
There are two sentences that say this:
1) Algorithms and data structures are an important part of programming. If you lose algorithms and data structures, you will lose everything. .
2) Programming is algorithms and data structures. Algorithms and data structures are the soul of programming.
Note, this is not what I said. It was summarized by countless programmers. What I said is very practical and insightful. If you want long-term sustainable development, it is still necessary to study more algorithms. Today I will tell you about the symmetric encryption algorithm among encryption algorithms, and I will teach you how to program and use the symmetric encryption algorithm here. It includes the programming and use of three symmetric encryption algorithms: DES, 3DES and AES, and is full of useful information.
1. Symmetric cryptographic algorithm
The symmetric cryptographic algorithm is the most widely used and most frequently used encryption algorithm today. It is not only used in the software industry, but is also popular in the hardware industry. Whenever security requirements are involved in various infrastructures, symmetric encryption algorithms will be given priority.
The encryption key and decryption key of the symmetric cryptographic algorithm are the same. For most symmetric cryptographic algorithms, the encryption and decryption processes are reversed.
(1) Encryption and decryption communication model
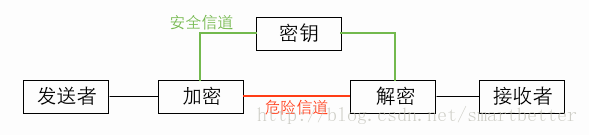
#(2) Features: open algorithm, small amount of calculation, fast encryption speed, high encryption efficiency
(3) Weakness: Both parties use the same key, and security cannot be guaranteed
There are two types of symmetric ciphers: stream ciphers and block ciphers, but block ciphers are commonly used now:
(4) Block cipher working mode
1) ECB: Electronic codebook (the most commonly used, each encryption generates an independent ciphertext group, and will not affect other ciphertext groups , that is, the same ciphertext will be generated after the same plaintext is encrypted)
2) CBC: Ciphertext link (commonly used, before plaintext encryption needs to be XORed with the previous ciphertext, also That is, the same plaintext is encrypted to produce different ciphertext)
In addition to these two commonly used working modes, there are also:
3) CFB: Ciphertext Feedback
4) OFB: Output feedback
5) CTR: Counter
These five working modes are mainly used by algorithms in cryptography when performing derivation calculations Arrived.
6. Block cipher padding method
1) NoPadding: No padding
2) PKCS5Padding:
3) ISO10126Padding:
7. Commonly used symmetric passwords:
1) DES (Data Encryption Standard, data encryption standard)
2) 3DES (Triple DES, DESede , an algorithm that performs triple DES encryption)
3) AES (Advanced Encryption Standard, advanced data encryption standard, the AES algorithm can effectively resist the attack algorithm against DES)
Let’s take a look at this first A simple comparison of the three algorithms:
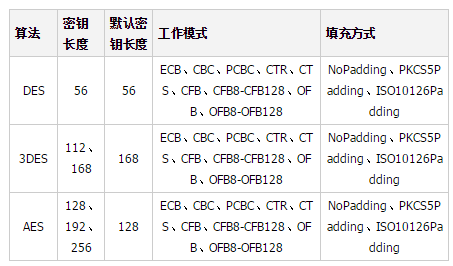
Let’s see how to use the three algorithms DES / 3DES / AES to achieve symmetric encryption:
2.DES algorithm
1.DES: Data encryption standard, a typical algorithm in the field of symmetric encryption algorithms
2. Features: short key (56 bits), short life cycle (to avoid being Crack)
3.Java implementation
1) Generate key
KeyGenerator keyGen = KeyGenerator.getInstance("DES");//密钥生成器
keyGen.init(56);//初始化密钥生成器
SecretKey secretKey = keyGen.generateKey();//生成密钥
byte[] key = secretKey.getEncoded();//密钥字节数组
2) Encryption
SecretKey secretKey = new SecretKeySpec(key, "DES");//恢复密钥
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("DES");//Cipher完成加密或解密工作类
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, secretKey);//对Cipher初始化,加密模式
byte[] cipherByte = cipher.doFinal(data);//加密data
3) Decryption
SecretKey secretKey = new SecretKeySpec(key, "DES");//恢复密钥
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("DES");//Cipher完成加密或解密工作类
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, secretKey);//对Cipher初始化,解密模式
byte[] cipherByte = cipher.doFinal(data);//解密data
We can find that we just set different settings for encryption and decryption It's just a pattern.
3.3DES algorithm
1.3DES: Increase the key length to 112 bits or 168 bits, and improve security by increasing the number of iterations
2. Disadvantages: The processing speed is slow, the key calculation time is long, and the encryption efficiency is not high
3.Java implementation
1) Generate key
KeyGenerator keyGen = KeyGenerator.getInstance("DESede");//密钥生成器
keyGen.init(168); //可指定密钥长度为112或168,默认为168
SecretKey secretKey = keyGen.generateKey();//生成密钥
byte[] key = secretKey.getEncoded();//密钥字节数组
2) 3DES encryption
SecretKey secretKey = new SecretKeySpec(key, "DESede");//恢复密钥
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("DESede");//Cipher完成加密或解密工作类
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, secretKey);//对Cipher初始化,解密模式
byte[] cipherByte = cipher.doFinal(data);//加密data
3) 3DES decryption
SecretKey secretKey = new SecretKeySpec(key, "DESede");//恢复密钥
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("DESede");//Cipher完成加密或解密工作类
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, secretKey);//对Cipher初始化,解密模式
byte[] cipherByte = cipher.doFinal(data);//解密data
4.AES algorithm (recommended)
1.AES: Advanced Data Encryption Standard, which can effectively resist all known attacks against the DES algorithm
2 .Features: short key establishment time, good sensitivity, low memory requirements, high security
3.Java implementation
1) Generate key
KeyGenerator keyGen = KeyGenerator.getInstance("AES");//密钥生成器
keygen.init(128); //默认128,获得无政策权限后可为192或256
SecretKey secretKey = keyGen.generateKey();//生成密钥
byte[] key = secretKey.getEncoded();//密钥字节数组
2) AES encryption
SecretKey secretKey = new SecretKeySpec(key, "AES");//恢复密钥
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("AES");//Cipher完成加密或解密工作类
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, secretKey);//对Cipher初始化,解密模式
byte[] cipherByte = cipher.doFinal(data);//加密data##3) AES decryption
SecretKey secretKey = new SecretKeySpec(key, "AES");//恢复密钥
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("AES");//Cipher完成加密或解密工作类
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, secretKey);//对Cipher初始化,解密模式
byte[] cipherByte = cipher.doFinal(data);//解密dataFor the convenience of use, I have written tool classes for the three algorithms DES/3DES/AES. Address: Download address (new DES/3DES/AES tool class). That’s it, DES/3DES/AES three algorithms implement symmetric encryption. I hope it will be helpful to everyone's learning, and I also hope that everyone will support the PHP Chinese website. For more detailed explanations of Java implementation of symmetric encryption (DES, 3DES, AES), please pay attention to the PHP Chinese website!
 Detailed explanation of linux dd command
Detailed explanation of linux dd command
 Unable to start your computer properly
Unable to start your computer properly
 How to open TIF format in windows
How to open TIF format in windows
 wap browser
wap browser
 How to open url file
How to open url file
 Win11 My Computer Added to Desktop Tutorial
Win11 My Computer Added to Desktop Tutorial
 How to use btbook magnetic search
How to use btbook magnetic search
 How to solve the problem that wlan does not have a valid ip configuration
How to solve the problem that wlan does not have a valid ip configuration
 Main contents of database conceptual design
Main contents of database conceptual design




