Python automated operation and maintenance course learning
This article is a summary of the learning content on the first day of the Old Boy Python automated operation and maintenance course.
The general content is as follows:
Introduction to Python
The first Python program: Hello World
Python variables
User interaction (user Input, output)
Process control: conditional statements (if/elif/else), loop statements (for/while/break/continue)
1. Introduction to Python language:
1. Python is a high-level programming language with interpreted language, dynamic type, and strong type definition language. Developed by Guido van Rossum during the Christmas period of 1989, the first official version of the Python compiler was born in 1991. It has become one of the mainstream programming languages.
2. Mainly used in cloud computing, WEB development, scientific research and data analysis, artificial intelligence, finance, system operation and maintenance, graphical GUI, etc.
3. Advantages and disadvantages of Python:
Advantages: simple, clear, elegant; high development efficiency; strong portability; scalability; embeddability.
Disadvantages: Slower execution than C language/JAVA (the PyPy interpreter sometimes executes faster than C); code cannot be encrypted (interpreted language); threads cannot take advantage of multi-CPU issues.
4. Python interpreter: There are many Python interpreters, such as CPython, IPython, PyPy, Jython, IronPython, etc., but the most widely used one is CPython.
2. Regarding the environment for running all Python codes in this article:
--Operating system: Ubuntu 16.10 (Linux 4.8.0)

--Python version: 3.5.2

--Python IDE: PyCharm 2016.3.2

三, The first program: Hello World
Use the vim/vi command to create a new Python File, the command is "HelloWorld.py", vim HelloWorld.py.
Enter the positive content in HelloWorld.py:
#!/usr/bin/python3.5
# 告诉Linux系统,要通过/usr/bin/python3.5解释器来执行正面的代码
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# Python2中必须添加这个一行,告诉Python解释器,要以UTF-8的编码形式执行正面的代码;Python3中默认UTF-8,可以不用添加本行。
# Author: Spencer Jiang
# 作者
print("Hello, World!")
# 打印Hello, World!Two operating modes:
1), give Grant executable permissions to HelloWorld.py, and then execute: chmod 755 HelloWorld.py
> chmod 755 HelloWorld.py > ./HelloWorld.py

2), directly through Python Execution: python installation path
> /usr/bin/python3.5 HelloWorld.py

3. Python variables
1 , Rules for variable definition:
The variable name can only be any combination of letters, numbers or underscores
Variable The first character of the name cannot be a number
The following keywords cannot be declared as variable names
['and', 'as', 'assert', 'break', ' class', 'continue', 'def', 'del', 'elif', 'else', 'except', 'exec', 'finally', 'for', 'from', 'global', 'if' , 'import', 'in', 'is', 'lambda', 'not', 'or', 'pass', 'print', 'raise', 'return', 'try', 'while', ' with', 'yield']- ## Examples of identifier names are i , __my_name, name_23 and a1b2_c3.
- Examples of identifier names are 2things, this is spaced out and my-name.
a, b = 3, "jmw" print(a, b) print(type(b), type(a)) ######### 下面为输出结果: 3 jmw <class> <class></class></class>
input()函数能接收从用户输入的任务字符,并以字符串类型返回用户输入的字符。
示例1(UserInput.py): name = input("Please input your name: ")
age = int(input("Please input you age: ")) # 将用户输入的字符转换成int类型,再赋值给变量 age。
#!/usr/bin/python3.5
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# Author: Spencer Jiang
name = input("Please input your name: ")
age = int(input("Please input you age: "))
print("Your Name: %s, Your Age: %d" % (name, age)) 
示例2: 用户名、密码的输入,通过getpass模块,将密码隐藏显示。(HidePassword.py)
#!/usr/bin/python3.5
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# Author: Spencer Jiang
import getpass
username = input("Please input your username: ")
password = getpass.getpass("Please input your password: ")
print(username, password) 
格式化输出:
1)、print()函数中添加%号来格式化输出。
输出字符串:%s ,输出数值 %d, 输出浮点数%f等, 示例:
#!/usr/bin/python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# Function : The format output
# Date : 2017-02-10
# Author : Spencer Jiang
username = "Spencer Jiang"
age = 45
salary = 231.32
print("Your name is : %s " % username)
print("Your age is : %d " % age)
print("Your salary is : %f " % salary)
print("Your salary2f is : %.2f " % salary)
# 保留2位小数 
2)、 通过format()函数进行格式化输出。
#!/usr/bin/python # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- # Function : The format output # Date : 2017-02-10 # Author : Spencer Jiang username = "Spencer Jiang" age = 45 job = "IT Service" salary = 231.32 info = ''' Name: [_username] Age: [_age] Job: [_job] Salary: [_salary] '''.format(_username = username, _age = age, _job = job, _salary = salary) print(info)

