Getting Started with XML
XMLGetting started
# Basic overview
## Extensible Markup Language, a subset of Standard Universal Markup Language, is a markup language used to mark electronic files to make them structural. In electronic computers, tags refer to information symbols that computers can understand. Through such tags, computers can process various information such as articles, etc. It can be used to mark data and define data types. It is a source language that allows users to define their own markup language. It is ideally suited for World Wide Web transport, providing a unified approach to describing and exchanging structured data independent of applications or vendors. It is a cross-platform, content-dependent technology in the
environment, and it is also an effective tool for processing distributed structured information today. As early as 1998, W3C released the XML1.0 specification, Use it to simplify the transmission of document information on the Internet.
The historical origin of XML
In 1969
,GML(Generalized Markup Language Generalized Markup Language)---->In 1985,SGML(Standard Generalized Markup LanguageStandard Generalized Markup Language)---> ;1993年,HTML(Hypertext Markup LanguageHypertext Markup Language)--->1998 Year, XML(Extensible Markup LanguageExtensible Markup Language)
What is extensible markup language?
1
, Extensible Markup Language is a markup language that is very similar to Hypertext Markup Language.2
, It is designed to transmit data, not display data.3
, its label is not predefined. You need to define the labels yourself.4
, It is designed to be self-descriptive.5
, it is the recommended standard ofW3C.
What is the difference between Extensible Markup Language and Hypertext Markup Language?
1
, it is not a replacement for Hypertext Markup Language.2
, it is a supplement to Hypertext Markup Language.3
, It is designed for different purposes from Hypertext Markup Language:4
, It is designed to transmit and store data , whose focus is the content of the data.5
, Hypertext Markup Language is designed to display data, with the focus being on the appearance of the data.6
, Hypertext Markup Language is designed to display information, while it is designed to transmit information.7
. The best description of it is: it is an information transmission tool independent of software and hardware.
Why do you need
XML? 1
, solves the problem of non-standard data transmission.2
, can describe things in a tree structure very well.3
, can be used as a configuration file.PS
: Nowadays, many languages and technologies are using XML as data transmission standard, so a deep understanding of XML is equivalent to mastering a general data transmission protocol. Reference document:
http://www.php.cn/
Case:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <class> <stu id="a001"> <name>张三</name> <sex>男</sex> <age>20</age> </stu> <stu id="a002"> <name>李四</name> <sex>女</sex> <age>18</age> </stu> </class>
XML基本语法
一个XML文件可分为如下几部分内容:
文档声明 、元素、属性、注释 、CDATA区 ,特殊字符 、处理指令(processing instruction)
基本语法:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!-- 上面是文档声明 - ->
<?xml-stylesheet type="text/css" href=”XML2.css”?>
<!-- 上面是处理指令 - ->
<根元素>
<!-- 注释 - ->
<![CDATA[ CDATA区,可以是任意字符 ]]>
<元素 属性=”属性值”>
<元素>元素内容</元素>
<空元素/>>
</元素>
</class>文档声明
<?xml version="1.0" encoding=“编码方式" standalone="yes|no"?>
XML声明放在XML文档的第一行
XML声明由以下几个部分组成:
version - -文档符合XML1.0规范
encoding - -文档字符编码,比如”utf-8”
standalone - -文档定义是否独立使用
standalone="yes“
standalone=“no” 默认
PS:虽说现在XML出了2.0版了,但是现在大多还是用1.0版。
元素
基本语法:
<元素>元素内容</元素> <元素/>
注意事项:
1、每个XML文档必须有且只有一个根元素。
2、根元素是一个完全包括文档中其他所有元素的元素。
3、根元素的起始标记要放在所有其他元素的起始标记之前。
4、根元素的结束标记要放在所有其他元素的结束标记之后。
5、XML元素指XML文件中出现的标签,一个标签分为开始标签和结束标签,一个标签有如下几种书写形式,例如:
6、一个标签中也可以嵌套若干子标签。但所有标签必须合理的嵌套,绝对不允许交叉嵌套 ,例如:
7、对于XML标签中出现的所有空格和换行,XML解析程序都会当作标签内容进行处理。
例如:
8、一个XML元素可以包含字母、数字以及其它一些可见字符,但必须遵守下面的一些规范:
1---区分大小写,例如,和是两个不同的标记。
2---不能以数字或"_" (下划线)开头。
3---不能包含空格。
4---名称中间不能包含冒号(:)。
9、元素、标签、节点意义都是一样的。
属性
基本语法
<元素 属性1=”属性值” 属性2=”属性值”>元素内容</元素>
注意事项:
1、属性值用双引号(")或单引号(')分隔(如果属性值中有',用"分隔;有",用'分隔)
2、一个元素可以有多个属性,它的基本格式为:
3、属性名称在同一个元素标记中只能出现一次
4、属性值不能包括<, >, &之类的特殊字符,否则需要使用转义字符。
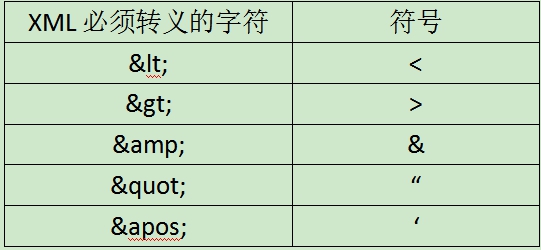
注释
这个和HTML一样,都是
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos. Undress images for free AI clothes remover Generate AI Hentai for free. Easy-to-use and free code editor Chinese version, very easy to use Powerful PHP integrated development environment Visual web development tools God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)
Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress

