 WeChat Applet
WeChat Applet
 Mini Program Development
Mini Program Development
 WeChat Mini Program Framework Detailed Explanation and Example Applications
WeChat Mini Program Framework Detailed Explanation and Example Applications
WeChat Mini Program Framework Detailed Explanation and Example Applications
Quickly understand the use of WeChat mini programs, a todos app developed based on the mini program framework
WeChat official has opened the official documentation and developer tools of WeChat mini programs. In the past two days, I have been reading relevant news to understand how to develop small programs. After the official documents came out in the past two days, I quickly glanced at them and focused on the two parts of the document: framework and components, and then based on Simple tutorial to make a regular todo app. This app is based on the WeChat applet platform and implements the regular functions of the todo app. At the same time, in order to make it closer to the actual work scenario, it also uses the loading and toast components to complete the interaction and feedback of some operations. My intuitive feeling about this platform is that, at a technical level, it is similar to Vue, but it is far less powerful than Vue; the development ideas are not like Vue, but more like backbone. Therefore, people who have used mvc, mvvm frameworks such as backbone and vue will find it easy to get started with this platform. This article mainly introduces some key points of the implementation of this todo app.
First add the information related to this article:
Official documentation: https://mp.weixin.qq.com/debug/wxadoc/dev/index.html
Official developer tool download: https://mp.weixin.qq.com/debug/wxadoc/dev/devtools/download.html
Function demonstration of todo app in this article:

Note: You need to long press the todo text to edit it directly. Because it is on the mobile phone, you cannot use the double-click event for editing, and changed it to the long-press event. The mini program platform also does not provide binding for double-click events.
Related source code: https://github.com/liuyunzhuge/blog/tree/master/todos/wx
If you want to run this project locally, you need to install the developer tools first. According to the description of the simple tutorial in the document, first build a project;
After the construction is completed, the developer tool will open the project;
Then find the folder of the built project on the disk, and copy the Delete all the content and paste all the files in the source code folder above;
Then reopen the developer tools, first enter the edit tab, and then click the compile button, you will directly enter the debugging interface to view the app's Function:
Let’s introduce the key points of this app development:
1. The directory structure and configuration of this app will not be introduced in detail. There are very detailed descriptions in the Document-Framework section. There is no html and css in this platform, replaced by wxml and wxss. There is almost no difference between wxss and css. The disadvantage is that it is not as powerful as css and supports limited selectors. But the advantage is that since there is only one platform, WeChat, there are almost no compatibility issues and you can use standard and updated CSS technology. Only the tags of those components provided by the platform can be used in wxml. HTML tags cannot be used directly. Examples of how to use each component in wxml can be found in the Document - Components section. So in fact, there is no problem in writing wxml and wxss.
2. wxml supports the following features:

In the todo app, except templates and references, all others are used, but The details of each feature are not used, only the appropriate functions are selected according to the needs of the app. I saw an article a few days ago saying that the WeChat applet may be implemented based on the vue framework, so I took a look at the vue documentation. For data binding, conditional rendering, list rendering, and events, we have looked at the usage of vue in detail. In comparison, the features provided by wxml are quite similar to the related features of vue, but there are not so many functions, so it is not easy to directly use the features of the vue framework into small programs. The best practice is still based on the instructions provided in the official documents. If the functions are not mentioned in the official documents, it will definitely not work if you use them by guessing. I checked the prototypes of some objects by printing, and I did not find more instance methods than in the official documents, which shows that the framework function of the mini program is indeed limited.
3. Wxss can actually be written in less or sass, as long as the selector meets the requirements of the framework. Due to time constraints, I didn’t try it in this app.
4. There is no two-way binding. In Vue, a Vue instance is a view-model; updates to data in the view layer will be fed back to the model in real time; updates to the model will also be fed back to the view in real time. In the mini program, there is no two-way binding, and the update of the view will not be directly synchronized to the model; you need to get the data directly from the view layer in the relevant event callback, and then update the model through setData. The mini program will use setData inside the mini program. Then re-render the page. For example, for a single todo item, the toggle operation is:
toggleTodo: function( e ) {
var id = this.getTodoId( e, 'todo-item-chk-' );
var value = e.detail.value[ 0 ];
var complete = !!value;
var todo = this.getTodo( id );
todo.complete = complete;
this.updateData( true );
this.updateStorage();
},In the above code, the value of the checkbox in a single todo item is obtained through e.detail.value[0] , use this value to determine the complete status of todo. Finally, inside updateData, the content of the model will be refreshed through the setData method. Only in this way will the statistics at the bottom of the app be updated after the toggle operation.
