 Web Front-end
Web Front-end
 CSS Tutorial
CSS Tutorial
 A brief discussion on how to display an element in the center of its parent element in CSS
A brief discussion on how to display an element in the center of its parent element in CSS
A brief discussion on how to display an element in the center of its parent element in CSS
The question of how to vertically center an element in css is already a commonplace question. Whether it is a newbie or a veteran, this question is often asked during the interview process. I was watching a flex video tutorial two days ago, and it mentioned the centering of elements, so today I will take a look at some common methods. Please criticize and correct any shortcomings (all the codes are typed by myself and available)
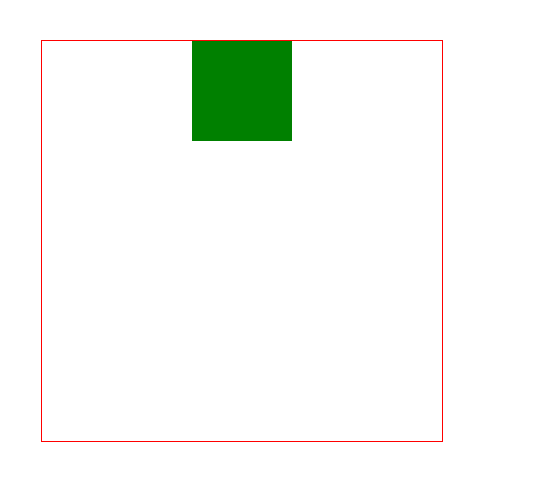
1. Horizontal centering (margin: 0 auto;)
About this, everyone should be the best If you are not unfamiliar with it, whether you are in a training class or studying by yourself. This should be the first method taught by the teacher (horizontally), but it has a premise that the wrapped elements cannot have floating attributes. Otherwise, this property will be invalid. The specific code is as follows:
<style>
body{margin: 0;}
.box{
width: 400px;
height: 400px;
border:1px solid red;
}
item{ margin:0 auto;
width: 100px;
height: 100x;
background: green;
}
</style>
<body>
<p class="box">
<p class="item"></p>
</p>
</body><br>
2. Horizontal centering (text-align: center;)
If this attribute does not float, we can convert it to inline/inline-block, and then add the text-align:center; attribute to its parent element to center it
<style>
body{margin: 0;}
.box{
width: 400px;
height: 400px;
border:1px solid red; text-align:center;
}
item{ display:inline/inline-block;
width: 100px;
height: 100x;
background: green;
}
</style>
<body>
<p class="box">
<p class="item"></p>
</p>
</body>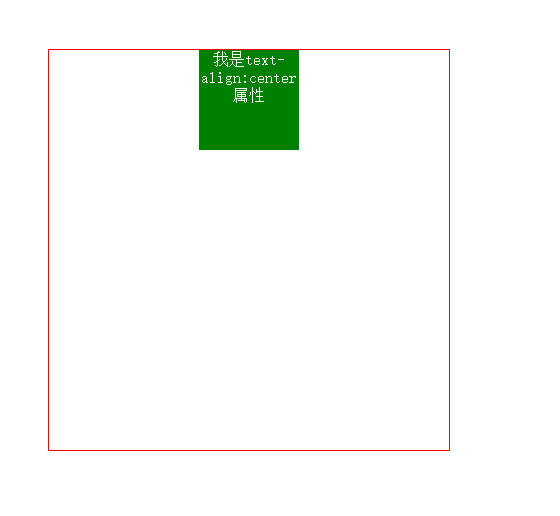
3. Horizontal and vertical centering (1) The child element is absolutely positioned relative to the parent element, and the margin value is minus half of its own width and height
This method has certain limitations, because it must know the width and height of the child element itself
<style>
body{margin: 0;}
.box{
width: 400px;
height: 400px;
border:1px solid red;
position: relative;
}
item{
position: absolute;
top: 50%;
left: 50%;
margin-top: -50px;
margin-left: -50px;
width: 100px;
height: 100x;
background: green;
}</style><body>
<p class="box">
<p class="item"></p>
</p></body>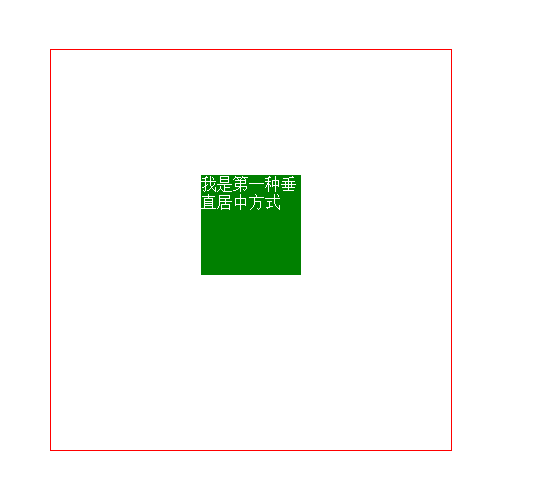
4, Horizontal and vertical centering (2) The child element is absolutely positioned relative to the parent element, and the margin value is auto
This method is not limited by the width and height of the element and is easier to use (recommended)
<style>
