 Backend Development
Backend Development
 C#.Net Tutorial
C#.Net Tutorial
 Analyze the differences and connections between delegates, events, Func, Action, and Predicate in C# through IL
Analyze the differences and connections between delegates, events, Func, Action, and Predicate in C# through IL
Analyze the differences and connections between delegates, events, Func, Action, and Predicate in C# through IL
I have always been confused about events and delegation, and I am not very good at using them. After taking some time to summarize it, I feel a lot clearer.
Let me first talk about the conclusion of my personal understanding:
delegate is a type in C# , which is actually a class that can hold a reference to a method.
There is no essential difference between variables declared by delegate and events declared by delegate. Events are packaged on the basis of variables declared by delegate, similar to The relationship between variables and attributes (you can see in the IL code that each event declared by a delegate corresponds to a variable declared by a private delegate) improves security.
Action and Func: These two are actually the Delegate defined by the system. It has many overloaded methods to facilitate various application situations. transfer. It is under the System namespace of the system and is therefore globally visible.
First of all, let’s understand the meaning of the icons in ILDasm:
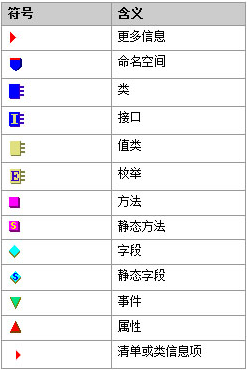
This picture comes from: http://www.php.cn/
Delegate creation steps:
1. Use delegate The keyword creates a delegate, including declaring the return value and parameter type
2. Receive the delegate where used
3. Create an instance of the delegate and specify a method whose return value matches the parameter type to pass it
##1. Events and Delegation
Create a new event delegation test project: EventDelegateTest
The specific code is as follows:
<span style="font-size:14px;"><span style="font-size:14px;">namespace EventDelegateTest
{
public class TestClass
{
public delegate int delegateAction();
public event delegateAction OnActionEvent;
public delegateAction daNew;
}
}</span></span>After compiling the code, use the ILDASM.EXE that comes with Visual Studio 2010:
Open the dll and you can see the following information:
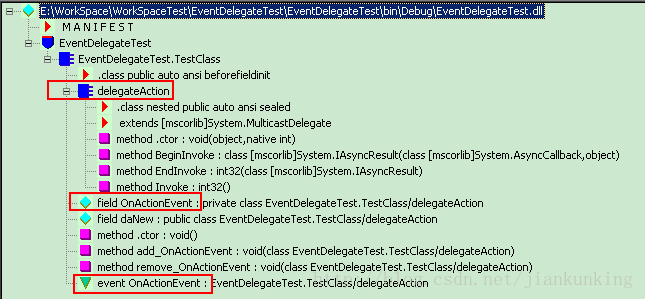
From the above picture we can see the following information:
1. Delegation public delegate int delegateAction();
exists in the form of a class (delegateAction) in IL
. NET defines a delegate as a sealed class, derived from the base class System.MulticastDelegate, and inherits the three methods of the base class
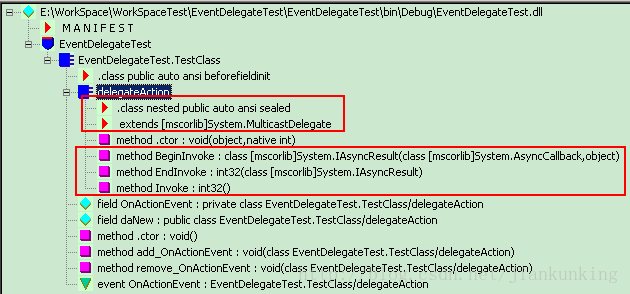
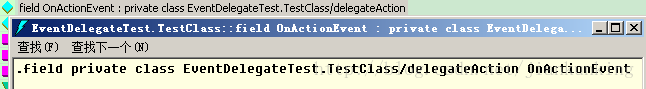
2. public event delegateAction OnActionEvent;
In IL, it not only corresponds to event OnActionEvent but also corresponds to a field OnActionEvent;
The field daNew generated by field OnActionEvent and public delegateAction daNew is the same
##
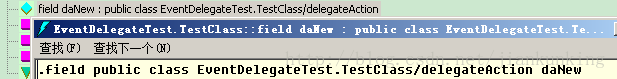
都是以字段(field )的形式存在的。
双击event OnActionEvent可以看到如下信息:
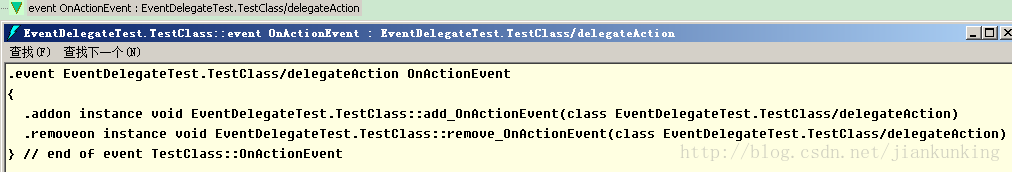
在IL中事件被封装成了包含一个add_前缀和一个remove_前缀的的代码段。
其中,add_前缀的方法其实是通过调用Delegate.Combine()方法来实现的,组成了一个多播委托;remove_就是调用Delegate.Remove()方法,用于移除多播委托中的某个委托。
也就是说:事件其实就是一个特殊的多播委托
那么对于事件进行这一次封装有什么好处呢?