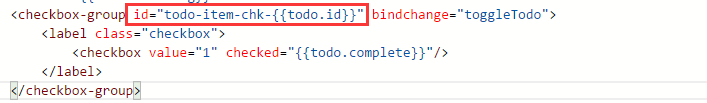
5. When event binding, parameters cannot be passed, only one event can be passed. For example, in the toggle operation above, I actually wanted to pass the current todo's ID to the callback, but I couldn't do it in every possible way. In the end, I could only handle it through the ID method: binding it in wxml. On the component of the event, add an id. This id cannot be repeated in the entire page, so the id must be prefixed, and then add the todo id value at the end of the id; when the event is triggered, it can be obtained through e.currentTarget.id For the component's id, remove the corresponding id prefix to get the todo's id value. This is a method currently used. I think it is not very elegant. I hope to find a better way to implement it later.
#6. The loading effect is taken into consideration in the app and must be achieved by using the loading attribute of the button component. But loading is just a style control, it does not control whether the button can be clicked repeatedly. Therefore, we must also use the disabled attribute of button to prevent repeated clicks.
The remaining implementation details are in the source code of the following two files. You are welcome to point out the problems.
Source code of index.wxml:
<!--list.wxml-->
<view class="container">
<view class="app-hd">
<view class="fx1">
<input class="new-todo-input" value="{{newTodoText}}" auto-focus bindinput="newTodoTextInput"/>
</view>
<button type="primary" size="mini" bindtap="addOne" loading="{{addOneLoading}}" disabled="{{addOneLoading}}">
+ Add
</button>
</view>
<view class="todos-list" >
<view class="todo-item {{index == 0 ? '' : 'todo-item-not-first'}} {{todo.complete ? 'todo-item-complete' : ''}}" wx:for="{{todos}}" wx:for-item="todo">
<view wx-if="{{!todo.editing}}">
<checkbox-group id="todo-item-chk-{{todo.id}}" bindchange="toggleTodo">
<label class="checkbox">
<checkbox value="1" checked="{{todo.complete}}"/>
</label>
</checkbox-group>
</view>
<view id="todo-item-txt-{{todo.id}}" class="todo-text" wx-if="{{!todo.editing}}" bindlongtap="startEdit">
<text>{{todo.text}}</text>
</view>
<view wx-if="{{!todo.editing}}">
<button id="btn-del-item-{{todo.id}}" bindtap="clearSingle" type="warn" size="mini" loading="{{todo.loading}}" disabled="{{todo.loading}}">
Clear
</button>
</view>
<input id="todo-item-edit-{{todo.id}}" class="todo-text-input" value="{{todo.text}}" auto-focus bindblur="endEditTodo" wx-if="{{todo.editing}}"/>
</view>
</view>
<view class="app-ft" wx:if="{{todos.length > 0}}">
<view class="fx1">
<checkbox-group bindchange="toggleAll">
<label class="checkbox">
<checkbox value="1" checked="{{todosOfUncomplted.length == 0}}"/>
</label>
</checkbox-group>
<text>{{todosOfUncomplted.length}} left.</text>
</view>
<view wx:if="{{todosOfComplted.length > 0}}">
<button type="warn" size="mini" bindtap="clearAll" loading="{{clearAllLoading}}" disabled="{{clearAllLoading}}">
Clear {{todosOfComplted.length}} of done.
