Speed up JavaScript loading and execution efficiency
The performance of JavaScript in the browser has become the most important usability issue faced by developers. This problem is complicated by the blocking nature of JavaScript, which means that when the browser is executing JavaScript code, it cannot do anything else at the same time. This article details how to properly load and execute JavaScript code to improve its performance in the browser.
Overview
No matter whether the current JavaScript code is embedded or in an external link file, the downloading and rendering of the page must stop and wait for the script execution to complete. The longer the JavaScript execution process takes, the longer the browser waits to respond to user input. The reason why browsers block when downloading and executing scripts is that the script may change the namespace of the page or JavaScript, which affects the content of subsequent pages. A typical example is using document.write() on the page.
JavaScript code inline example
<html>
<head>
<title>Source Example</title>
</head>
<body>
<p>
<script type="text/javascript">
document.write("Today is " + (new Date()).toDateString());
</script>
</p>
</body>
</html>When the browser encounters the

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
![Error loading plugin in Illustrator [Fixed]](https://img.php.cn/upload/article/000/465/014/170831522770626.jpg?x-oss-process=image/resize,m_fill,h_207,w_330) Error loading plugin in Illustrator [Fixed]
Feb 19, 2024 pm 12:00 PM
Error loading plugin in Illustrator [Fixed]
Feb 19, 2024 pm 12:00 PM
When launching Adobe Illustrator, does a message about an error loading the plug-in pop up? Some Illustrator users have encountered this error when opening the application. The message is followed by a list of problematic plugins. This error message indicates that there is a problem with the installed plug-in, but it may also be caused by other reasons such as a damaged Visual C++ DLL file or a damaged preference file. If you encounter this error, we will guide you in this article to fix the problem, so continue reading below. Error loading plug-in in Illustrator If you receive an "Error loading plug-in" error message when trying to launch Adobe Illustrator, you can use the following: As an administrator
 How to implement an online speech recognition system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 pm 02:54 PM
How to implement an online speech recognition system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 pm 02:54 PM
How to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online speech recognition system Introduction: With the continuous development of technology, speech recognition technology has become an important part of the field of artificial intelligence. The online speech recognition system based on WebSocket and JavaScript has the characteristics of low latency, real-time and cross-platform, and has become a widely used solution. This article will introduce how to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online speech recognition system.
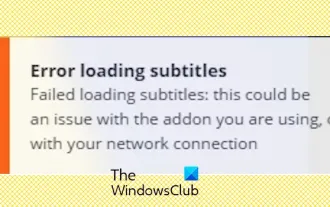 Stremio subtitles not working; error loading subtitles
Feb 24, 2024 am 09:50 AM
Stremio subtitles not working; error loading subtitles
Feb 24, 2024 am 09:50 AM
Subtitles not working on Stremio on your Windows PC? Some Stremio users reported that subtitles were not displayed in the videos. Many users reported encountering an error message that said "Error loading subtitles." Here is the full error message that appears with this error: An error occurred while loading subtitles Failed to load subtitles: This could be a problem with the plugin you are using or your network. As the error message says, it could be your internet connection that is causing the error. So please check your network connection and make sure your internet is working properly. Apart from this, there could be other reasons behind this error, including conflicting subtitles add-on, unsupported subtitles for specific video content, and outdated Stremio app. like
 WebSocket and JavaScript: key technologies for implementing real-time monitoring systems
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:30 PM
WebSocket and JavaScript: key technologies for implementing real-time monitoring systems
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:30 PM
WebSocket and JavaScript: Key technologies for realizing real-time monitoring systems Introduction: With the rapid development of Internet technology, real-time monitoring systems have been widely used in various fields. One of the key technologies to achieve real-time monitoring is the combination of WebSocket and JavaScript. This article will introduce the application of WebSocket and JavaScript in real-time monitoring systems, give code examples, and explain their implementation principles in detail. 1. WebSocket technology
 How to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 12:09 PM
How to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 12:09 PM
Introduction to how to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system: With the popularity of the Internet and the advancement of technology, more and more restaurants have begun to provide online ordering services. In order to implement a real-time online ordering system, we can use JavaScript and WebSocket technology. WebSocket is a full-duplex communication protocol based on the TCP protocol, which can realize real-time two-way communication between the client and the server. In the real-time online ordering system, when the user selects dishes and places an order
 How to implement an online reservation system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 am 09:39 AM
How to implement an online reservation system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 am 09:39 AM
How to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online reservation system. In today's digital era, more and more businesses and services need to provide online reservation functions. It is crucial to implement an efficient and real-time online reservation system. This article will introduce how to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online reservation system, and provide specific code examples. 1. What is WebSocket? WebSocket is a full-duplex method on a single TCP connection.
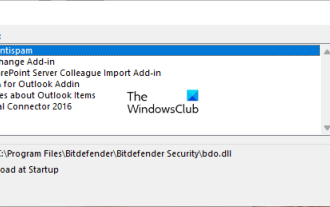 Outlook freezes when inserting hyperlink
Feb 19, 2024 pm 03:00 PM
Outlook freezes when inserting hyperlink
Feb 19, 2024 pm 03:00 PM
If you encounter freezing issues when inserting hyperlinks into Outlook, it may be due to unstable network connections, old Outlook versions, interference from antivirus software, or add-in conflicts. These factors may cause Outlook to fail to handle hyperlink operations properly. Fix Outlook freezes when inserting hyperlinks Use the following fixes to fix Outlook freezes when inserting hyperlinks: Check installed add-ins Update Outlook Temporarily disable your antivirus software and then try creating a new user profile Fix Office apps Program Uninstall and reinstall Office Let’s get started. 1] Check the installed add-ins. It may be that an add-in installed in Outlook is causing the problem.
 JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecasting system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecasting system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecast system Introduction: Today, the accuracy of weather forecasts is of great significance to daily life and decision-making. As technology develops, we can provide more accurate and reliable weather forecasts by obtaining weather data in real time. In this article, we will learn how to use JavaScript and WebSocket technology to build an efficient real-time weather forecast system. This article will demonstrate the implementation process through specific code examples. We