1、因为delegate可以支持的操作非常多,比如我们可以写onXXXChanged += aaaFunc,把某个函数指针挂载到这个委托上面,但是我们也可以简单粗暴地直接写onXXXChanged = aaaFunc,让这个委托只包含这一个函数指针。不过这样一来会产生一个安全问题:如果我们用onXXXChanged = aaaFunc这样的写法,那么会把这个委托已拥有的其他函数指针给覆盖掉,这大概不是定义onXXXChanged的程序员想要看到的结果。
小注:
虽然事件不能直接=某个函数,也不可以直接=null
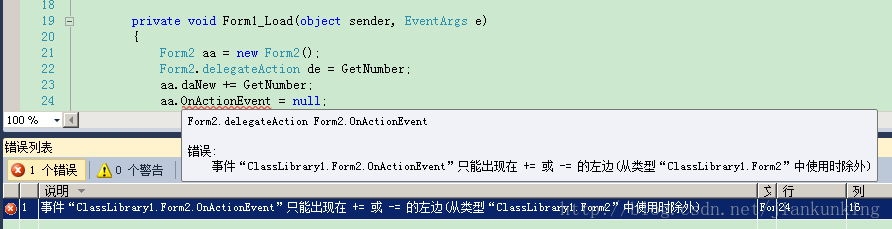
2、还有一个问题就是onXXXChanged这个委托应该什么时候触发(即调用它所包含的函数指针)。从面向对象的角度来说,XXX改变了这个事实(即onXXXChaned的字面含义)应该由包含它的那个对象来决定。但实际上我们可以从这个对象的外部环境调用onXXXChanged,这既产生了安全问题也不符合面向对象的初衷。
说到这里对于事件与委托的管理算是说明白了,那么平时常用的Action与Func,与委托又有什么关系呢?
二、Action 与Func
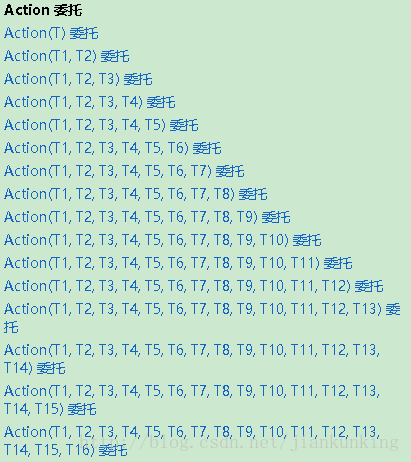
Action 委托:封装一个方法,该方法具有参数(0到16个参数)并且不返回值。
具体形式如下:http://www.php.cn/(v=vs.110).aspx
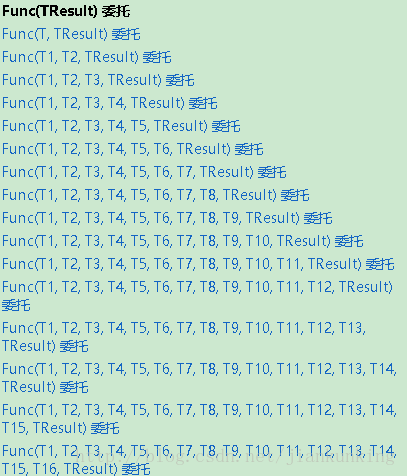
Func
具体形式如下:http://www.php.cn/(v=vs.110).aspx
那么这Action与Func是怎么实现的呢?
