house seller, the price that can be discounted is also different. Different positions can form a chain for processing requests. We tentatively decide: * Grassroots salespersons can only get a 3% discount * Sales managers: can get a 5% discount * Sales directors: can get an 8% discount * Boss (Boss): can get a 10% discount
Java Example
Class diagram:
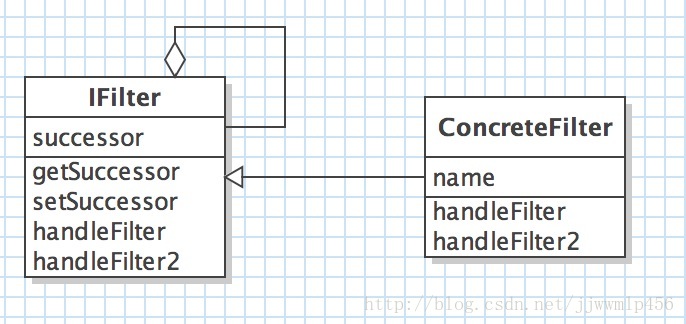
/**
* 抽象责任
*/
public abstract class IFilter {
private IFilter successor;
public IFilter getSuccessor() {
return successor;
}
public void setSuccessor(IFilter successor) {
this.successor = successor;
}
public abstract void handleFilter();
public abstract void handleFilter2();
}/**
* 具体责任
*/
public class ConcreteFilter extends IFilter {
private String name;
public ConcreteFilter(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public void handleFilter() {
/*
* 自己先处理,如有后继者,再由它处理一次
*/
System.out.println(name + " 处理了请求");
if (getSuccessor() != null) {
getSuccessor().handleFilter();
}
}
@Override
public void handleFilter2() {
/*
* 有后继者就后继者处理, 否则自己处理
*/
if (getSuccessor() != null) {
getSuccessor().handleFilter2();
} else {
System.out.println(name + " 处理了请求");
}
}
}public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
IFilter filter1 = new ConcreteFilter("permission-filter");//权限过滤
IFilter filter2 = new ConcreteFilter("suffix-filter");//后缀名过滤
IFilter filter3 = new ConcreteFilter("style-filter");//风格过滤
filter1.setSuccessor(filter2);
filter2.setSuccessor(filter3);
System.out.println("------以下是每一个处理者(包括后继者)都处理了, 顺序也是一级一级的传递------");
filter1.handleFilter();
System.out.println("------以下是交由最后一个后继者处理------");
filter1.handleFilter2();
}
}Print:
------以下是每一个处理者(包括后继者)都处理了, 顺序也是一级一级的传递------ permission-filter 处理了请求 suffix-filter 处理了请求 style-filter 处理了请求 ------以下是交由最后一个后继者处理------ style-filter 处理了请求
For more examples of chain of responsibility pattern usage in Java design pattern programming, please pay attention to the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1385
1385
 52
52