body{margin: 0;}
.box{
width: 400px;
height: 400px;
border:1px solid red;
position: relative;
}
item{
position: absolute;
left: 0;
right: 0;
bottom: 0;
top:0;
margin: auto;
width: 100px;
height: 100x;
background: green;
}</style><body>
<p class="box">
<p class="item"></p>
</p></body>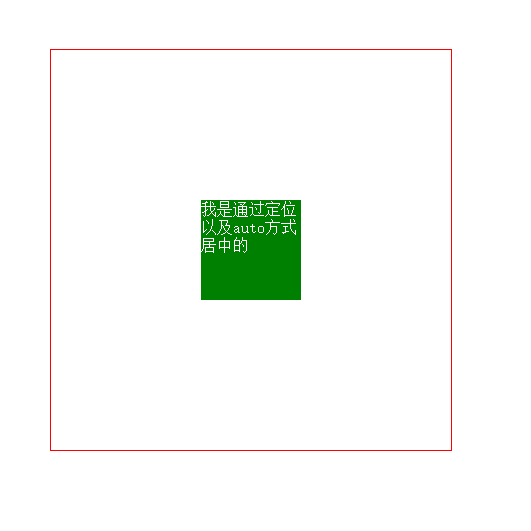
5. Horizontal and vertical centering (3) diplay: table-cell
This method is to convert elements into table style. Then use the style of the table to center (recommended)
<style>
body{margin: 0;}
.box{
width: 400px;
height: 400px;
border:1px solid red;
display: table-cell;
vertical-align: middle;
}
item{
margin:0 auto;
width: 100px;
height: 100x;
background: green;
}</style><body>
<p class="box">
<p class="item"></p>
</p></body>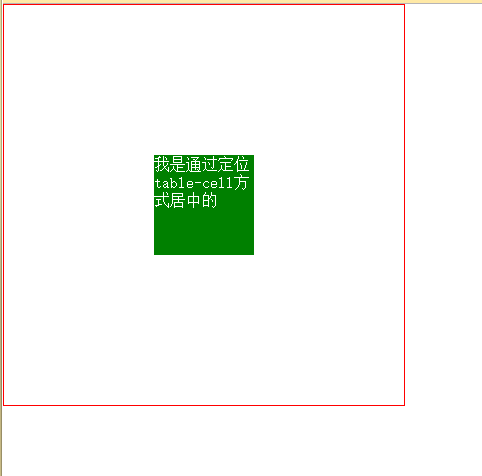
6. Horizontal and vertical centering (4) Absolute positioning and transfrom
This method is the best way to show off your coolness. It uses css3 transformation. When the interviewer sees this in your code, your coolness will instantly rise. Of course, you know, cool stuff. There are compatibility issues
<style>
body{margin: 0;}
.box{
width: 400px;
height: 400px;
border:1px solid red;
position:relative;
}
item{
width: 100px;
height: 100x;
background: green;
position: absolute;
left: 50%;
top: 50%;
transform: translate(-50%,-50%);
}</style><body>
<p class="box">
<p class="item"></p>
</p></body>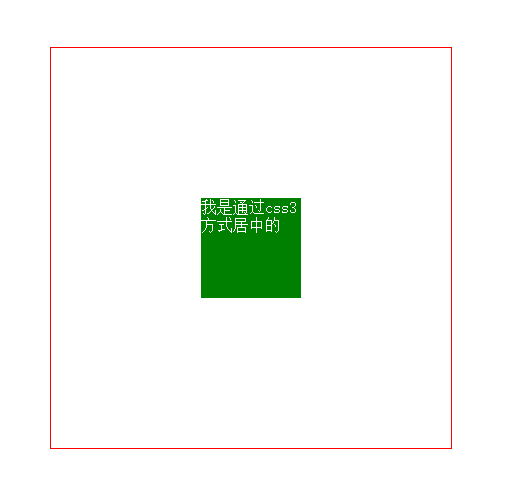
7. Horizontal and vertical centering (5) flex attribute in css3
This attribute is easy to use, but it definitely has compatibility issues. Users should pay attention
<style>
body{margin: 0;}
.box{
width: 400px;
height: 400px;
border:1px solid red;
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
}
item{
width: 100px;
height: 100x;
background: green;
}</style><body>
<p class="box">
<p class="item"></p>
</p></body>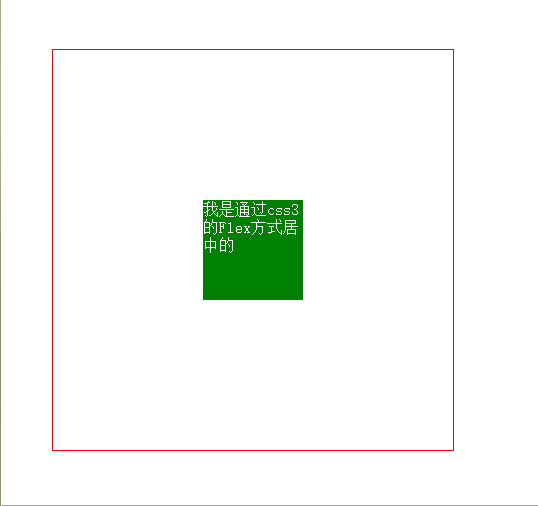
Did you suddenly feel that the method of centering is so simple? ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! !
For more on how an element in CSS is displayed in the center of its parent element, please pay attention to the PHP Chinese website for related articles!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to use bootstrap in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:33 PM
How to use bootstrap in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:33 PM
Using Bootstrap in Vue.js is divided into five steps: Install Bootstrap. Import Bootstrap in main.js. Use the Bootstrap component directly in the template. Optional: Custom style. Optional: Use plug-ins.
 The Roles of HTML, CSS, and JavaScript: Core Responsibilities
Apr 08, 2025 pm 07:05 PM
The Roles of HTML, CSS, and JavaScript: Core Responsibilities
Apr 08, 2025 pm 07:05 PM