1、Action(以Action
从微软公布的源码中,可以看到,如下实现:
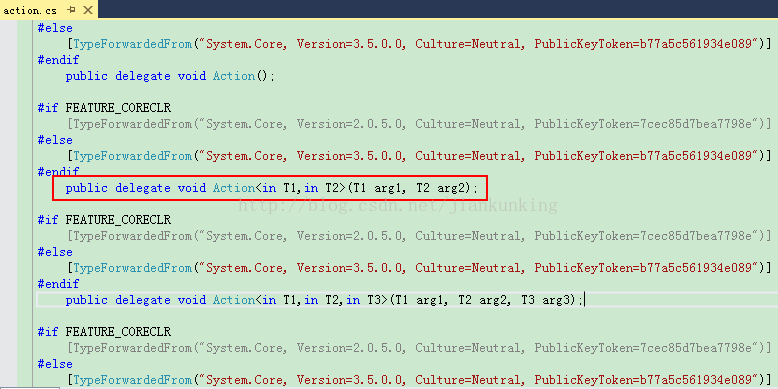
public Action<bool,bool> ac;
上面这个声明就是:该方法具有两个参数并且不返回值的委托。
其余使用方式与委托变量一样。
2、Func(以Func
从微软公布的源码中,可以看到,如下实现:
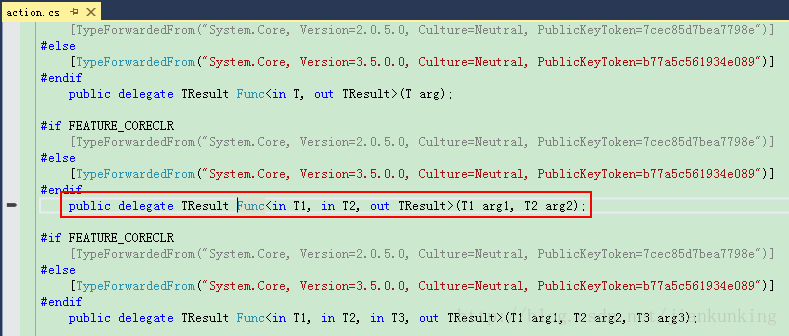
此处,可以看出Func与Action是类似的,唯一的区别就是,Func必须指定返回值的类型,使用方式与委托咱们自己使用委托变量是一样的,直接使用相应参数的Func或者Action声明变量,=或者+=挂载函数(方法即可)
这两个其实说白了就是系统定义好的Delegate,他有很多重载的方法,便于各种应用情况下的调用。他在系统的System命名空间下,因此全局可见。
三、Predicate
是返回bool型的泛型委托,Predicate有且只有一个参数,返回值固定为bool。表示定义一组条件并确定指定对象是否符合这些条件的方法。此方法常在集合(Array 和 List
官方文档:点击打开链接
具体用法demo如下:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace IconTest
{
public partial class Form2 : Form
{
Predicate<int> myPredicate;
int[] myNum = new int[8] { 12, 33, 89, 21, 15, 29, 40, 52 };
public int[] myResult;
public Form2()
{
InitializeComponent();
myPredicate = delegate(int curNum)
{
if (curNum % 2 == 0)
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
};
}
private void Form2_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
myResult = Array.FindAll(myNum, myPredicate);
}
}
}上例中说明了Predicate的使用,FindAll方法中,参数2即是一个Predicate,在具体的执行中,每一个数组的元素都会执行指定的方法,如果满足要求返回true,并会被存放在结果集中,不符合的则被剔除,最终返回的集合,即是结果判断后想要的集合。
Array.FindAll 泛型方法:点击打开链接
以上代码执行结果为:
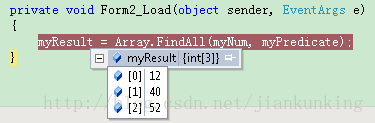
那么Predicate
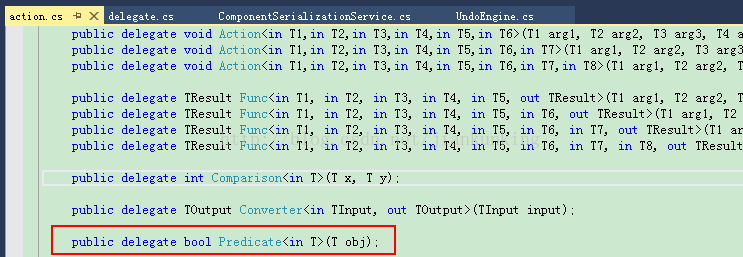
从微软源码中可以看出Predicate
以上就是通过IL分析C#中的委托、事件、Func、Action、Predicate之间的区别与联系的内容,更多相关内容请关注PHP中文网(www.php.cn)!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 How to handle special characters in C language
Apr 03, 2025 pm 03:18 PM
How to handle special characters in C language
Apr 03, 2025 pm 03:18 PM
In C language, special characters are processed through escape sequences, such as: \n represents line breaks. \t means tab character. Use escape sequences or character constants to represent special characters, such as char c = '\n'. Note that the backslash needs to be escaped twice. Different platforms and compilers may have different escape sequences, please consult the documentation.
