Algorithm summary of Photoshop Gaussian blur filter
recently felt that some netizens' research on Gaussian blur filter is now summarized as follows. Gaussian blur is a kind of digital image template processing method. Its template is calculated based on a two-dimensional normal distribution (Gaussian distribution) function.
The normal distribution was first obtained by A. Demoivre in finding the asymptotic formula of the binomial distribution. C.F. Gauss derived it from another angle when studying measurement error. P.S. Laplace and Gauss studied its properties. Hence the name Gaussian blur.
Function definition of one-dimensional normal distribution:
Distribution of type random variables, the first parameter μ is the mean value of the random variable that follows the normal distribution , the second parameter σ2 is the variance of this random variable, so the normal distribution is recorded as N(μ, σ2). The probability rule of a random variable that follows a normal distribution is that the probability of taking a value near μ is high, and the probability of taking a value that is farther away from μ is smaller; the smaller σ, the more concentrated the distribution is near μ, and the larger σ, the smaller the distribution. dispersion. The characteristics of the density function of the normal distribution are: symmetric about μ, reaching a maximum value at μ, taking a value of 0 at positive (negative) infinity, and having an inflection point at μ±σ. Its shape is high in the middle and low on both sides, and the image is a bell-shaped curve above the x-axis. When μ = 0, σ2 = 1, it is called the standard normal distribution, recorded as N (0, 1). 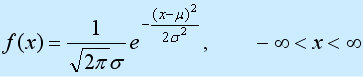
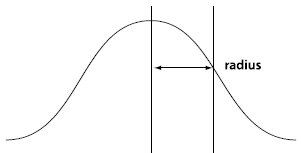
Based on this formula, we can calculate the Gaussian templates under different radii. In fact, the templates are infinite, but they will approach 0 far away from the center. For example, we calculate r A normalized Gaussian template when =0.7:
高斯模板(guass radius=0.700000)
在网络上众所周知流传的高斯3*3模板实际上是对高斯曲面的一个整数除法形式的近似:
1 2 1
2 4 2 /16
1 2 1
Actual verification, we found that this 3*3 template is actually an approximation of the Gaussian radius when it is about 0.849. When r=0.849, its 3*3 normalized template is (in MATLAB, enter h=fspecial('gaussian', 3, 0.849);You can get this template): 0.062467 0.125000 0.062467
0.125000 0.250131 0.125000 0.062467 0.125000 0.06246 7## Then we can use imfilter in Matlab to perform Gaussian blur processing on the image:
img = imread('c:\demo.bmp'); h = fspecial('gaussian', 3, 0.849);
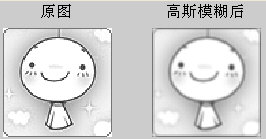
subplot(121), imshow(img); title('Original image')
subplot(122), imshow(img2); title('After Gaussian blur')
# The effect is as follows: We can use it in Matlab as follows Statement to draw Gaussian surface:
Matlab code for drawing Gaussian surface
http:/ /www.php.cn/
-->%math.h>include
stdio.h>
define## N 3 3 / * Template size: (2N+1) * (2N+1) */
void main(){
double a[2*N+1][2*N+1]; /* Gaussian template*/ /* Gaussian radius: [0.1, 250] */
double A=1/
(2*##M_PI*r*r); int i,j; for(i=-
1*
N;i N;i++) for(j=-1 *N;j
N;j++)a[i+N][j+N]=A *exp((-1)*(i*i+j*j)/ (2*r*r));
}
case 'gaussian' % Gaussian filter
siz = (p2-1)/2; %注:p2即模板边长,默认值为33
std = p3; %注:p3即高斯半径,默认为为0.5
[x,y] = meshgrid(-siz(2):siz(2),-siz(1):siz(1));
arg = -(x.*x + y.*y)/(2*std*std);
h = exp(arg);
h(h<eps*max(h(:))) = 0;
sumh = sum(h(:)); %注:模板归一化
if sumh ~= 0,
h = h/sumh;
end;
Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1377
1377
 52
52
 How do I use Photoshop for creating social media graphics?
Mar 18, 2025 pm 01:41 PM
How do I use Photoshop for creating social media graphics?
Mar 18, 2025 pm 01:41 PM
The article details using Photoshop for social media graphics, covering setup, design tools, and optimization techniques. It emphasizes efficiency and quality in graphic creation.
 How do I use Photoshop's Content-Aware Fill and Content-Aware Move tools effectively?
Mar 13, 2025 pm 07:35 PM
How do I use Photoshop's Content-Aware Fill and Content-Aware Move tools effectively?
Mar 13, 2025 pm 07:35 PM
Article discusses using Photoshop's Content-Aware Fill and Move tools effectively, offering tips on selecting source areas, avoiding mistakes, and adjusting settings for optimal results.
 How do I prepare images for web use in Photoshop (file size, resolution, color space)?
Mar 13, 2025 pm 07:28 PM
How do I prepare images for web use in Photoshop (file size, resolution, color space)?
Mar 13, 2025 pm 07:28 PM
Article discusses preparing images for web use in Photoshop, focusing on optimizing file size, resolution, and color space. Main issue is balancing image quality with quick loading times.
 How do I calibrate my monitor for accurate color in Photoshop?
Mar 13, 2025 pm 07:31 PM
How do I calibrate my monitor for accurate color in Photoshop?
Mar 13, 2025 pm 07:31 PM
Article discusses calibrating monitors for accurate color in Photoshop, tools for calibration, effects of improper calibration, and recalibration frequency. Main issue is ensuring color accuracy.
 How do I prepare images for print using Photoshop (resolution, color profiles)?
Mar 18, 2025 pm 01:36 PM
How do I prepare images for print using Photoshop (resolution, color profiles)?
Mar 18, 2025 pm 01:36 PM
The article guides on preparing images for print in Photoshop, focusing on resolution, color profiles, and sharpness. It argues that 300 PPI and CMYK profiles are essential for quality prints.
 How do I prepare images for web using Photoshop (optimize file size, resolution)?
Mar 18, 2025 pm 01:35 PM
How do I prepare images for web using Photoshop (optimize file size, resolution)?
Mar 18, 2025 pm 01:35 PM
Article discusses optimizing images for web using Photoshop, focusing on file size and resolution. Main issue is balancing quality and load times.
 How do I create animated GIFs in Photoshop?
Mar 18, 2025 pm 01:38 PM
How do I create animated GIFs in Photoshop?
Mar 18, 2025 pm 01:38 PM
Article discusses creating and optimizing animated GIFs in Photoshop, including adding frames to existing GIFs. Main focus is on balancing quality and file size.
 What is the reason why PS keeps showing loading?
Apr 06, 2025 pm 06:39 PM
What is the reason why PS keeps showing loading?
Apr 06, 2025 pm 06:39 PM
PS "Loading" problems are caused by resource access or processing problems: hard disk reading speed is slow or bad: Use CrystalDiskInfo to check the hard disk health and replace the problematic hard disk. Insufficient memory: Upgrade memory to meet PS's needs for high-resolution images and complex layer processing. Graphics card drivers are outdated or corrupted: Update the drivers to optimize communication between the PS and the graphics card. File paths are too long or file names have special characters: use short paths and avoid special characters. PS's own problem: Reinstall or repair the PS installer.




