Socket network programming in python
What is a network?
A network is composed of nodes and connections, representing many objects and their interconnections. In mathematics, a network is a kind of graph, which is generally considered to refer specifically to weighted graphs. In addition to mathematical definitions, networks also have specific physical meanings, that is, networks are models abstracted from a certain type of practical problem. In the computer field, the network is a virtual platform for information transmission, reception, and sharing. It connects information from various points, surfaces, and bodies together, thereby realizing the sharing of these resources. The Internet is the most important invention in the history of human development, improving the development of science and technology and human society.
Three elements of network communication
IP address
is used to represent an independent host
Special IP address 127.0.0.1 or localhost (indicating local loopback address, reserved address, etc.), can be used for local testing
Port number
To send data to the application specified by the other party, in order to identify these applications, these network applications are identified with numbers. For the convenience of naming these numbers, these numbers are called ports
Transmission Protocol
TCP Protocol: Transmission Control Protocol
Connection-oriented: a connection needs to be established before transmission
A large amount of data is transmitted during the connection process
Connected through a three-way handshake, which is a safe and reliable connection
The transmission rate is slow and the efficiency is low
UDP protocol: User transmission protocol
For connectionless: the transmission process does not require the establishment of a connection to transmit
The size of each data transmission is limited to 64K
The transmission process is unreliable
Fast transmission rate and high efficiency
SOCKET network programming
Simple implementation of a WEB applet
import socket
def handle_request(client):
buf = client.recv(1024)
client.send(bytes("HTTP/1.1 200 OK\r\n\r\n",'utf8'))
client.send(bytes("Hello, World",'utf8'))
def main():
sock = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
sock.bind(('localhost', 8080))
sock.listen(5)
while True:
connection, address = sock.accept()
handle_request(connection)
connection.close()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()Python provides two levels of access network services:
The low-level network service supports basic Sockets, which provides the standard BSD Sockets API, which can All methods to access the underlying operating system Socket interface.
High-level network service module SocketServer, which provides server center classes that can simplify the development of network servers.
What is a socket?
Socket is also called "socket". Applications usually send requests to or respond to the network through "sockets" Requests enable communication between hosts or between processes on a computer.
Socket() function:
socket.socket([family[, type[, proto]]])
Parameters
family: The socket family can be AF_UNIX or AF_INET
type: The socket type can be divided into SOCK_STREAM or SOCK_DGRAM according to whether it is connection-oriented or non-connection.
protocol: Generally left unfilled, the default is 0 .
Communication process
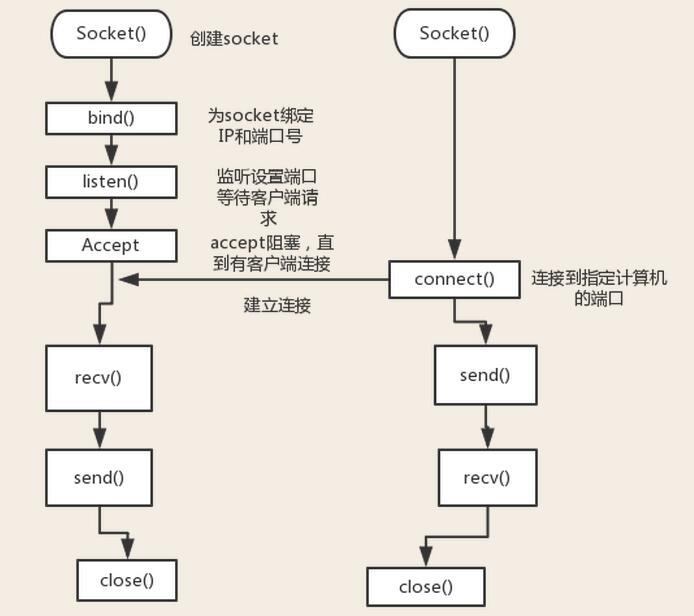
##
#######server端##########
import socket
sk = socket.socket()
address = ('127.0.0.1', 8000)
sk.bind(address)
