How to use ES in C#
Introduction to Elasticsearch
Elasticsearch (ES) is an open source search engine based on Lucene. It is not only stable, reliable, and fast, but also has good horizontal scalability. It is specially designed for distributed environments.
What is Elasticsearch
Elasticsearch is an open source search engine based on Apache Lucene(TM). Whether in the open source or proprietary fields, Lucene can be considered to be the most advanced and best-performing to date. , the most comprehensive search engine library.
However, Lucene is just a library. To take advantage of its power, you need to integrate it into your application using C#. Lucene is very complex and you need a deep understanding of retrieval to understand how it works.
Elasticsearch is also written in Java and uses Lucene to build indexes and implement search functions, but its purpose is to make full-text search simple and hide the complexity of Lucene through a simple and coherent RESTful API.
However, Elasticsearch is not just Lucene and full-text search engine, it also provides:
Distributed real-time file storage, each field is indexed and searchable
Real-time analysis The distributed search engine
can scale to hundreds of servers and handle petabytes of structured or unstructured data
And, all these functions are integrated into one server, your Applications can interact with it through a simple RESTful API, clients in various languages, and even the command line. Getting started with Elasticsearch is easy, provides many sensible defaults, and hides complex search engine theory from beginners. It works out of the box (installed and ready to use) and requires minimal learning for use in a production environment. Elasticsearch is licensed under the Apache 2 license and is free to download, use and modify.
With the accumulation of knowledge, you can customize the advanced features of Elasticsearch according to different problem areas. All of this is configurable and the configuration is very flexible.
Use C# to operate ES
NEST is a high-level client that can map all request and response objects, has a strongly typed query DSL (domain specific language), and can use .net Features such as covariance and Auto Mapping Of POCOs, NEST still uses the Elasticsearch.Net client internally. The elasticsearch.net (NEST) client provides a strongly typed query DSL, which is convenient for users to use. The source code can be downloaded.
1. How to install NEST
Open the tools menu of VS, through the NuGet package manager console, enter the following command to install NEST
Install-Package NEST
The following three DLLs are referenced after installation
Elasticsearch.Net.dll (2.4.4) Nest.dll (2.4.4) Newtonsoft.Json.dll (version 9.0)
2. Link elasticsearch
You can use a connection pool to connect to the Elasticsearch cluster through a single node or specify multiple nodes. Using a connection pool has more advantages than connecting a single node to Elasticsearch, such as supporting load. Balancing, failover, etc.
Through single point link:
var node = new Uri("http://myserver:9200");
var settings = new ConnectionSettings(node);
var client = new ElasticClient(settings);
Connect through the connection pool:
var nodes = new Uri[]
{
new Uri("http ://myserver1:9200"),
new Uri("http://myserver2:9200"),
new Uri("http://myserver3:9200")
};
var pool = new StaticConnectionPool(nodes);
var settings = new ConnectionSettings(pool);
var client = new ElasticClient(settings);
NEST Index
In order to know which index the request needs to operate on, the Elasticsearch API expects to receive one or more index names as part of the request.
1. Specify the index
1. You can use .DefaultIndex() through ConnectionSettings to specify the default index. When no specific index is specified in a request, NEST will request the default index.
var settings = new ConnectionSettings()
.DefaultIndex("defaultindex");
2. You can use .MapDefaultTypeIndices() through ConnectionSettings to specify the index mapped to the CLR type. .
var settings = new ConnectionSettings()
.MapDefaultTypeIndices(m => m
.Add(typeof(Project), "projects")
);
Note: Specifying indexes through .MapDefaultTypeIndices() has a higher priority than specifying indices through .DefaultIndex(), and is more suitable for simple objects (POCO)
3. In addition, you can also explicitly specify the index name for the request, for example:
var response = client.Index(student, s=>s.Index("db_test"));
var result = client.Search
var result = client.Delete
Note: When the index name is actually specified for the request, this priority is the highest, higher than the index specified in the above two ways.
4. Some Elasticsearch APIs (such as query) can use one or multiple index names or use the _all special flag to send requests to multiple or all nodes on NEST
//Request Single node
var singleString = Nest.Indices.Index("db_studnet");
var singleTyped = Nest.Indices.Index
ISearchRequest singleStringRequest = new SearchDescriptor
ISearchRequest singleTypedRequest = new SearchDescriptor
//Request multiple nodes
var manyStrings = Nest.Indices.Index("db_studnet", "db_other_student");
var manyTypes = Nest .Indices.Index
##ISearchRequest indicesAllRequest = new SearchDescriptor
ISearchRequest allIndicesRequest = new SearchDescriptor
2. Create index
Elasticsearch API Allows you to configure the index while creating the index, for example:
var descriptor = new CreateIndexDescriptor("db_student")
.Settings(s => s.NumberOfShards(5).NumberOfReplicas(1) );client.CreateIndex(descriptor);
This specifies that the number of shards of the index is 5 and the number of copies is 1.