</button>
</view>
</view>
<loading hidden="{{loadingHidden}}" bindchange="loadingChange">
{{loadingText}}
</loading>
<toast hidden="{{toastHidden}}" bindchange="toastChange">
{{toastText}}
</toast>
</view>Source code of index.js:
var app = getApp();
Page( {
data: {
todos: [],
todosOfUncomplted: [],
todosOfComplted: [],
newTodoText: '',
addOneLoading: false,
loadingHidden: true,
loadingText: '',
toastHidden: true,
toastText: '',
clearAllLoading: false
},
updateData: function( resetTodos ) {
var data = {};
if( resetTodos ) {
data.todos = this.data.todos;
}
data.todosOfUncomplted = this.data.todos.filter( function( t ) {
return !t.complete;
});
data.todosOfComplted = this.data.todos.filter( function( t ) {
return t.complete;
});
this.setData( data );
},
updateStorage: function() {
var storage = [];
this.data.todos.forEach( function( t ) {
storage.push( {
id: t.id,
text: t.text,
complete: t.complete
})
});
wx.setStorageSync( 'todos', storage );
},
onLoad: function() {
this.setData( {
todos: wx.getStorageSync( 'todos' ) || []
});
this.updateData( false );
},
getTodo: function( id ) {
return this.data.todos.filter( function( t ) {
return id == t.id;
})[ 0 ];
},
getTodoId: function( e, prefix ) {
return e.currentTarget.id.substring( prefix.length );
},
toggleTodo: function( e ) {
var id = this.getTodoId( e, 'todo-item-chk-' );
var value = e.detail.value[ 0 ];
var complete = !!value;
var todo = this.getTodo( id );
todo.complete = complete;
this.updateData( true );
this.updateStorage();
},
toggleAll: function( e ) {
var value = e.detail.value[ 0 ];
var complete = !!value;
this.data.todos.forEach( function( t ) {
t.complete = complete;
});
this.updateData( true );
this.updateStorage();
},
clearTodo: function( id ) {
var targetIndex;
this.data.todos.forEach( function( t, i ) {
if( targetIndex !== undefined ) return;
if( t.id == id ) {
targetIndex = i;
}
});
this.data.todos.splice( targetIndex, 1 );
},
clearSingle: function( e ) {
var id = this.getTodoId( e, 'btn-del-item-' );
var todo = this.getTodo( id );
todo.loading = true;
this.updateData( true );
var that = this;
setTimeout( function() {
that.clearTodo( id );
that.updateData( true );
that.updateStorage();
}, 500 );
},
clearAll: function() {
this.setData( {
clearAllLoading: true
});
var that = this;
setTimeout( function() {
that.data.todosOfComplted.forEach( function( t ) {
that.clearTodo( t.id );
});
that.setData( {
clearAllLoading: false
});
that.updateData( true );
that.updateStorage();
that.setData( {
toastHidden: false,
toastText: 'Success'
});
}, 500 );
},
startEdit: function( e ) {
var id = this.getTodoId( e, 'todo-item-txt-' );
var todo = this.getTodo( id );
todo.editing = true;
this.updateData( true );
this.updateStorage();
},
newTodoTextInput: function( e ) {
this.setData( {
newTodoText: e.detail.value
});
},
endEditTodo: function( e ) {
var id = this.getTodoId( e, 'todo-item-edit-' );
var todo = this.getTodo( id );
todo.editing = false;
todo.text = e.detail.value;
this.updateData( true );
this.updateStorage();
},
addOne: function( e ) {
if( !this.data.newTodoText ) return;
this.setData( {
addOneLoading: true
});
//open loading
this.setData( {
loadingHidden: false,
loadingText: 'Waiting...'
});
var that = this;
setTimeout( function() {
//close loading and toggle button loading status
that.setData( {
loadingHidden: true,
addOneLoading: false,
loadingText: ''
});
that.data.todos.push( {
id: app.getId(),
text: that.data.newTodoText,
compelte: false
});
that.setData( {
newTodoText: ''
});
that.updateData( true );
that.updateStorage();
}, 500 );
},
loadingChange: function() {
this.setData( {
loadingHidden: true,
loadingText: ''
});
},
toastChange: function() {
this.setData( {
toastHidden: true,
toastText: ''
});
}
});Finally, I need to add that this app was developed based on WeChat’s official documents within a limited time, so I don’t know whether the implementation method here is reasonable. I only use this app to understand the usage of the mini program platform. I hope WeChat officials can launch some more comprehensive, preferably project-based demos to provide us developers with a best practice specification at the code level. Friends who have other development ideas are welcome to help me point out the problems in my above implementation.
Through this article, I hope everyone will understand the framework of WeChat mini programs. Thank you for your support of this site!