AI Clothes Remover

Undress AI Tool

Clothoff.io

AI Hentai Generator

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1

SublimeText3 Chinese version

Zend Studio 13.0.1

Dreamweaver CS6

SublimeText3 Mac version

Hot Topics
 How to Use RSS Feeds for News Aggregation and Content Curation?
Mar 10, 2025 pm 03:47 PM
How to Use RSS Feeds for News Aggregation and Content Curation?
Mar 10, 2025 pm 03:47 PM
This article explains how to use RSS feeds for efficient news aggregation and content curation. It details subscribing to feeds, using RSS readers (like Feedly and Inoreader), organizing feeds, and leveraging features for targeted content. The bene
 How Can I Integrate XML and Semantic Web Technologies?
Mar 10, 2025 pm 05:50 PM
How Can I Integrate XML and Semantic Web Technologies?
Mar 10, 2025 pm 05:50 PM
This article explores integrating XML and Semantic Web technologies. The core issue is mapping XML's structured data to RDF triples for semantic interoperability. Best practices involve ontology definition, strategic mapping approaches, careful att
 How Do I Implement Content Syndication Using RSS?
Mar 10, 2025 pm 03:41 PM
How Do I Implement Content Syndication Using RSS?
Mar 10, 2025 pm 03:41 PM
This article details implementing content syndication using RSS feeds. It covers creating RSS feeds, identifying target websites, submitting feeds, and monitoring effectiveness. Challenges like limited control and rich media support are also discus
 How Do I Use Atom Publishing Protocol for Web Content Management?
Mar 10, 2025 pm 05:48 PM
How Do I Use Atom Publishing Protocol for Web Content Management?
Mar 10, 2025 pm 05:48 PM
This article explains Atom Publishing Protocol (AtomPub) for web content management. It details using HTTP methods (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE) with Atom format for content creation, retrieval, updating, and deletion. The article also discusses AtomPub
 How Do I Use XML for Data Interoperability in Healthcare/Finance/etc.?
Mar 10, 2025 pm 05:50 PM
How Do I Use XML for Data Interoperability in Healthcare/Finance/etc.?
Mar 10, 2025 pm 05:50 PM
This article details using XML for data interoperability, focusing on healthcare and finance. It covers schema definition, XML document creation, data transformation, parsing, and exchange mechanisms. Key XML standards (HL7, DICOM, FinML, ISO 20022)
 How Can I Secure RSS Feeds Against Unauthorized Access?
Mar 10, 2025 pm 03:42 PM
How Can I Secure RSS Feeds Against Unauthorized Access?
Mar 10, 2025 pm 03:42 PM
This article details securing RSS feeds against unauthorized access. It examines various methods including HTTP authentication, API keys with rate limiting, HTTPS, and content obfuscation (discouraged). Best practices involve IP restriction, revers
 How Can I Create a Custom XML Vocabulary for My Domain?
Mar 10, 2025 pm 05:48 PM
How Can I Create a Custom XML Vocabulary for My Domain?
Mar 10, 2025 pm 05:48 PM
This article details creating custom XML vocabularies (schemas) for data consistency. It covers defining scope, identifying entities & attributes, designing XML structure, choosing a schema language (XSD or Relax NG), schema development, testing
 How Can I Optimize RSS Feeds for SEO?
Mar 10, 2025 pm 03:39 PM
How Can I Optimize RSS Feeds for SEO?
Mar 10, 2025 pm 03:39 PM
This article explains how optimizing RSS feeds indirectly improves website SEO. It focuses on enhancing feed content (descriptions, keywords, metadata), structure (XML, formatting, encoding), and distribution to boost user engagement, content discov