3. Delete index
Elasticsearch API allows you to delete index, for example:
var descriptor = new DeleteIndexDescriptor("db_student").Index("db_student");
client.DeleteIndex(descriptor)The index name "db_student" to be deleted is specified here. The following are more deletion use cases:
//Delete the specified index All indexes under the node
var descriptor = new DeleteIndexDescriptor("db_student").AllIndices();
NEST Mapping
NEST provides a variety of mapping methods, which are introduced here. Attribute custom mapping.
1. Simple implementation
1. Define the POCO required by the business and specify the required Attribute
[ElasticsearchType(Name = "student")]
public class Student
{
[Nest.String(Index = FieldIndexOption.NotAnalyzed)]
public string Id { get; set; }
[Nest.String(Analyzer = "standard")]
public string Name { get; set; }
[Nest.String(Analyzer = "standard")]
public string Description { get; set; }
## public DateTime DateTime { get; set ; }
client.CreateIndex(descriptor);
2, NumberAttribute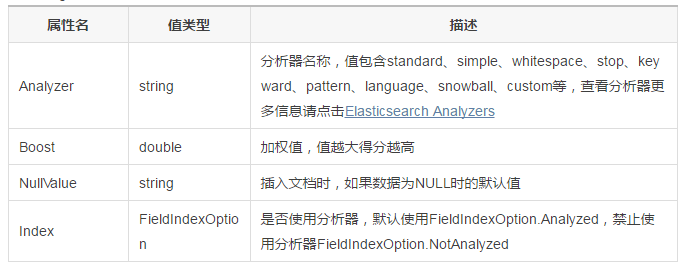
3, BooleanAttribute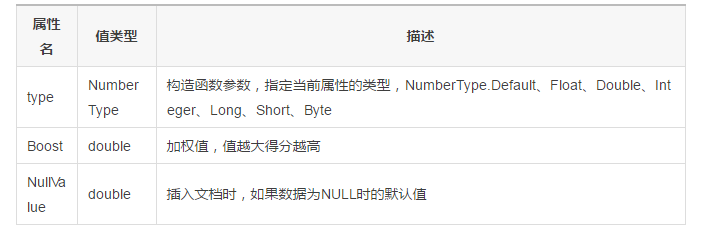
4, DateAttribute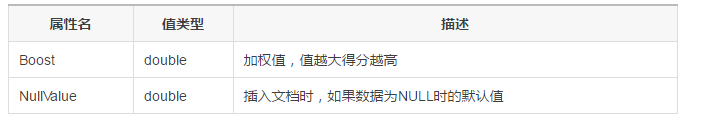
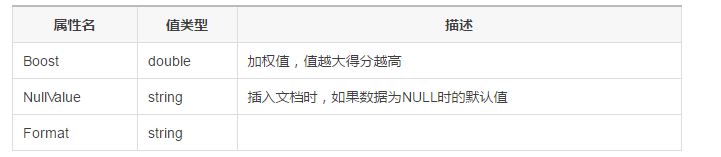
NEST Search
NEST provides support for Lambda chain query DLS (domain specific language). The following is a simple implementation and a brief description of each query.
1. Simple implementation
1. Define SearchDescriptor to facilitate the implementation of complex business in the project
var query = new Nest.SearchDescriptor
var result = client.Search
2. Retrieve documents whose title and content contain key and the author is not equal to "Pretty Girl"
query.Query(q =>
q.Bool(b =>
) b.Must(m =>
MultiMatch(t => t.Fields(f => f.Field(obj => obj.Title).Field(obj => obj.Content)).Query(key))
)
.MustNot(m =>
m.QueryString(t => t.Fields(f => f.Field(obj => obj.Author)). Query("wenli"))
)
)
);
##Note: If Elasticsearch uses the default word segmentation, and the attributes of Title and Content are [Nest.String(Analyzer = "standard")]If Elasticsearch uses IK word segmentation, the attributes of Title and Content are [Nest.String(Analyzer = "ikmaxword")] or [Nest.String(Analyzer = "ik_smart")]Author's attribute is [Nest.String(Index = FieldIndexOption.NotAnalyzed)], prohibiting the use of analyzers3. Filter documents whose author is equal to "Historical River" query.PostFilter(x => x.Term(t => t.Field(obj => obj.Author).Value(" wenli")));
5. Filter documents whose number is between 1 and 100
query.PostFilter(x => x.Range(t => t.Field(obj => obj. Number).GreaterThanOrEquals(1).LessThanOrEquals(100)));
6. Sort according to the score flashback
query.Sort(x = > query.Highlight(h => h
.PreTags("")
.Fields (
f => f.Field(obj => obj.Title),
f => f.Field(obj => obj.Content),
f => f.Field("_all")
)
);
8. Assemble the query content and organize the data to facilitate the previous call
var list = result.Hits.Select(c => new Models.ESObject(){ Id = c.Source .Id,
Title = c.Highlights == null ? c.Source.Title : c.Highlights.Keys.Contains("title") ? string.Join("", c.Highlights["title "].Highlights): c.Source.Title, //The highlighted content appears several times in a record
Content = c.Highlights == null? c.Source.Content: c. Highlights.Keys.Contains("content") ? string.Join("", c.Highlights["content"].Highlights) : c.Source.Content, //The highlighted content, how many times appear in a record Times
Author = c.Source.Author,
Number = c.Source.Number,
IsDisplay = c.Source.IsDisplay,
Tags = c.Source.Tags,
Comments = c.Source.Comments,
DateTime = c.Source.DateTime,
})
2. Introduction to query DSL
To be sorted out...
