
Closure is a very important concept in JavaScript. Closure means that a copy of the variables (key-value pairs) obtained from the upper-level function or scope is saved in another scope, and these key-value pairs will not be closed as the execution of the upper-level function is completed. Destroyed. Closure essentially discusses when the member properties of an object are processed by GC (garbage collection mechanism).
We have actually come into contact with closures in the value transfer of the previous function. When explaining function value transfer, we listed a function sortByProperty that compares object properties. In this function, its return value is an anonymous function, which is actually a closure. We still use this example to explain the scope of closures. The code of this function is slightly modified as follows:
// 比较对象属性大小的通用函数
function compareObjectFunction(prop){
//匿名函数
return function(obj1,obj2){
if(obj1[prop] > obj2[prop]) return 1;
else if(obj1[prop] < obj2[prop]) return -1;
else return 0;
}
}
// 创建2个对象
var o1 = {name:"Leon",age:22}
var o2 = {name:"Ada",age:25}
// 比较对象的name属性
var compare = compareObjectFunction("name");
// 返回值
var returnValue = compare(o1,o2);
console.info(rel); //比较name属性会返回1,比较age属性会返回-1In the above example, the biggest benefit of using closures is that the scope of compareObjectFunction has become larger. After the compareObjectFunction function is executed, the prop variable still exists. .
In static object-oriented programming languages such as java and C++, after executing the sentence var compare = compareObjectFunction("name"), the memory will be released and the prop attribute will be garbage collected. But in JavaScript, when the code is executed to var rel = compare(o1,o2);, you can still access the prop attribute. This method of expanding the scope of a function by returning a function is a closure.
One thing to note is: closure is not equal to anonymous function. The way we create closures is usually by creating a function inside another function. So, how does a closure enlarge the scope of a function? We still use the scope memory model when the function is executed to explain this problem.
First we created the compareObjectFunction function, and then created 2 objects o1 and o2. After completing these codes, the scope chain model in memory is as shown below:
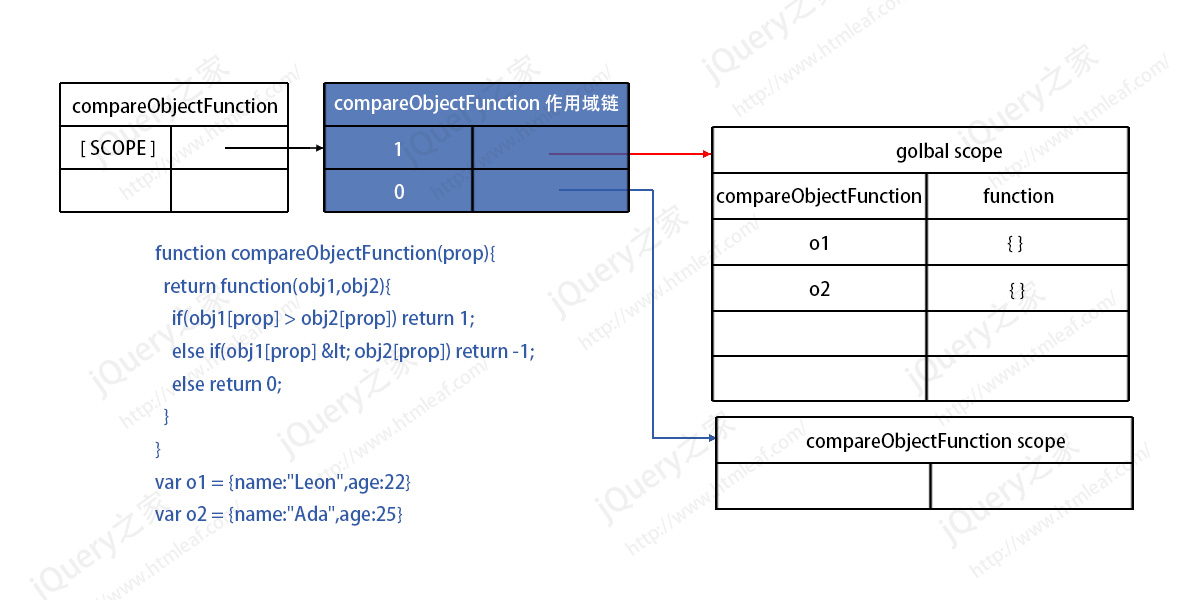
The high bit of the scope chain of compareObjectFunction points to the global scope, and the low bit points to its own scope. There are 3 variables in the global scope at this time.