五、流程控制:条件判断语句(if/elif/else):
每个条件后面都以冒号结束,换行(条件为真时要执行的代码,以缩进作为代码块标志,python官方建议缩进4个空格)
示例1:猜年龄(数字)游戏(GuessAge.py)。
#!/usr/bin/python3.5
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# Author: Spencer Jiang
age_of_spencer = 65
#先设定的年龄的数值
guess_age = int(input("guess an age: "))
if guess_age == age_of_spencer :
print("Yes, You got it!")
elif guess_age > age_of_spencer :
print("No, your number is a litter bigger")
else:
print("No, your number is a litter smaller") 
六、流程控制:for循环(for x in range(10))、break、continue:
当满足循环条件时,执行循环语句块的代码,当不满足循环条件时,循环语句就结束。
for/while 循环外也可以跟一个else。
break: 当执行break时,就结束整个循环;
continue: 当执行continue,就结束本次循环,直接进行下次循环。
示例1:输出0到15中的2、4、6、8等4个数字(PrintNumber.py)。
#!/usr/bin/python3.5 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # Author: Spencer Jiang for i in range(0,15,2): if i == 0 : # 跳过 0 这个数字 continue if i > 9 : # 大于9 就退出循环 break else: print(i)

七、流程控制:while循环、break、continue(与for循环类似)
while 循环,需要有一个计数器,或者在循环语句块中有终止while条件的语句,否则会一直运行下去。
示例1(WhileLoop.py): 打印0~9数字
#!/usr/bin/python3.5 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # Author: Spencer Jiang count = 0 # 计数器 while True : print(count) count = count + 1 if count > 9 : break