elasticsearch.net DocumentDocument operations include adding/updating documents and partially updating documents , delete documents and corresponding batch operation document methods. 1. Add/update documents and batch operationsAdd/update a single document
Client.Index(student);
var list = new List
2. Partial update of single document and batch operation
Partially update a single document
client.Update
Partial update batch document
var ids = new List
##foreach (var v in ids)
{
bulkQuest.Operations.Add(new BulkDeleteOperation
}
##var result = client.Bulk (bulkQuest);

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to use char array in C language
Apr 03, 2025 pm 03:24 PM
How to use char array in C language
Apr 03, 2025 pm 03:24 PM
The char array stores character sequences in C language and is declared as char array_name[size]. The access element is passed through the subscript operator, and the element ends with the null terminator '\0', which represents the end point of the string. The C language provides a variety of string manipulation functions, such as strlen(), strcpy(), strcat() and strcmp().
 .NET Deep Dive: Mastering Asynchronous Programming, LINQ, and EF Core
Mar 31, 2025 pm 04:07 PM
.NET Deep Dive: Mastering Asynchronous Programming, LINQ, and EF Core
Mar 31, 2025 pm 04:07 PM
The core concepts of .NET asynchronous programming, LINQ and EFCore are: 1. Asynchronous programming improves application responsiveness through async and await; 2. LINQ simplifies data query through unified syntax; 3. EFCore simplifies database operations through ORM.
 How to use various symbols in C language
Apr 03, 2025 pm 04:48 PM
How to use various symbols in C language
Apr 03, 2025 pm 04:48 PM
The usage methods of symbols in C language cover arithmetic, assignment, conditions, logic, bit operators, etc. Arithmetic operators are used for basic mathematical operations, assignment operators are used for assignment and addition, subtraction, multiplication and division assignment, condition operators are used for different operations according to conditions, logical operators are used for logical operations, bit operators are used for bit-level operations, and special constants are used to represent null pointers, end-of-file markers, and non-numeric values.
 What is the role of char in C strings
Apr 03, 2025 pm 03:15 PM
What is the role of char in C strings
Apr 03, 2025 pm 03:15 PM
In C, the char type is used in strings: 1. Store a single character; 2. Use an array to represent a string and end with a null terminator; 3. Operate through a string operation function; 4. Read or output a string from the keyboard.
 Avoid errors caused by default in C switch statements
Apr 03, 2025 pm 03:45 PM
Avoid errors caused by default in C switch statements
Apr 03, 2025 pm 03:45 PM
A strategy to avoid errors caused by default in C switch statements: use enums instead of constants, limiting the value of the case statement to a valid member of the enum. Use fallthrough in the last case statement to let the program continue to execute the following code. For switch statements without fallthrough, always add a default statement for error handling or provide default behavior.
 What is the function of C language sum?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 02:21 PM
What is the function of C language sum?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 02:21 PM
There is no built-in sum function in C language, so it needs to be written by yourself. Sum can be achieved by traversing the array and accumulating elements: Loop version: Sum is calculated using for loop and array length. Pointer version: Use pointers to point to array elements, and efficient summing is achieved through self-increment pointers. Dynamically allocate array version: Dynamically allocate arrays and manage memory yourself, ensuring that allocated memory is freed to prevent memory leaks.
 How to handle special characters in C language
Apr 03, 2025 pm 03:18 PM
How to handle special characters in C language
Apr 03, 2025 pm 03:18 PM
In C language, special characters are processed through escape sequences, such as: \n represents line breaks. \t means tab character. Use escape sequences or character constants to represent special characters, such as char c = '\n'. Note that the backslash needs to be escaped twice. Different platforms and compilers may have different escape sequences, please consult the documentation.
 How to convert char in C language
Apr 03, 2025 pm 03:21 PM
How to convert char in C language
Apr 03, 2025 pm 03:21 PM
In C language, char type conversion can be directly converted to another type by: casting: using casting characters. Automatic type conversion: When one type of data can accommodate another type of value, the compiler automatically converts it.