For more articles related to WeChat applet framework details and example applications, please pay attention to the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 How to evaluate the cost-effectiveness of commercial support for Java frameworks
Jun 05, 2024 pm 05:25 PM
How to evaluate the cost-effectiveness of commercial support for Java frameworks
Jun 05, 2024 pm 05:25 PM
Evaluating the cost/performance of commercial support for a Java framework involves the following steps: Determine the required level of assurance and service level agreement (SLA) guarantees. The experience and expertise of the research support team. Consider additional services such as upgrades, troubleshooting, and performance optimization. Weigh business support costs against risk mitigation and increased efficiency.
 How does the learning curve of PHP frameworks compare to other language frameworks?
Jun 06, 2024 pm 12:41 PM
How does the learning curve of PHP frameworks compare to other language frameworks?
Jun 06, 2024 pm 12:41 PM
The learning curve of a PHP framework depends on language proficiency, framework complexity, documentation quality, and community support. The learning curve of PHP frameworks is higher when compared to Python frameworks and lower when compared to Ruby frameworks. Compared to Java frameworks, PHP frameworks have a moderate learning curve but a shorter time to get started.
 How do the lightweight options of PHP frameworks affect application performance?
Jun 06, 2024 am 10:53 AM
How do the lightweight options of PHP frameworks affect application performance?
Jun 06, 2024 am 10:53 AM
The lightweight PHP framework improves application performance through small size and low resource consumption. Its features include: small size, fast startup, low memory usage, improved response speed and throughput, and reduced resource consumption. Practical case: SlimFramework creates REST API, only 500KB, high responsiveness and high throughput
 Performance comparison of Java frameworks
Jun 04, 2024 pm 03:56 PM
Performance comparison of Java frameworks
Jun 04, 2024 pm 03:56 PM
According to benchmarks, for small, high-performance applications, Quarkus (fast startup, low memory) or Micronaut (TechEmpower excellent) are ideal choices. SpringBoot is suitable for large, full-stack applications, but has slightly slower startup times and memory usage.
 Golang framework documentation best practices
Jun 04, 2024 pm 05:00 PM
Golang framework documentation best practices
Jun 04, 2024 pm 05:00 PM
Writing clear and comprehensive documentation is crucial for the Golang framework. Best practices include following an established documentation style, such as Google's Go Coding Style Guide. Use a clear organizational structure, including headings, subheadings, and lists, and provide navigation. Provides comprehensive and accurate information, including getting started guides, API references, and concepts. Use code examples to illustrate concepts and usage. Keep documentation updated, track changes and document new features. Provide support and community resources such as GitHub issues and forums. Create practical examples, such as API documentation.
 How to choose the best golang framework for different application scenarios
Jun 05, 2024 pm 04:05 PM
How to choose the best golang framework for different application scenarios
Jun 05, 2024 pm 04:05 PM
Choose the best Go framework based on application scenarios: consider application type, language features, performance requirements, and ecosystem. Common Go frameworks: Gin (Web application), Echo (Web service), Fiber (high throughput), gorm (ORM), fasthttp (speed). Practical case: building REST API (Fiber) and interacting with the database (gorm). Choose a framework: choose fasthttp for key performance, Gin/Echo for flexible web applications, and gorm for database interaction.
 Detailed practical explanation of golang framework development: Questions and Answers
Jun 06, 2024 am 10:57 AM
Detailed practical explanation of golang framework development: Questions and Answers
Jun 06, 2024 am 10:57 AM
In Go framework development, common challenges and their solutions are: Error handling: Use the errors package for management, and use middleware to centrally handle errors. Authentication and authorization: Integrate third-party libraries and create custom middleware to check credentials. Concurrency processing: Use goroutines, mutexes, and channels to control resource access. Unit testing: Use gotest packages, mocks, and stubs for isolation, and code coverage tools to ensure sufficiency. Deployment and monitoring: Use Docker containers to package deployments, set up data backups, and track performance and errors with logging and monitoring tools.
 What are the common misunderstandings in the learning process of Golang framework?
Jun 05, 2024 pm 09:59 PM
What are the common misunderstandings in the learning process of Golang framework?
Jun 05, 2024 pm 09:59 PM
There are five misunderstandings in Go framework learning: over-reliance on the framework and limited flexibility. If you don’t follow the framework conventions, the code will be difficult to maintain. Using outdated libraries can cause security and compatibility issues. Excessive use of packages obfuscates code structure. Ignoring error handling leads to unexpected behavior and crashes.



