
Originally, I was going to continue the last article in the series of expressions from simple to deep, but recently the team has suddenly become busy, busier than ever before! But friends who like expressions, don't worry, I'm already writing it :) At work, I found that everyone has a little understanding of some basic principles of Javascript here or there, so I decided to spend some time sorting out these basic knowledge and share them with you. At first I planned to write one article, but as I continued writing, I found more and more, so I decided to write a series. All the content in this series involves the basics of Javascript, and there is no fancy stuff, but I believe these basic things will help you understand the interesting things.
Yes, when it comes to Javascript, all I can think of is fun and fun! So which places are fun and why are they fun? Let's have some fun together, and let's understand Javascript thoroughly while playing. Contents included in this article:
Basic types
Object and object
Basic packaging types
Value types and reference types
function types
Basic types
Javascript has 5 basic data types (also called simple data types): Undefined, Null, Boolean, Number, String and 1 complex data type Object.
var undefinedVariable;
var nullValue = null;
var cnblogs = new Object();
var func = function () { };
typeof ("string");
typeof (100);
typeof (true);
typeof (undefinedVariable);
typeof (cnblogs);
typeof (undeclaredValue);
typeof (nullValue);
typeof (null)
typeof (func)Tell me what the result is?
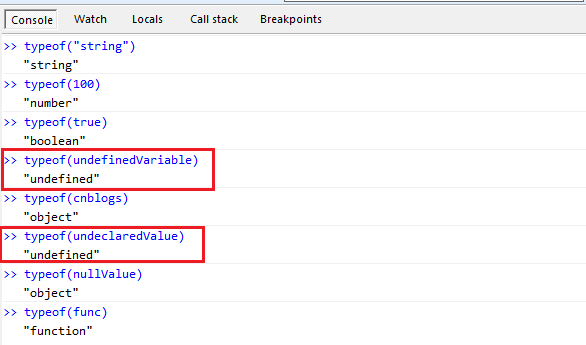
Fun One: Declared but not assigned and undeclared variables are all undefined
Fun Two: Only declarations and If the value is null, its value will be null
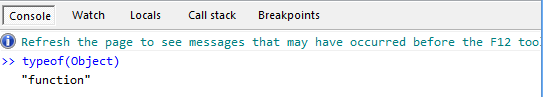
Fun No. 3: typeof(Object) turns out to be a function
Fun No. 4: typeof(null) turns out to be an object
Null and Undefined Both types have only one value, null and undefined. Logically, the null value represents a pointer to a null object, which is why typeof(null) returns Object. And undefined is derived from the null value, so...
Fun No. 5: null == undefined is true.
But think about it, Null and Undefined are two different types after all. Even if they are the relationship between parent class and subclass, parent class and subclass cannot be equal in C#, right? In fact, null == undefined is a hard rule. ECMA stipulates that they should return true when doing equality tests, so they returned true. It's like we overridden the equlas method in C#.
As for why typeof(Object) returns function, please see Object and object below.
Object and object
The book Javascript Advanced Programming says that "functions in ECMAScript are objects, not a data type." It seems that the translator added it. Since typeof(Object) returns function, why is it said that function is not a data type? What is the relationship between Object and function?
In my opinion, Object is actually a function, or we say Object is a function whose name is easier to understand. The official name is constructor.
var p = new Object();
p.name = "jesse";
p.age = 18;
function Person(name,age)
{
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
var p2 = new Person("jesse", 18);In the above code, if we treat Object as a function name, then the properties of new Object() and new Person() are the same. A function instance is obtained through the new operator, and the function inside is already a class concept. So the Object here is actually a function. In this way we can explain why typeof(Object) is function.
Then what is the complex type Object we mentioned above?
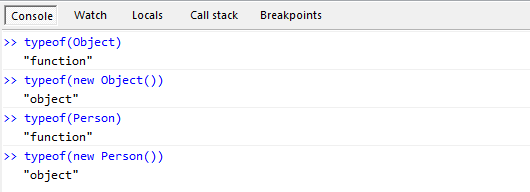
Object is a function, but new Object() is an object. At this point, it is clear that the Object with the first letter in capital letters is a function, and the object with the first letter in lowercase letters is a data type. So I suggest that everyone use lowercase letters when talking about types in the future. Our basic types are string, number, and boolean. Uppercase String, Number, Boolean are just a function. The result of calling these functions is, yes, object.
