

Determine the target: Determine which part of the data of which pages of which website to crawl. This example captures the title and introduction of the Baidu Encyclopedia Python entry page and the Python related entry page.
Analysis goal: analyze the format of the URL to be crawled and limit the crawling scope. Analyze the format of the data to be captured. In this example, we need to analyze the format of the tags where the two data, title and introduction, are located. Analyze the format of the page encoding to be crawled. In the web page parser section, you must specify the web page encoding before correct parsing can be performed.
Writing code: In the web page parser part, the results obtained by analyzing the target are used.
Execute crawler: perform data capture.
1. URL format
Enter the Baidu Encyclopedia python entry page. The links to related entries on the page are relatively uniform, mostly /view/xxx.htm . 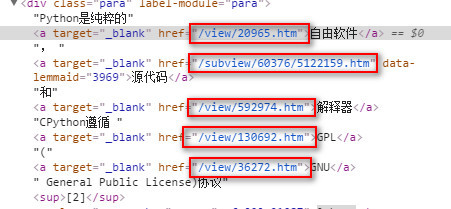
2. Data format
The title is located in the h1 sub-tag under the class lemmaWgt-lemmaTitle-title, and the introduction is located under the class lemma-summary. 

3. Encoding format
Check the page encoding format, which is utf-8. 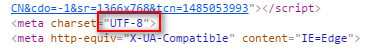
After the above analysis, the results are as follows: 
In sublime Next, create a new folder baike-spider as the project root directory.
Create new spider_main.py as the crawler scheduler.
Create a new url_manger.py as the url manager.
Create a new html_downloader.py as an html downloader.
Create new html_parser.py as the html parser.
Create a new html_outputer.py as a tool for writing data.
The final project structure is as follows: 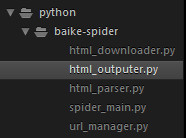
# coding:utf-8
import url_manager, html_downloader, html_parser, html_outputer
class SpiderMain(object):
def __init__(self):
self.urls = url_manager.UrlManager()
self.downloader = html_downloader.HtmlDownloader()
self.parser = html_parser.HtmlParser()
self.outputer = html_outputer.HtmlOutputer()
def craw(self, root_url):
count = 1
self.urls.add_new_url(root_url)
while self.urls.has_new_url():
try:
new_url = self.urls.get_new_url()
print('craw %d : %s' % (count, new_url))
html_cont = self.downloader.download(new_url)
new_urls, new_data = self.parser.parse(new_url, html_cont)
self.urls.add_new_urls(new_urls)
self.outputer.collect_data(new_data)
if count == 10:
break
count = count + 1
except:
print('craw failed')
self.outputer.output_html()
if __name__=='__main__':
root_url = 'http://baike.baidu.com/view/21087.htm'
obj_spider = SpiderMain()
obj_spider.craw(root_url)# coding:utf-8 class UrlManager(object): def __init__(self): self.new_urls = set() self.old_urls = set() def add_new_url(self, url): if url is None: return if url not in self.new_urls and url not in self.old_urls: self.new_urls.add(url) def add_new_urls(self, urls): if urls is None or len(urls) == 0: return for url in urls: self.add_new_url(url) def has_new_url(self): return len(self.new_urls) != 0 def get_new_url(self): new_url = self.new_urls.pop() self.old_urls.add(new_url) return new_url
# coding:utf-8 import urllib.request class HtmlDownloader(object): def download(self, url): if url is None: return None response = urllib.request.urlopen(url) if response.getcode() != 200: return None return response.read()
# coding:utf-8
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import re
from urllib.parse import urljoin
class HtmlParser(object):
def _get_new_urls(self, page_url, soup):
new_urls = set()
# /view/123.htm
links = soup.find_all('a', href=re.compile(r'/view/\d+\.htm'))
for link in links:
new_url = link['href']
new_full_url = urljoin(page_url, new_url)
# print(new_full_url)
new_urls.add(new_full_url)
#print(new_urls)
return new_urls
def _get_new_data(self, page_url, soup):
res_data = {}
# url
res_data['url'] = page_url
# <dd class="lemmaWgt-lemmaTitle-title"> <h1>Python</h1>
title_node = soup.find('dd', class_='lemmaWgt-lemmaTitle-title').find('h1')
res_data['title'] = title_node.get_text()
# <p class="lemma-summary" label-module="lemmaSummary">
summary_node = soup.find('p', class_='lemma-summary')
res_data['summary'] = summary_node.get_text()
# print(res_data)
return res_data
def parse(self, page_url, html_cont):
if page_url is None or html_cont is None:
return
soup = BeautifulSoup(html_cont, 'html.parser')
# print(soup.prettify())
new_urls = self._get_new_urls(page_url, soup)
new_data = self._get_new_data(page_url, soup)
# print('mark')
return new_urls, new_data# coding:utf-8
class HtmlOutputer(object):
def __init__(self):
self.datas = []
def collect_data(self, data):
if data is None:
return
self.datas.append(data)
def output_html(self):
fout = open('output.html','w', encoding='utf-8')
fout.write('<html>')
fout.write('<body>')
fout.write('<table>')
for data in self.datas:
fout.write('<tr>')
fout.write('<td>%s</td>' % data['url'])
fout.write('<td>%s</td>' % data['title'])
fout.write('<td>%s</td>' % data['summary'])
fout.write('</tr>')
fout.write('</table>')
fout.write('</body>')
fout.write('</html>')
fout.close()At the command line, execute python spider_main.py.
Problem description: UnicodeEncodeError: 'gbk' codec can't encode character 'xa0' in position ...
When writing a file using Python, or When writing network data streams to local files, you will encounter this problem in most cases. There are many similar articles on the Internet about how to solve this problem, but they are nothing more than encoding and decoding. Is this the real cause of this problem? no. Many times, we use decode and encode, and try various encodings, such as utf8, utf-8, gbk, gb2312, etc. We have tried all the encodings, but the error still occurs, which is frustrating.
When writing python scripts under windows, the coding problem is very serious. When writing network data streams to files, we will encounter several encodings:
1, #encoding='XXX'
The encoding here (that is, the content of the first line of the python file) refers to the python script The encoding of the file itself, doesn't matter. As long as the encoding of XXX and the file itself are the same, it will be fine.
For example, various encodings can be set in the "Format" menu of notepad++. In this case, you need to ensure that the encoding set in the menu is the same as encoding XXX. If they are different, an error will be reported.
2. Encoding of network data stream
For example, if you obtain a web page, then the encoding of the network data stream is the encoding of the web page. Need to use decode to decode into unicode encoding.
3. Encoding of the target file
Write the network data stream to the new file. The file writing code is as follows:
fout = open('output.html','w')
fout.write(str)Under windows, the default encoding of the new file is gbk, python The interpreter will use gbk encoding to parse our network data stream str. However, str is a decoded unicode encoding. This will cause the parsing to fail and the above problems will occur. The solution is to change the encoding of the target file:
fout = open('output.html','w', encoding='utf-8')

更多Python抓取百度百科数据 相关文章请关注PHP中文网!