示例2(GuessAgeWhile.py):猜年龄(数字): 只能猜3次机会。
#!/usr/bin/python3.5
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# Author: Spencer Jiang
age_of_spencer = 65
count = 0
while count age_of_spencer :
print("No, your number is a litter bigger")
else:
print("No, your number is a litter smaller")
count += 1
else:
print("You guess to much times!!!") 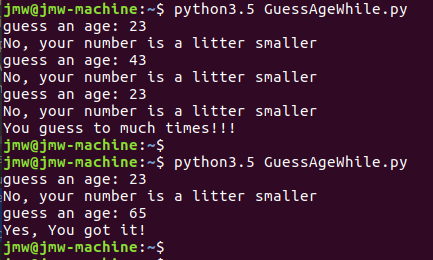
示例2,每猜3次不正确后,弹出提示,看用户是否还要继续猜下去。如果用户输入的是“n"就表示停止。
#!/usr/bin/python3.5
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# Author: Spencer Jiang
age_of_spencer = 65
count = 0
while count age_of_spencer :
print("No, your number is a litter bigger")
else:
print("No, your number is a litter smaller")
count += 1 if count == 3 :
continue_confirm = input("Do you want to continue to guess?")
if continue_confirm != 'n' :
count = 0else:
print("You guess to much times!!!") 
八、 Python代码注释:
# 单行注释用 井号“#” 开头
''' 或者 """ 多行注释采用3对单引号或3对双引号将要注释的行包围进来。
同时3对引号,也可以表示对字符串的赋值(段落文字),如:
info = """ your information : name : jmw age : 32 """
九、作业:
1. Simulate user login interface: 1) The user enters the user name and password; 2) If the login is successful, a welcome message is displayed; 3) If the login fails more than 3 times, the account will be locked.
2. Three-level menu: The three-level regions of province, city and county are menus.
For more articles related to learning Python automated operation and maintenance courses, please pay attention to the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 How to run programs in terminal vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 06:42 PM
How to run programs in terminal vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 06:42 PM
In VS Code, you can run the program in the terminal through the following steps: Prepare the code and open the integrated terminal to ensure that the code directory is consistent with the terminal working directory. Select the run command according to the programming language (such as Python's python your_file_name.py) to check whether it runs successfully and resolve errors. Use the debugger to improve debugging efficiency.
 Can visual studio code be used in python
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
Can visual studio code be used in python
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
VS Code can be used to write Python and provides many features that make it an ideal tool for developing Python applications. It allows users to: install Python extensions to get functions such as code completion, syntax highlighting, and debugging. Use the debugger to track code step by step, find and fix errors. Integrate Git for version control. Use code formatting tools to maintain code consistency. Use the Linting tool to spot potential problems ahead of time.
 Is the vscode extension malicious?
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:57 PM
Is the vscode extension malicious?
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:57 PM
VS Code extensions pose malicious risks, such as hiding malicious code, exploiting vulnerabilities, and masturbating as legitimate extensions. Methods to identify malicious extensions include: checking publishers, reading comments, checking code, and installing with caution. Security measures also include: security awareness, good habits, regular updates and antivirus software.
 Can vs code run in Windows 8
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
Can vs code run in Windows 8
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
VS Code can run on Windows 8, but the experience may not be great. First make sure the system has been updated to the latest patch, then download the VS Code installation package that matches the system architecture and install it as prompted. After installation, be aware that some extensions may be incompatible with Windows 8 and need to look for alternative extensions or use newer Windows systems in a virtual machine. Install the necessary extensions to check whether they work properly. Although VS Code is feasible on Windows 8, it is recommended to upgrade to a newer Windows system for a better development experience and security.
 Python: Automation, Scripting, and Task Management
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:14 AM
Python: Automation, Scripting, and Task Management
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:14 AM
Python excels in automation, scripting, and task management. 1) Automation: File backup is realized through standard libraries such as os and shutil. 2) Script writing: Use the psutil library to monitor system resources. 3) Task management: Use the schedule library to schedule tasks. Python's ease of use and rich library support makes it the preferred tool in these areas.
 What is vscode What is vscode for?
Apr 15, 2025 pm 06:45 PM
What is vscode What is vscode for?
Apr 15, 2025 pm 06:45 PM
VS Code is the full name Visual Studio Code, which is a free and open source cross-platform code editor and development environment developed by Microsoft. It supports a wide range of programming languages and provides syntax highlighting, code automatic completion, code snippets and smart prompts to improve development efficiency. Through a rich extension ecosystem, users can add extensions to specific needs and languages, such as debuggers, code formatting tools, and Git integrations. VS Code also includes an intuitive debugger that helps quickly find and resolve bugs in your code.
 Can visual studio code run python
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:00 PM
Can visual studio code run python
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:00 PM
VS Code not only can run Python, but also provides powerful functions, including: automatically identifying Python files after installing Python extensions, providing functions such as code completion, syntax highlighting, and debugging. Relying on the installed Python environment, extensions act as bridge connection editing and Python environment. The debugging functions include setting breakpoints, step-by-step debugging, viewing variable values, and improving debugging efficiency. The integrated terminal supports running complex commands such as unit testing and package management. Supports extended configuration and enhances features such as code formatting, analysis and version control.
 Can vs code run python
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:21 PM
Can vs code run python
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:21 PM
Yes, VS Code can run Python code. To run Python efficiently in VS Code, complete the following steps: Install the Python interpreter and configure environment variables. Install the Python extension in VS Code. Run Python code in VS Code's terminal via the command line. Use VS Code's debugging capabilities and code formatting to improve development efficiency. Adopt good programming habits and use performance analysis tools to optimize code performance.