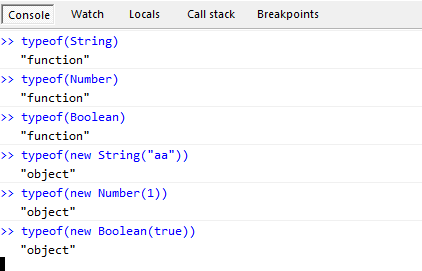
Finally, we can’t find the two functions Undefined and Null, so the two data types are undefined and null (why typeof(null) will get object Already said)

Fun No. 6: Object is not an object type
基本包装类型
我们上面讲了string, number, boolean是基本类型,基本类型和复杂类型最大的区别就是基本类型没有prototype属性。也就意味着你不能给基本类型随意的添加方法或属性。
var str = "str"; // typeof(str): string
var strObj = new String("str"); // typeof(strObj):object
strObj.name = "strObj";
strObj.alert = function () {
alert(this.name);
};
strObj.alert(); // strObj
str.name = "str"; //wrong...
str.alert = function () {
alert(this);
}
str.alert(); // this is wrong.... nothing is gonna happen.同时我们还说到了首字母大写的这个String是一个function,所以new String("str")得到的是一个object而不是一个string,这里大家要搞清楚了。我们的问题来了,为什么基本类型string会有一些初始的方法呢?它不是基本类型么?方法是怎么加上去的?
str = str.concat("str2");
strObj = strObj.concat("str2");
strObj.alert(); //之后返回 string 不再是一个对象了, 所以这里也不再有alert方法了。str是string类型的变量,记住它不是一个对象。它是不应该有方法的,那么它的contact方法从何而来呢?这里后台在调用str.contact的时候实际上偷偷的完成了几步操作:
基于str创建一个String类型的实例
在实例上调用指定的方法
销毁这个实例
将这三个步骤想象成这样:
var str2 = new String(str);
str = str2.concat("str2");
str2= null;我们可以把String,Number,Boolean叫做封装类型, 他们就好像我们在C#里面的自定义类型一样。 但是不要忘记了我们真正的基本类型是string, number, boolean。用String所构造出来的对象是属于object类型的。
好玩之七: String 不是 string
值类型和引用类型
我们上面讲到了5种基本类型:string, number, boolean, null, undefined 全部是值类型。Javascript中只有一种引用类型,也就是我们的复杂类型object。那么有人可能会好奇,那么像Date, Regex, Arrary这些是什么类型呢 ? 其实这里面的概念有一点混淆,如果你很好的理解了上面的Object 和object之间的区别,可能会比较好理解一点。 我们可以把function 看成是C#里面 class关键字,我们可以用class定义类,同样我们可以在Javascript中用function来定义类。
在C#中定义类:
namespace ConsoleApplication1
{
class Person
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public int Age { get; set; }
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
var p =new Person();
Console.WriteLine(p.GetType()); // ConsoleApplication1.Person
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}在Javascript定义类:
function Person(name,age)
{
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
var p = new Person();
typeof(p); //object你发现区别了么?如果我们在Javascript中用function定义类,他们的实例将永远是object, 包括原生的那些Date, Array, RegExp。
typeof (new Date()); // object typeof (new Array()); // object typeof (new RegExp()); // object
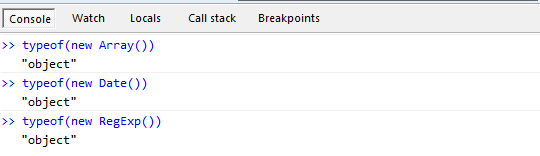
好玩之八: 全部都是object
如果全部都是object的话,那我怎么能知道这个对象到底是不是Date或者Person的实例呢?借助于instanceof 就可以了。
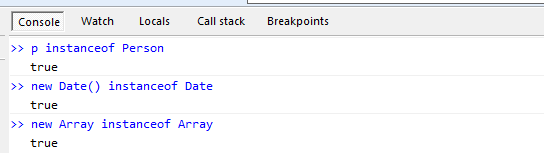
终级好玩:我用function创建了一个Person类,然后用new得到一个Person的实例,结果它却不是Person类型的。 这就好像生了个孩子,供他吃穿,但是他却不跟你姓,这得有多么无私伟大才干得出来的事啊!
