
This article mainly introduces the Position attribute of the element. This attribute can set the positioning method of the element on the page.
1. Introduction to position: Introducing the value and auxiliary attributes of position.
2. Position positioning method: Introducing the four positioning methods of position: absolute, relative, fixed, and default.
3. Summary position: Show position as an example.
Position attribute: Specifies the positioning type of the element. That is, the elements are separated from the layout of the document flow and displayed anywhere on the page.
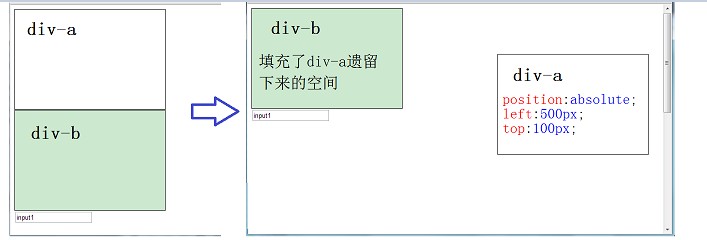
①Absolute: Absolute positioning; out of the layout of the document flow, the remaining space is filled by subsequent elements. The starting position of positioning is the nearest parent element (postion is not static), otherwise it is the Body document itself.
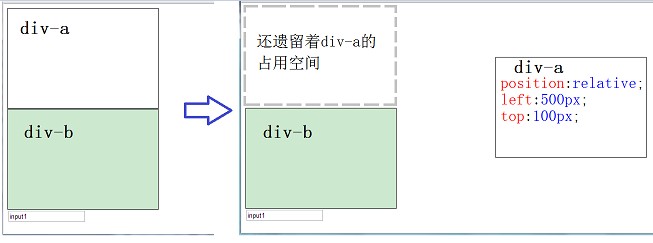
②relative: Relative positioning; does not break away from the layout of the document flow, only changes its own position, leaving a blank area in the original position of the document flow. The starting position of positioning is the original position of this element in the document flow.
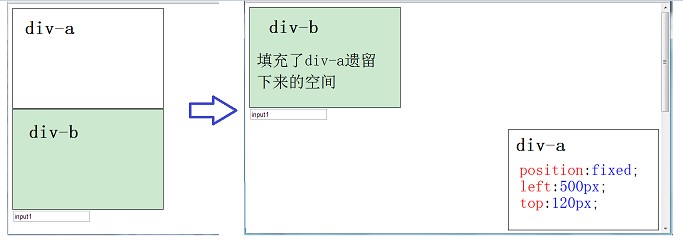
③fixed: Fixed positioning; similar to absolute, but does not change position as the scroll bar moves.
④static: Default value; default layout.
The position attribute only takes the element out of the document flow. If you want this element to be displayed in the desired position, you need to use the following attributes (position: static does not support these):
①left: Indicates how many pixels to insert to the left of the element and how many pixels to move the element to the right.
②right: Indicates how many pixels to insert to the right of the element and how many pixels to move the element to the left.
③top: Indicates how many pixels to insert above the element and how many pixels to move the element downward.
④bottom: Indicates how many pixels to insert below the element and how many pixels to move the element upward.
The value of the above attributes can be negative, unit: px.
Absolute positioning; out of the document flow Layout, the remaining space is filled by subsequent elements. The starting position of positioning is the nearest parent element (postion is not static), otherwise it is the Body document itself.
Relative positioning; does not break away from the layout of the document flow, only changes its own position, leaving a blank area in the original position of the document flow. The starting position of positioning is the original position of this element in the document flow.
Fixed positioning; similar to absolute, but does not change position as the scroll bar moves.
①Login box overlay: such as the login of dz forum.
②False QQ message advertisements.
Default positioning means that this element is the default positioning method.
Special processing of IE6.
When the element containing the position attribute is the edge element:
①Absolute and relative: For edge elements containing these two values, when the browser is zoomed out to the point where this element is invisible, a scroll bar will appear.
②fixed: For edge elements containing this value, when the browser is zoomed out to the point where this element is invisible, the scroll bar will not appear.

<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd"><html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml"><head>
<title>position</title>
<style type="text/css">
p {
height: 200px;
width: 300px;
border-color: Black;
border-style: solid;
border-width: 1px;
}
#a {
position:absolute;
left:900px;
top:150px;
}
#b {
position:relative;
left:500px;
top:100px;
}
#c {
position:fixed;
left:970px;
top:400px;
}
#d {
position:static;
background-color:Window;
}
</style></head><body> <p id="a" > p-a<br /> position:absolute;<br /> 绝对定位;脱离文档流,遗留空间由后续元素填充。
</p> <p id="b" > p-b<br /> position:relative;<br /> 相对定位;不脱离文档流,只改变自身的位置,在文档流原先的位置遗留空白区域。
</p> <p id="c" > p-c<br /> position:fixed;<br /> 固定定位;固定在页面中,不随浏览器的大小改变而改变位置。
</p> <p id="d"></p> <input type="text" value="input1" /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /></body></html>