HTML defines the web structure, CSS is responsible for style and layout, and JavaScript gives dynamic interaction. The three perform their duties in web development and jointly build a colorful website.
 Understanding HTML, CSS, and JavaScript: A Beginner's Guide
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:02 AM
Understanding HTML, CSS, and JavaScript: A Beginner's Guide
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:02 AM
WebdevelopmentreliesonHTML,CSS,andJavaScript:1)HTMLstructurescontent,2)CSSstylesit,and3)JavaScriptaddsinteractivity,formingthebasisofmodernwebexperiences.
 How to set up the framework for bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:27 PM
How to set up the framework for bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:27 PM
To set up the Bootstrap framework, you need to follow these steps: 1. Reference the Bootstrap file via CDN; 2. Download and host the file on your own server; 3. Include the Bootstrap file in HTML; 4. Compile Sass/Less as needed; 5. Import a custom file (optional). Once setup is complete, you can use Bootstrap's grid systems, components, and styles to create responsive websites and applications.
 How to write split lines on bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:12 PM
How to write split lines on bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:12 PM
There are two ways to create a Bootstrap split line: using the tag, which creates a horizontal split line. Use the CSS border property to create custom style split lines.
 How to insert pictures on bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:30 PM
How to insert pictures on bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:30 PM
There are several ways to insert images in Bootstrap: insert images directly, using the HTML img tag. With the Bootstrap image component, you can provide responsive images and more styles. Set the image size, use the img-fluid class to make the image adaptable. Set the border, using the img-bordered class. Set the rounded corners and use the img-rounded class. Set the shadow, use the shadow class. Resize and position the image, using CSS style. Using the background image, use the background-image CSS property.
 How to use bootstrap button
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:09 PM
How to use bootstrap button
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:09 PM
How to use the Bootstrap button? Introduce Bootstrap CSS to create button elements and add Bootstrap button class to add button text
 How to resize bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:18 PM
How to resize bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:18 PM
To adjust the size of elements in Bootstrap, you can use the dimension class, which includes: adjusting width: .col-, .w-, .mw-adjust height: .h-, .min-h-, .max-h-





