 Web Front-end
Web Front-end
 JS Tutorial
JS Tutorial
 JavaScript implements dragging elements to align to the grid (moving a fixed distance each time)
JavaScript implements dragging elements to align to the grid (moving a fixed distance each time)
JavaScript implements dragging elements to align to the grid (moving a fixed distance each time)
In the past few days, I have been working on an additional function for dragging elements, which is to align to the grid. In fact, it means determining the initial position of the element, and then moving the element a fixed distance each time when dragging it. Allows elements to be aligned within the grid. First show the renderings, and then explain the details in detail
I made a gif. You can see that every time the element moves, it moves according to the minimum unit distance. . And each time the elements are aligned to the grid.
First explain the ideas and details based on the demo, and the demo code will be given later.
1. Determine the minimum unit of each movement of the element (10px and 10px in the demo), that is, each horizontal or vertical displacement is 10px. Laying a layer of grid background is to help us see the effect better (each grid in the demo is also 10px * 10px).
2. In order to see the effect more clearly, the width and height of the element (both are multiples of 10px) and the default position (also multiples of 10px) are initialized. For example: the width and height of the element are 50px * 50px, and the initial position of the element is 0xp * 0px. The advantage of this is that when loading initially, the element can be guaranteed to cover an integral number of small grids (that is, 5 * 5 small grids), and there will be no incomplete grid coverage. This article is actually to prevent users or people with obsessive-compulsive disorder from having to worry so much. It is actually just an operation to beautify the placement position. Friends who understand don't need to be so deliberate, just understand.
3. The most important thing is how to determine when to move a fixed distance. There is one thing to understand about this demo effect: mouse movement and element movement correspond, but they are not equivalent in real time (of course, if you do not consider the smallest unit and just drag the element, and then set the element's position to the mouse position, At this time, it can be understood that mouse movement and element movement are equivalent in real time). Back to the demo instructions, when the mouse moves on the web page, it moves pixel by pixel (you can observe the position of the mouse movement through console.log(e.pageX)). The element moves every 10px. This is the key to our understanding and the key to the entire demo.
After understanding the above idea, combined with the code and comments, let me explain again:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head lang="en">
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title></title>
<style>
body{
margin:0px;
padding:0px;
}
p{
margin:0px;
padding:0px;
}
</style>
<script src="js/jquery-1.11.2.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<p style="height: 600px;background: url(data:image/svg+xml;base64,PHN2ZyB3aWR0aD0iMTAwJSIgaGVpZ2h0PSIxMDAlIiB4bWxucz0iaHR0cDovL3d3dy53My5vcmcvMjAwMC9zdmciPiAgIC
A8ZGVmcz4gICAgICAgIDxwYXR0ZXJuIGlkPSJncmlkIiB3aWR0aD0iMTAiIGhlaWdodD0iMTAiIHBhdHRlcm5Vbml0cz0idXNlclNwYWNlT25Vc2UiPiAgICAgICAgICAgIDxwYXRoIGQ9Ik0gMTAgMCBMIDAgMCAw
IDEwIiBmaWxsPSJub25lIiBzdHJva2U9IiNkZGRkZGQiIHN0cm9rZS13aWR0aD0iMSIgb3BhY2l0eT0iMSIgLz4gICAgICAgIDwvcGF0dGVybj4gICAgPC9kZWZzPiAgICA8cmVjdCB3aWR0aD0iMTAwJSIgaGVpZ
2h0PSIxMDAlIiBmaWxsPSJ1cmwoI2dyaWQpIiAvPjwvc3ZnPg==)">
<p id="bk" style="width:50px;height:50px;background: red;position: absolute"></p>
</p>
</body>
<script>
$(function(){
var orgX,orgY,eleX,eleY,hasMove=false;
$("#bk").on("mousedown",function(e){
orgX= e.pageX; //记录鼠标的水平位置
orgY= e.pageY; //记录鼠标的垂直位置
eleX=$(this).offset().left; //记录元素的水平位置
eleY=$(this).offset().top; //记录元素的垂直位置
hasMove=true; //鼠标按下时标明当前元素可以拖拽标识
});
$(document).on("mousemove",function(e){
if(hasMove){ //当元素可以拖拽时执行操作
//新位置计算方法为元素的上次位置加上新的位移量
var left=eleX+Math.round( ( e.pageX - orgX ) / 10 ) * 10;
var top= eleY+Math.round( ( e.pageY - orgY) / 10 ) * 10;
//更新位置信息
$("#bk").css({
top:top,
left:left
});
}
}).on("mouseup",function(e){
hasMove=false; //鼠标松开时设置元素不可拖拽
});
})
</script>
</html>
The above code gives more detailed comments , among them, the most critical code is
Math.round( ( e.pageX - orgX ) / 10 ) * 10;
This code is to calculate the new displacement of the element, subtracting the latest position of the mouse when the element is pressed The mouse position is divided by the minimum unit of 10, rounded to obtain an integer value, and then multiplied by the minimum unit of 10. You can get the unit distance that the element should move. If you don’t understand this, you can run the code and think about it yourself. (Of course, you can also use Mach’s ceil and floor methods).