function类型
function类型有两种,函数声明和函数表达式。函数声明具有优先级,可以在声明之前被使用,表达式却不能。
sayGoodNight(); // right
sayHello(); // wrong
var sayHello = function (name) {
alert("Hello, " + name);
};
function sayGoodNight(Name) {
alert("Good Night, "+ name);
}除此之外,函数表达式还可以像object一样,随意的添加属性。
var sayHello = function (name) {
alert("Hello, " + name);
};
sayHello.age = 18;
sayHello.sayAge = function () {
alert("I am" + 18) ;
}
sayHello.sayAge(); // I am 18但是,函数表达式到底是个什么玩意儿呢? 不能实例化,但是可以随意的添加属性,它和object有什么区别?我们在上面说过,object其实就是一个对象实例。
我们还有大写的Function, 它和function之间的关系会不会和String 和string 一样?( 以下内容比较费脑力,慎入!)
var sayHello = new Function('name','alert("My name is " + name );');
sayHello('Jesse');
sayHello instanceof Function; // true
var sayHello2 = function (name) {
alert('My name is' + name);
};
sayHello2 instanceof Function; // true我们上面调用Function去构造了一个函数。既没有用函数声明,也没有用函数表达式,不管怎么说这是第三种创建函数的方法,虽然肯定没有多少人用它,因为它不管是参数,还是函数体全部都是字符串,这写起来还不让人崩溃么?
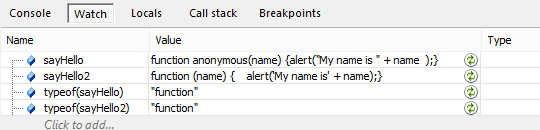
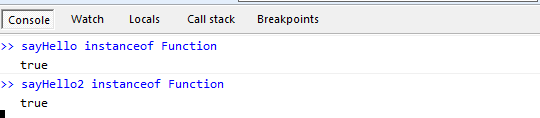
看出什么猫腻来了么?所谓的函数表达式,其实是用一个变量接收了一个function的对象而已。而这个function的对象则是Function的实例。包括用函数声明写出来的函数也是Function的实例。
function sayHello3(name)
{
alert('My name is' + name);
}
sayHello3 instanceof Function; // true但是,等等,我们前面说到的String, Date, Array都是function类型的,那Function也是么?
我们前面说所有function的实例都是object类型的,但是对于Function 这个奇异的function来说,它的实例仍然是function类型的,并且我们可以用Function的实例再创造实例。原来我们所说的用function创造出来的类,它不是类,而是Function的实例。
function Person(name) {
this.name = name;
}
Person instanceof Function; // true我们再结合自执行函数理解一下,也许会好一点:
(function () {
alert("something...");
}());实际上我们上面的function(){} 会返回给我们一个function的实例,那么我们当然可以直接执行它了。这么看来function应该是Javascript里面最特别的类型了。
好玩之十:所有的function都是Function的实例
好玩之十一:Function 本身也是一个function
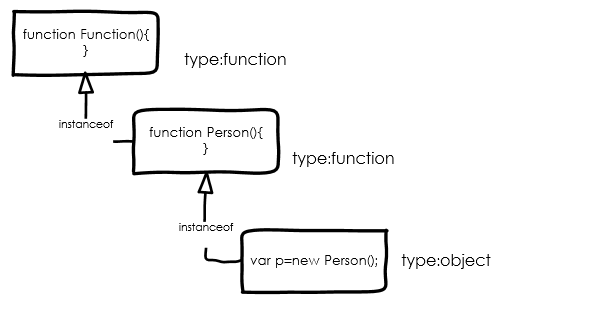
最后我们来总结一下:
Javascript中有5种基本类型:string, number, boolean, null, undefined。
另外一种复杂类型object 其实是function的实例。
除了Function这个系统里面的function构造器以外,其它所有function的实例都是object类型的。
Date, Array, RegExp 这些都是function类型,同时也是Function的实例。同理,它们的实例也是object类型的。
总结完了,好像也不多,不是么?关于function其实javascript是非常强大的一个功能,作用域以及面向对象的一些知识也是和它息息相关的,我们下一篇就来看看作用域的问题。谢谢大家的关注!
更多Javascript基础回顾之(一) 类型相关文章请关注PHP中文网!