Next, start comparing the name attribute of the object and execute the following code:
var compare = compareObjectFunction("name");
var returnValue = compare(o1,o2);Compare the name sizes of the two objects by passing name as a parameter into the compareObjectFunction function. After executing the above two lines of code, the memory model of the scope chain is as shown below:
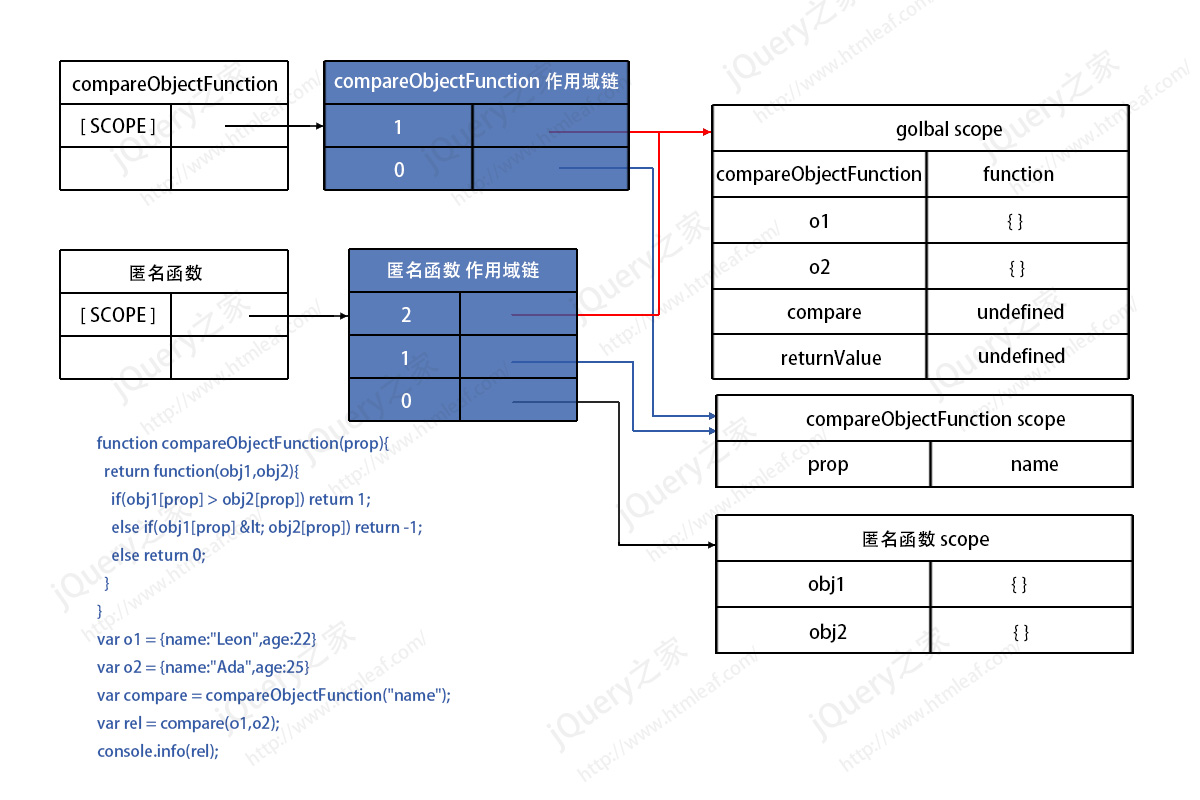
When the compareObjectFunction function is executed, it returns an anonymous function, anonymous A function also has its scope chain. Its high bit points to the global scope, the middle bit points to the scope containing its compareObjectFunction, and the low bit points to its own scope.
After the program executes the compareObjectFunction("name") code, the compareObjectFunction function is executed and the GC begins to recycle it. But then the GC will find that there is another anonymous function pointing to the scope of compareObjectFunction. At this time, the GC will not reclaim this scope memory. The scope chain of compareObjectFunction and the memory of the function itself will be garbage collected by GC.
When the program executes compare(o1,o2), it first changes the values of obj1 and obj2 to o1 and o2 respectively in its own scope, and then it needs to call the prop attribute, because in its own scope If this attribute is not found in the scope space, it will search in the scope compareObjectFunction pointed to by the upper level of the linked list. At this time, it finds that the prop attribute is name, so it uses the name attribute to compare and get the return value.
It can be seen that it is precisely because an anonymous function points to the scope of compareObjectFunction that after the compareObjectFunction function is executed, its scope space will not be garbage collected by GC, thereby reducing the role of the prop attribute. The domain is enlarged.
Although JavaScript's closure can enlarge the scope of the function, the price is that it will occupy more memory space when the program is executed, so we cannot abuse closures and only use them when needed. it.
The above is the content of JavaScript closure-closure scope. For more related content, please pay attention to the PHP Chinese website (www.php.cn)!




