
1. What is AJAX?
AJAX stands for "Asynchronous JavaScript and XML" (Asynchronous JavaScript and XML), which is a web development technology for creating interactive web applications. It uses:
Use XHTML+CSS to standardize presentation;
Use XML and XSLT for data exchange and related operations;
Use XMLHttpRequest object for asynchronous data communication with the Web server;
Use Javascript to operate Document Object Model performs dynamic display and interaction;
Use JavaScript to bind and process all data.
2. Comparison with traditional web applications
In traditional web application interaction, the user triggers an HTTP request to the server, and the server processes it and then returns a new HTHL page to the client. Whenever When the server processes the request submitted by the client, the client can only wait idle, and even if it is only a small interaction and only needs to get a simple piece of data from the server, a complete HTML page must be returned, and every time the user It wastes time and bandwidth to re-read the entire page. This approach wastes a lot of bandwidth. Since each application interaction needs to send a request to the server, the response time of the application depends on the response time of the server. This results in a user interface that is much less responsive than native apps.
Unlike this, an AJAX application can only send and retrieve the necessary data to the server. It uses SOAP or some other XML-based Web Service interface, and uses JavaScript on the client to process the response from the server. Because less data is exchanged between the server and the browser, we see more responsive applications as a result. At the same time, a lot of processing work can be completed on the client machine that makes the request, so the processing time of the Web server is also reduced.
3. The working principle of AJAX
The working principle of Ajax is equivalent to adding an intermediate layer (AJAX engine) between the user and the server, making user operations and server responses asynchronous. Not all user requests are submitted to the server. Some data verification and data processing are left to the Ajax engine itself. Only when it is determined that new data needs to be read from the server, the Ajax engine will submit the request to the server on its behalf.
The core of Ajax is composed of JavaScript, XMLHTTPRequest, and DOM objects. It sends asynchronous requests to the server through the XmlHttpRequest object, obtains data from the server, and then uses JavaScript to operate the DOM and update the page. The most critical step in this is to obtain the request data from the server. Let's learn about these objects.
(1).XMLHTTPRequest object
One of the biggest features of Ajax is that it can transmit or read and write data to the server without refreshing the page (also known as updating the page without refreshing). This feature mainly benefits from the XMLHTTP component XMLHTTPRequest. object.
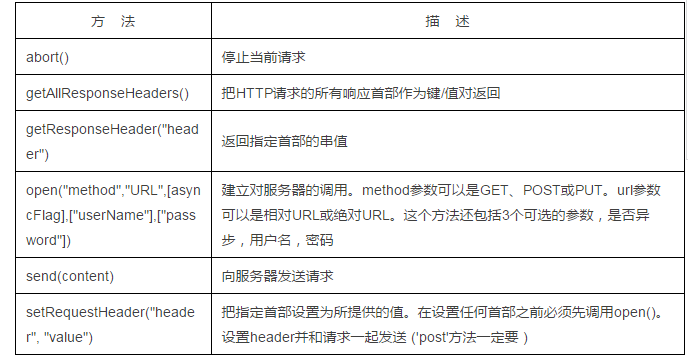
XMLHttpRequest Object Method Description
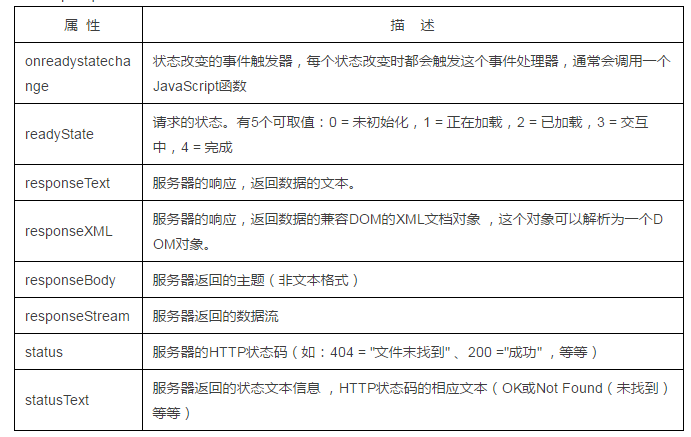
XMLHttpRequest Object Property Description
(2).JavaScript
JavaScript It is a programming language widely used in browsers.