 What is the role of char in C strings
Apr 03, 2025 pm 03:15 PM
What is the role of char in C strings
Apr 03, 2025 pm 03:15 PM
In C, the char type is used in strings: 1. Store a single character; 2. Use an array to represent a string and end with a null terminator; 3. Operate through a string operation function; 4. Read or output a string from the keyboard.
 How to use various symbols in C language
Apr 03, 2025 pm 04:48 PM
How to use various symbols in C language
Apr 03, 2025 pm 04:48 PM
The usage methods of symbols in C language cover arithmetic, assignment, conditions, logic, bit operators, etc. Arithmetic operators are used for basic mathematical operations, assignment operators are used for assignment and addition, subtraction, multiplication and division assignment, condition operators are used for different operations according to conditions, logical operators are used for logical operations, bit operators are used for bit-level operations, and special constants are used to represent null pointers, end-of-file markers, and non-numeric values.
 The difference between char and wchar_t in C language
Apr 03, 2025 pm 03:09 PM
The difference between char and wchar_t in C language
Apr 03, 2025 pm 03:09 PM
In C language, the main difference between char and wchar_t is character encoding: char uses ASCII or extends ASCII, wchar_t uses Unicode; char takes up 1-2 bytes, wchar_t takes up 2-4 bytes; char is suitable for English text, wchar_t is suitable for multilingual text; char is widely supported, wchar_t depends on whether the compiler and operating system support Unicode; char is limited in character range, wchar_t has a larger character range, and special functions are used for arithmetic operations.
 The difference between multithreading and asynchronous c#
Apr 03, 2025 pm 02:57 PM
The difference between multithreading and asynchronous c#
Apr 03, 2025 pm 02:57 PM
The difference between multithreading and asynchronous is that multithreading executes multiple threads at the same time, while asynchronously performs operations without blocking the current thread. Multithreading is used for compute-intensive tasks, while asynchronously is used for user interaction. The advantage of multi-threading is to improve computing performance, while the advantage of asynchronous is to not block UI threads. Choosing multithreading or asynchronous depends on the nature of the task: Computation-intensive tasks use multithreading, tasks that interact with external resources and need to keep UI responsiveness use asynchronous.
 How to convert char in C language
Apr 03, 2025 pm 03:21 PM
How to convert char in C language
Apr 03, 2025 pm 03:21 PM
In C language, char type conversion can be directly converted to another type by: casting: using casting characters. Automatic type conversion: When one type of data can accommodate another type of value, the compiler automatically converts it.
 How to use char array in C language
Apr 03, 2025 pm 03:24 PM
How to use char array in C language
Apr 03, 2025 pm 03:24 PM
The char array stores character sequences in C language and is declared as char array_name[size]. The access element is passed through the subscript operator, and the element ends with the null terminator '\0', which represents the end point of the string. The C language provides a variety of string manipulation functions, such as strlen(), strcpy(), strcat() and strcmp().
 What is the function of C language sum?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 02:21 PM
What is the function of C language sum?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 02:21 PM
There is no built-in sum function in C language, so it needs to be written by yourself. Sum can be achieved by traversing the array and accumulating elements: Loop version: Sum is calculated using for loop and array length. Pointer version: Use pointers to point to array elements, and efficient summing is achieved through self-increment pointers. Dynamically allocate array version: Dynamically allocate arrays and manage memory yourself, ensuring that allocated memory is freed to prevent memory leaks.



