ASP.NET Forms authentication
In the asp.net program, users can access corresponding pages and functions based on their roles. This article will introduce this, which has a very good reference value. Let’s take a look at it with the editor
asp.net program development. Users access corresponding pages and functions according to their roles.
The project structure is as follows:
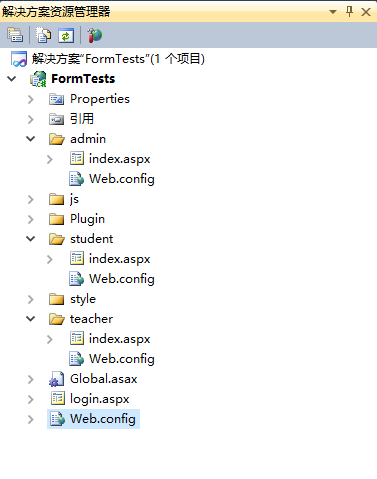
##Root directory Web.config code:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<!--
有关如何配置 ASP.NET 应用程序的详细消息,请访问
http://www.php.cn/
-->
<configuration>
<system.web>
<compilation debug="true" targetFramework="4.0" />
<authentication mode="Forms">
<forms loginUrl="login.aspx"></forms>
</authentication>
<!--<authorization>
<allow users="*"></allow>
</authorization>-->
</system.web>
</configuration>Web.config code in the admin folder:
<?xml version="1.0"?> <configuration> <system.web> <authorization> <allow roles="admin" /> <deny users="*"/> </authorization> </system.web> </configuration>
Web.config code in the teacher folder:
<?xml version="1.0"?> <configuration> <system.web> <authorization> <allow roles="teacher" /> <deny users="*"/> </authorization> </system.web> </configuration>
Web.config code in student folder:
<?xml version="1.0"?> <configuration> <system.web> <authorization> <allow roles="student" /> <deny users="*"/> </authorization> </system.web> </configuration>
Login Set Cookie after successful login in .aspx, set Cookie code:
protected void SetLoginCookie(string username, string roles)
{
System.Web.Security.FormsAuthentication.SetAuthCookie(username, false);
System.Web.Security.FormsAuthenticationTicket ticket = new FormsAuthenticationTicket(1, username, DateTime.Now, DateTime.Now.AddDays(1), false, roles, "/");
string hashTicket = FormsAuthentication.Encrypt(ticket);
HttpCookie userCookie = new HttpCookie(FormsAuthentication.FormsCookieName, hashTicket);
HttpContext.Current.Response.SetCookie(userCookie);
}Global.asax for identity Verification:
protected void Application_AuthenticateRequest(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
HttpApplication app = (HttpApplication)sender;
HttpContext ctx = app.Context; //获取本次Http请求的HttpContext对象
if (ctx.User != null)
{
if (ctx.Request.IsAuthenticated == true) //验证过的一般用户才能进行角色验证
{
System.Web.Security.FormsIdentity fi = (System.Web.Security.FormsIdentity)ctx.User.Identity;
System.Web.Security.FormsAuthenticationTicket ticket = fi.Ticket; //取得身份验证票
string userData = ticket.UserData;//从UserData中恢复role信息
string[] roles = userData.Split(','); //将角色数据转成字符串数组,得到相关的角色信息
ctx.User = new System.Security.Principal.GenericPrincipal(fi, roles); //这样当前用户就拥有角色信息了
}
}
}
Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1664
1664
 14
14
 1423
1423
 52
52
 1317
1317
 25
25
 1268
1268
 29
29
 1243
1243
 24
24
 Testing C# .NET Applications: Unit, Integration, and End-to-End Testing
Apr 09, 2025 am 12:04 AM
Testing C# .NET Applications: Unit, Integration, and End-to-End Testing
Apr 09, 2025 am 12:04 AM
Testing strategies for C#.NET applications include unit testing, integration testing, and end-to-end testing. 1. Unit testing ensures that the minimum unit of the code works independently, using the MSTest, NUnit or xUnit framework. 2. Integrated tests verify the functions of multiple units combined, commonly used simulated data and external services. 3. End-to-end testing simulates the user's complete operation process, and Selenium is usually used for automated testing.
 C# .NET: Exploring Core Concepts and Programming Fundamentals
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:32 AM
C# .NET: Exploring Core Concepts and Programming Fundamentals
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:32 AM
C# is a modern, object-oriented programming language developed by Microsoft and as part of the .NET framework. 1.C# supports object-oriented programming (OOP), including encapsulation, inheritance and polymorphism. 2. Asynchronous programming in C# is implemented through async and await keywords to improve application responsiveness. 3. Use LINQ to process data collections concisely. 4. Common errors include null reference exceptions and index out-of-range exceptions. Debugging skills include using a debugger and exception handling. 5. Performance optimization includes using StringBuilder and avoiding unnecessary packing and unboxing.
 The Continued Relevance of C# .NET: A Look at Current Usage
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:07 AM
The Continued Relevance of C# .NET: A Look at Current Usage
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:07 AM
C#.NET is still important because it provides powerful tools and libraries that support multiple application development. 1) C# combines .NET framework to make development efficient and convenient. 2) C#'s type safety and garbage collection mechanism enhance its advantages. 3) .NET provides a cross-platform running environment and rich APIs, improving development flexibility.
 From Web to Desktop: The Versatility of C# .NET
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:07 AM
From Web to Desktop: The Versatility of C# .NET
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:07 AM
C#.NETisversatileforbothwebanddesktopdevelopment.1)Forweb,useASP.NETfordynamicapplications.2)Fordesktop,employWindowsFormsorWPFforrichinterfaces.3)UseXamarinforcross-platformdevelopment,enablingcodesharingacrossWindows,macOS,Linux,andmobiledevices.
 C# as a Versatile .NET Language: Applications and Examples
Apr 26, 2025 am 12:26 AM
C# as a Versatile .NET Language: Applications and Examples
Apr 26, 2025 am 12:26 AM
C# is widely used in enterprise-level applications, game development, mobile applications and web development. 1) In enterprise-level applications, C# is often used for ASP.NETCore to develop WebAPI. 2) In game development, C# is combined with the Unity engine to realize role control and other functions. 3) C# supports polymorphism and asynchronous programming to improve code flexibility and application performance.
 Is C# .NET Right for You? Evaluating its Applicability
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:03 AM
Is C# .NET Right for You? Evaluating its Applicability
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:03 AM
C#.NETissuitableforenterprise-levelapplicationswithintheMicrosoftecosystemduetoitsstrongtyping,richlibraries,androbustperformance.However,itmaynotbeidealforcross-platformdevelopmentorwhenrawspeediscritical,wherelanguageslikeRustorGomightbepreferable.
 C# Code within .NET: Exploring the Programming Process
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:02 AM
C# Code within .NET: Exploring the Programming Process
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:02 AM
The programming process of C# in .NET includes the following steps: 1) writing C# code, 2) compiling into an intermediate language (IL), and 3) executing by the .NET runtime (CLR). The advantages of C# in .NET are its modern syntax, powerful type system and tight integration with the .NET framework, suitable for various development scenarios from desktop applications to web services.
 C# .NET and the Future: Adapting to New Technologies
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:06 AM
C# .NET and the Future: Adapting to New Technologies
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:06 AM
C# and .NET adapt to the needs of emerging technologies through continuous updates and optimizations. 1) C# 9.0 and .NET5 introduce record type and performance optimization. 2) .NETCore enhances cloud native and containerized support. 3) ASP.NETCore integrates with modern web technologies. 4) ML.NET supports machine learning and artificial intelligence. 5) Asynchronous programming and best practices improve performance.