(3).DOM Document Object Model
DOM is a set of APIs for HTML and XML files. It provides a structural representation of the file, allowing you to change its content and visibility. Its essence is to establish a bridge between web pages and Script or programming languages. All properties, methods and events that WEB developers can operate and create files are represented by objects (for example, document represents the object "the file itself", table object represents the HTML table object, etc.). These objects can be accessed from Script by most browsers today. A web page built with HTML or XHTML can also be regarded as a set of structured data. This data is enclosed in DOM (Document Object Model). DOM provides support for reading and writing various objects in the web page.
(4).XML
Extensible Markup Language (Extensible Markup Language) has an open, extensible, self-describing language structure. It has become the standard for online data and document transmission. Exchange data with other applications.
(5). Comprehensive
The Ajax engine is actually a relatively complex JavaScript application used to process user requests, read and write servers, and change DOM content. JavaScript's Ajax engine reads the information and interactively rewrites the DOM. This allows web pages to be seamlessly reconstructed, that is, changing page content after the page has been downloaded. This is what we have been using extensively with JavaScript and the DOM. method, but to make a web page truly dynamic, it requires not only internal interaction, but also data acquisition from the outside. In the past, we let users enter data and change the content of the web page through the DOM, but now, XMLHTTPRequest allows us to Read and write data on the server without reloading the page, minimizing user input.
Ajax separates the interface and application in the WEB (it can also be said to separate data and presentation). In the past, there was no clear boundary between the two. The separation of data and presentation is conducive to division of labor and cooperation and reduces non-technical It eliminates WEB application errors caused by personnel's modification of pages, improves efficiency, and is more suitable for the current publishing system. You can also transfer some of the previous work burdened by the server to the client, which can be processed by the client's idle processing power.
4.Advantages and disadvantages of AJAX
(1).Advantages of AJAX
. No refresh to update data.
The biggest advantage of AJAX is that it can communicate with the server to maintain data without refreshing the entire page. This allows web applications to respond to user interactions more quickly and avoids sending unchanged information over the network, reducing user waiting time and bringing a very good user experience.
. Communicate with the server asynchronously.
AJAX uses an asynchronous method to communicate with the server, without interrupting the user's operation, and has a faster response capability. Optimizes the communication between Browser and Server, reducing unnecessary data transmission, time and data traffic on the network.
. Front-end and back-end load balancing.
AJAX can transfer some of the work previously burdened by the server to the client, using the client's idle capabilities to process it, reducing the burden on the server and bandwidth, and saving space and broadband rental costs. And to reduce the burden on the server, the principle of AJAX is to "get data on demand", which can minimize the burden on the server caused by redundant requests and responses and improve site performance.
. Widely supported based on standards.
AJAX is based on standardized and widely supported technology and does not require downloading browser plug-ins or applets, but requires the customer to allow JavaScript to execute on the browser. As Ajax matures, some program libraries that simplify the use of Ajax have also come out. Likewise, another assistive programming technology has emerged to provide alternative functionality for users who do not support JavaScript.
.Separation of interface and application.
Ajax separates the interface and application in the WEB (it can also be said to separate data and presentation), which is conducive to division of labor and cooperation, reduces WEB application errors caused by non-technical personnel modifying the page, improves efficiency, and is more suitable for Current publishing system.
(2).Disadvantages of AJAX
.AJAX kills the Back and History functions, which is a destruction of the browser mechanism.
In the case of dynamically updated pages, users cannot return to the previous page state because the browser can only remember static pages in the history. The difference between a page that has been completely read and a page that has been dynamically modified is very subtle; users will often expect that clicking the back button will cancel their previous operation, but in an Ajax application, this will not be possible. .