The above is the JavaScript implementation of dragging elements to align to the grid (moving a fixed distance each time). For more related content, please pay attention to the PHP Chinese website (www.php.cn)!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to implement an online speech recognition system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 pm 02:54 PM
How to implement an online speech recognition system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 pm 02:54 PM
How to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online speech recognition system Introduction: With the continuous development of technology, speech recognition technology has become an important part of the field of artificial intelligence. The online speech recognition system based on WebSocket and JavaScript has the characteristics of low latency, real-time and cross-platform, and has become a widely used solution. This article will introduce how to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online speech recognition system.
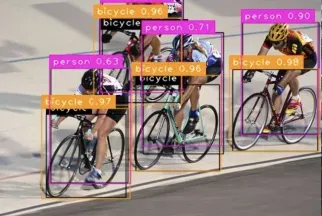 Multi-grid redundant bounding box annotation for accurate object detection
Jun 01, 2024 pm 09:46 PM
Multi-grid redundant bounding box annotation for accurate object detection
Jun 01, 2024 pm 09:46 PM
1. Introduction Currently, the leading object detectors are two-stage or single-stage networks based on the repurposed backbone classifier network of deep CNN. YOLOv3 is one such well-known state-of-the-art single-stage detector that receives an input image and divides it into an equal-sized grid matrix. Grid cells with target centers are responsible for detecting specific targets. What I’m sharing today is a new mathematical method that allocates multiple grids to each target to achieve accurate tight-fit bounding box prediction. The researchers also proposed an effective offline copy-paste data enhancement for target detection. The newly proposed method significantly outperforms some current state-of-the-art object detectors and promises better performance. 2. The background target detection network is designed to use
 WebSocket and JavaScript: key technologies for implementing real-time monitoring systems
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:30 PM
WebSocket and JavaScript: key technologies for implementing real-time monitoring systems
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:30 PM
WebSocket and JavaScript: Key technologies for realizing real-time monitoring systems Introduction: With the rapid development of Internet technology, real-time monitoring systems have been widely used in various fields. One of the key technologies to achieve real-time monitoring is the combination of WebSocket and JavaScript. This article will introduce the application of WebSocket and JavaScript in real-time monitoring systems, give code examples, and explain their implementation principles in detail. 1. WebSocket technology
 How to implement an online reservation system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 am 09:39 AM
How to implement an online reservation system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 am 09:39 AM
How to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online reservation system. In today's digital era, more and more businesses and services need to provide online reservation functions. It is crucial to implement an efficient and real-time online reservation system. This article will introduce how to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online reservation system, and provide specific code examples. 1. What is WebSocket? WebSocket is a full-duplex method on a single TCP connection.
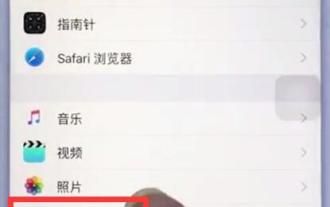 Steps to set up camera grid on iPhone
Mar 26, 2024 pm 07:21 PM
Steps to set up camera grid on iPhone
Mar 26, 2024 pm 07:21 PM
1. Open the desktop of your iPhone, find and click to enter [Settings], 2. Click to enter [Camera] on the settings page. 3. Click to turn on the switch on the right side of [Grid].
 How to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 12:09 PM
How to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 12:09 PM
Introduction to how to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system: With the popularity of the Internet and the advancement of technology, more and more restaurants have begun to provide online ordering services. In order to implement a real-time online ordering system, we can use JavaScript and WebSocket technology. WebSocket is a full-duplex communication protocol based on the TCP protocol, which can realize real-time two-way communication between the client and the server. In the real-time online ordering system, when the user selects dishes and places an order
 JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecasting system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecasting system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecast system Introduction: Today, the accuracy of weather forecasts is of great significance to daily life and decision-making. As technology develops, we can provide more accurate and reliable weather forecasts by obtaining weather data in real time. In this article, we will learn how to use JavaScript and WebSocket technology to build an efficient real-time weather forecast system. This article will demonstrate the implementation process through specific code examples. We
 Simple JavaScript Tutorial: How to Get HTTP Status Code
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
Simple JavaScript Tutorial: How to Get HTTP Status Code
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
JavaScript tutorial: How to get HTTP status code, specific code examples are required. Preface: In web development, data interaction with the server is often involved. When communicating with the server, we often need to obtain the returned HTTP status code to determine whether the operation is successful, and perform corresponding processing based on different status codes. This article will teach you how to use JavaScript to obtain HTTP status codes and provide some practical code examples. Using XMLHttpRequest





