
Smptp class definition: smtplib.SMTP(host[,port[,local_hostname[,,timeout]]]), as the constructor of SMTP, its function is to establish a connection with the smtp server. After the connection is successful, you can send a request to the server Send related requests, such as login, verification, sending, exit, etc. The host parameter is the remote SMTP host address, such as stmp.163.com; port is the connection port, the default is 25; local_hostname is used to send HELO/EHLO instructions at the local FQDN (complete domain name), and timeout is the connection or attempt to connect in the majority seconds timeout, the SMTP class has the following methods:
SMTP.connect([host[,port]]) method, method to connect to the remote SMTP host, host is the remote host address, port is the remote host SMTP port, the default is 25 , or you can directly use the host:port format, for example: SMTP.connect("smtp.163.com","25').
SMTP.login(user,password) method, verification method of remote SMTP host , the parameters are user name and password, such as SMTP.login("18801457794@139.com",'123456').
SMTP.sendmail(from_addr,to_addrs,msg[,mail_options,rcpt_options]) method to implement the mail Send function, the parameters are sender, recipient, and email content, for example: SMTP.sendmail("python@163.com",'404408853@qq.com',body), where the body content is defined as follows:
"""From:python@163.com
To:404408853@qq.com
Subject:test mail
test mail body"""
SMTP.starttls([keyfile[,certfile] ]) method, enable TLS (secure transmission) mode, all SMTP instructions are encrypted transmission, for example, when using gmail's stmp server, you need to enable this to send emails normally
SMTP.quit() method, port smtp server connection
Let’s learn how python sends emails through examples
[root@localhost smtplib]# cat simple1.py
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import smtplib
import string
HOST = "smtp.139.com" #定义smtp主机
SUBJECT = "test" #定义邮件主题
TO = "404408853@qq.com" #定义邮件收件人
FROM = "18801457794@139.com" #定义邮件发件人
text = "python test mail" #邮件的内容
BODY=string.join(( #组装sendmail方法的邮件主体内容,各段以"\r\n"进行分隔
"From:%s" %FROM,
"To:%s" %TO,
"Subject:%s"%SUBJECT,
"",
text
),"\r\n")
server = smtplib.SMTP() #创建一个SMTP对象
server.connect(HOST,"25") #通过connect方法连接smtp主机
server.starttls() #启动安全传输模式
server.login("18801457794@139.com","123456") #邮件账户登录校验
server.sendmail(FROM,TO,BODY) #邮件发送
server.quit() #断开smtp连接Execute this code, we will receive an email
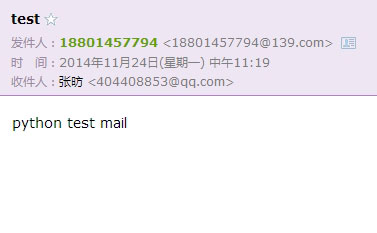
Implementing data report emails in HTML format
Plain text email content can no longer meet our diverse needs. This example introduces email.mime The MIMETex class is used to support emails in HTML format, supporting all HTML elements, including tables, pictures, animations, CSS styles, forms, etc. This example uses HTML tables to customize perfect business traffic reports. The implementation code is as follows:
#!/usr/bin/env python
#coding:utf-8
import smtplib
from email.mime.text import MIMEText #导入MIMEText类
HOST = "smtp.139.com"
SUBJECT = u"官网流量数据报表"
TO = "404408853@qq.com"
FROM = "18801457794@139.com"
msg = MIMEText("""
<table width="800" border="0" cellspacing="0" cellpadding="4">
<tr>
<td bgcolor="#CECFAD" height="20" style="font-size:14px">*官网数据<a href="monitor.domain.com">更多</a></td>
</tr>
<td bgcolor="#EFEBDE" height="100" style="font-size:13px">