The back button is an important function of a standard web site, but it cannot cooperate well with js. This is a serious problem caused by Ajax, because users often hope to cancel the previous operation by going back. So is there any solution to this problem? The answer is yes. Those who have used Gmail know that the Ajax technology used under Gmail solves this problem. You can go back under Gmail. However, it does not change the mechanism of Ajax. It is just a stupid but effective one. The way to do this is by creating or using a hidden IFRAME to reproduce the changes on the page when the user clicks the back button to access the history. (For example, when the user clicks back in Google Maps, it searches in a hidden IFRAME and then reflects the search results onto the Ajax element to restore the application state to what it was at that time.)
But , although this problem can be solved, the development cost it brings is very high, and is contrary to the rapid development required by the Ajax framework. This is a very serious problem caused by Ajax.
A related point is that using dynamic page updates makes it difficult for users to save a specific state to favorites. Solutions to this problem have also emerged, most of which use URL fragment identifiers (often called anchors, the part after the # in the URL) to keep track of and allow the user to return to a specified application state. (Many browsers allow JavaScript to dynamically update anchors, allowing Ajax applications to update anchors while updating the displayed content.) These solutions also resolve many of the arguments surrounding not supporting a back button.
.AJAX security issues.
AJAX technology not only brings a good user experience to users, but also brings new security threats to IT companies. Ajax technology is like establishing a direct channel for enterprise data. This allows developers to inadvertently expose more data and server logic than before. Ajax logic can be hidden from client-side security scanning technology, allowing hackers to create new attacks from remote servers. Ajax is also difficult to avoid some known security weaknesses, such as cross-site scripting attacks, SQL injection attacks, and Credentials-based security vulnerabilities, etc.
. Weak support for search engines.
The support for search engines is relatively weak. If used improperly, AJAX will increase network data traffic, thereby reducing the performance of the entire system.
. Destroy the exception handling mechanism of the program.
At least from the current perspective, Ajax frameworks such as Ajax.dll and Ajaxpro.dll will destroy the exception mechanism of the program. Regarding this problem, I have encountered it during the development process, but after checking, there is almost no relevant introduction on the Internet. Later, we did an experiment and used Ajax and traditional form submission modes to delete a piece of data... which brought great difficulties to our debugging.
.Violates the original intention of URL and resource positioning.
For example, if I give you a URL address, if Ajax technology is used, maybe what you see under the URL address is different from what I see under this URL address. This is contrary to the original intention of resource positioning.
.AJAX does not support mobile devices well.
Some handheld devices (such as mobile phones, PDAs, etc.) currently do not support Ajax very well. For example, when we open a website using Ajax technology on the mobile phone's browser, it currently does not support it.
. The client is too fat and too much client code causes development costs.
It is complex to write and error-prone; there are many redundant codes (it is a common problem of AJAX to include js files in layers, plus a lot of server-side code in the past is now placed on the client); it destroys the original standards of the Web.
5. AJAX Notes and Applicable and Unapplicable Scenarios
(1). Notes
When developing Ajax, network delay—that is, the interval between the user making a request and the server sending a response—needs to be cautious. consider. Not giving users a clear response, not properly pre-reading data, or improperly handling XMLHttpRequest will cause users to experience delays that they don't want to see and that they can't understand. A common solution is to use a visual component to tell the user that the system is performing background operations and reading data and content.
(2).Ajax applicable scenarios
.Form-driven interaction
.Deep-level tree navigation
.Fast user-to-user interaction Communication responses
. Insignificant scenarios such as voting, yes/no, etc.
. Scenarios of filtering and manipulating relevant data
. Ordinary text Input prompts and auto-complete scenarios
(3).Ajax is not applicable to scenarios
.Some simple forms
.Search
.Basic navigation
.Replace a large amount of text
.Manipulation of presentation
For more articles related to the working principle of Ajax and its advantages and disadvantages, please pay attention to the PHP Chinese website!