1)日访问量:<font color=read>152433</font>访问次数:23651 页面浏览量:45123 点击数:545122 数据流量:504Mb<br>
2)状态码消息<br>
500:105 404;3264 503;214<br>
3)访客浏览器信息<br>
IE:50% firefox:10% chrome:30% other:10%<br>
4)页面信息<br>
/index.php 42153<br>
/view.php 21451<br>
</td>
</tr>
</table>""","html","utf-8")
msg['Subject'] = SUBJECT
msg['FROM'] = FROM
msg['To'] = TO
try:
server = smtplib.SMTP()
server.connect(HOST,'25')
server.starttls()
server.login('18801457794@139.com','123456')
server.sendmail(FROM,TO,msg.as_string())
server.quit()
print "邮件发送成功"
except Exception,e:
print "失败:" + str(e)The result of running the code is as shown in the figure,
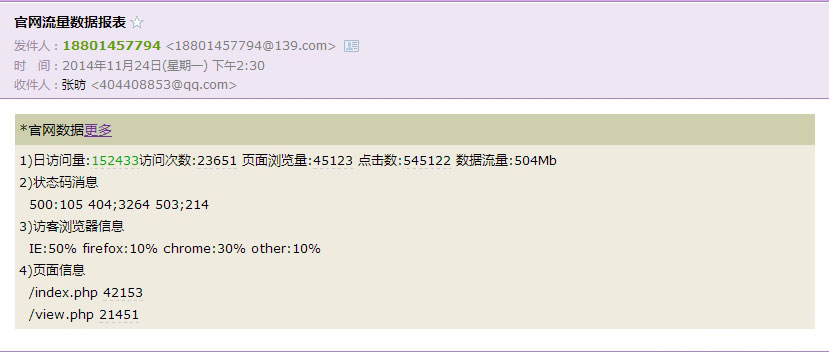
Example 2: Implementing server performance report email in graphic and text format
When requesting email content containing image data, you need to reference the MIMEImage class. If the email body consists of multiple MIME objects, you need to reference the MIMEMultipart class for encapsulation. This example uses the combination of MIMEText and MIMEImage classes to customize the server performance report email in graphic and text format. The implementation code is as follows
#!/usr/bin/env python
#coding: utf-8
import smtplib,string
from email.mime.multipart import MIMEMultipart
from email.mime.text import MIMEText
from email.mime.image import MIMEImage
HOST ="smtp.139.com" #定义smtp主机
SUBJECT = "金美美平台系统状态报表" #定义邮件主题
TO = "404408853@qq.com,302803690@qq.com" #定义邮件收件人
FROM = "18801457794@139.com" #定义邮件发件人
TO_list = TO.split(TO)
def addimg(src,imgid): #添加图片函数,参数1:图片路径,参数2:图片ID
fp = open(src,'rb') #打开文件
msgImage = MIMEImage(fp.read()) #创建MIMEImage对象,读取图片内容并作为参数
fp.close() #关闭文件
msgImage.add_header('Content-ID',imgid) #指定图片文件的Content-ID,<img alt="How to use the email module smtplib in Python" >标签src用到
return msgImage #返回msgImage对象
msg = MIMEMultipart('related') #创建MIMEMultipart对象,采用related定义内嵌资源的邮件体
msgtext = MIMEText("""
<table width="600" border="0" cellspacing="0" cellspacing="4">
<tr bgcolor="#CECFAD" height="20" style="font-size:14px">
<td colspan=2>以下是211.157.111.41系统状态图</td>
</tr>
<tr bgcolor="#EFEBDE" height="100" style="font-size:13px">
<td>
<img src="cid:io" alt="How to use the email module smtplib in Python" ></td><td>
<img src="cid:load" alt="How to use the email module smtplib in Python" ></td>
</tr>
<tr bgcolor="#EFEBDE" height="100" style="font-size:13px">
<td>
<img src="cid:mem" alt="How to use the email module smtplib in Python" ></td><td>
<img src="cid:disk" alt="How to use the email module smtplib in Python" ></td>
</tr>
</table>""","html","utf-8") #<img alt="How to use the email module smtplib in Python" >标签的src属性是通过Content-ID来引用的
msg.attach(msgtext) #MIMEMultipart对象附加MIMEText的内容
msg.attach(addimg("img/bytes_io.png","io")) #使用MIMEMultipart对象附加MIMEImage的内容
msg.attach(addimg("img/os_load.png","load"))
msg.attach(addimg("img/os_mem.png","mem"))
msg.attach(addimg("img/os_disk.png","disk"))
msg['Subject'] = SUBJECT
msg['FROM']=FROM
msg['To'] = TO
try:
server = smtplib.SMTP()
server.connect(HOST,"25")
server.starttls()
server.login('18801457794@139.com','123456')
server.sendmail(FROM,TO_list,msg.as_string())
server.quit()
print "邮件发送成功!"
except Exception,e:
print "失败:"+ str(e)The code running effect is as shown in the figure
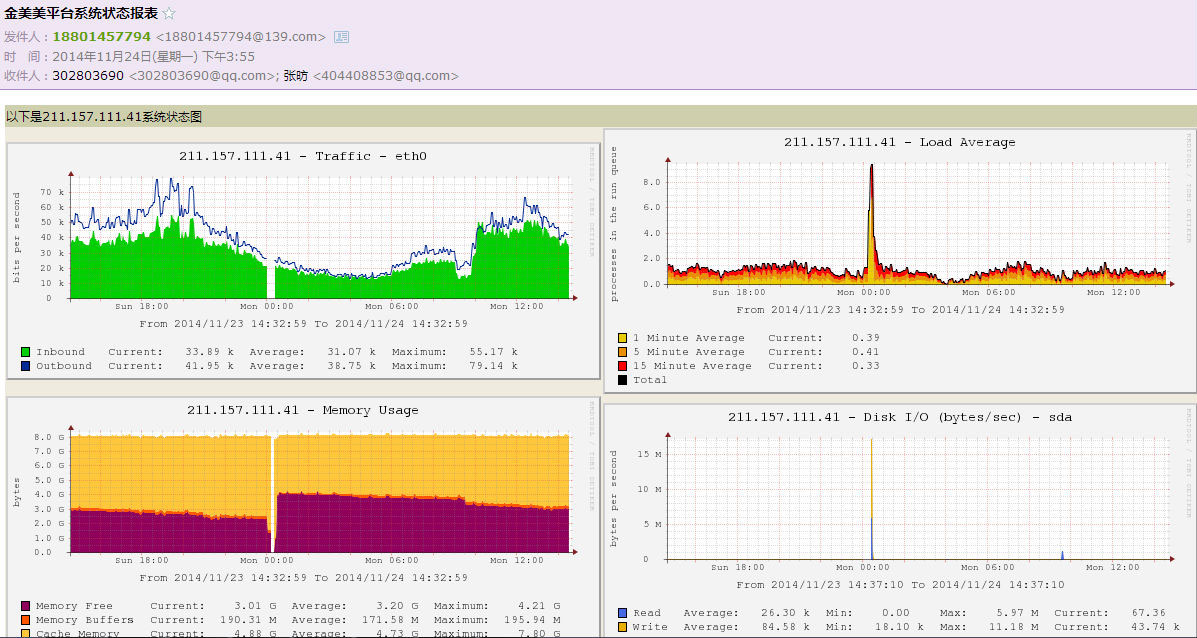
For more related articles on how to use the email module smtplib in python, please pay attention to the PHP Chinese website!