sk.listen(3)
while True:
conn, addr = sk.accept()
while True:
try:
data = conn.recv(1024)
print(str(data, 'utf8'))
if not data:
break
inp = input(">>>")
conn.send(bytes(inp, 'utf8'))
except Exception:
break
conn.close()
##########Client端###########
import socket
sk = socket.socket()
address = ('127.0.0.1', 8000)
sk.connect(address)
while True:
inp = input(">>>")
if inp == "exit":
break
sk.send(bytes(inp, 'utf8'))
data = sk.recv(1024)
print(str(data, 'utf8'))
sk.close()Socket built-in method
s.bind() 绑定地址(host,port)到套接字, 在AF_INET下,以元组(host,port)的形式表示地址。
s.listen() 开始TCP监听。backlog指定在拒绝连接之前,操作系统可以挂起的最大连接数量。该值至少为1,大部分应用程序设为5就可以了。
s.accept() 被动接受TCP客户端连接,(阻塞式)等待连接的到来
客户端套接字
s.connect() 主动初始化TCP服务器连接,。一般address的格式为元组(hostname,port),如果连接出错,返回socket.error错误。
s.connect_ex() connect()函数的扩展版本,出错时返回出错码,而不是抛出异常
公共用途的套接字函数
s.recv() 接收TCP数据,数据以字符串形式返回,bufsize指定要接收的最大数据量。flag提供有关消息的其他信息,通常可以忽略。
s.send() 发送TCP数据,将string中的数据发送到连接的套接字。返回值是要发送的字节数量,该数量可能小于string的字节大小。
s.sendall() 完整发送TCP数据,完整发送TCP数据。将string中的数据发送到连接的套接字,但在返回之前会尝试发送所有数据。成功返回None,失败则抛出异常。
s.recvform() 接收UDP数据,与recv()类似,但返回值是(data,address)。其中data是包含接收数据的字符串,address是发送数据的套接字地址。
s.sendto() 发送UDP数据,将数据发送到套接字,address是形式为(ipaddr,port)的元组,指定远程地址。返回值是发送的字节数。
s.close() 关闭套接字
s.getpeername() 返回连接套接字的远程地址。返回值通常是元组(ipaddr,port)。
s.getsockname() 返回套接字自己的地址。通常是一个元组(ipaddr,port)
s.setsockopt(level,optname,value) 设置给定套接字选项的值。
s.getsockopt(level,optname[.buflen]) 返回套接字选项的值。
s.settimeout(timeout) 设置套接字操作的超时期,timeout是一个浮点数,单位是秒。值为None表示没有超时期。一般,超时期应该在刚创建套接字时设置,因为它们可能用于连接的操作(如connect())
s.gettimeout() 返回当前超时期的值,单位是秒,如果没有设置超时期,则返回None。
s.fileno() 返回套接字的文件描述符。
s.setblocking(flag) 如果flag为0,则将套接字设为非阻塞模式,否则将套接字设为阻塞模式(默认值)。非阻塞模式下,如果调用recv()没有发现任何数据,或send()调用无法立即发送数据,那么将引起socket.error异常。
s.makefile() 创建一个与该套接字相关连的文件
实例
#########Server端##########
import socket
import subprocess
sk = socket.socket()
address = ('127.0.0.1', 8000)
sk.bind(address)
sk.listen(3)
while True:
conn, addr = sk.accept()
while True:
try:
data = conn.recv(1024)
except Exception:
break
if not data:
break
# print(str(data, 'utf8'))
# data = str(data, 'utf8')#解码同decode
obj = subprocess.Popen(data.decode('utf8'), shell=True, stdout=subprocess.PIPE)
ssh_result = obj.stdout.read()
result_len = bytes(str(len(ssh_result)),'utf8')
conn.send(result_len)
conn.send(ssh_result)
conn.close()
#########Client#########
import socket
sk = socket.socket()
address = ('127.0.0.1', 8000)
sk.connect(address)
while True:
inp = input(">>>")
if inp == "exit":
break
sk.send(bytes(inp, 'utf8'))
result_len = int(str(sk.recv(1024), 'utf8'))
print(result_len)
data = bytes()
while len(data) != result_len:
recv = sk.recv(1024)
data += recv
print(str(data, 'gbk'))
sk.close()文件上传
Server
import socket import os sk = socket.socket() address = ('127.0.0.1', 8000) sk.bind(address) sk.listen(3) BASE_DIR = os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__)) while True: conn, addr = sk.accept() while True: data = conn.recv(1024) cmd, file_name, file_size = str(data, 'utf8').split('|') path = os.path.join(BASE_DIR, 'model', file_name) file_size = int(file_size) f = open(path, 'ab') has_recv = 0 while has_recv != file_size: data = conn.recv(1024) f.write(data) has_recv += len(data) f.close()
Client
import socket
import os
sk = socket.socket()
address = ('127.0.0.1', 8000)
sk.connect(address)
BASE_DIR = os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__))
while True:
inp = input(">>>>").strip()
path = os.path.join(BASE_DIR, inp)
file_name = os.path.basename(path)
file_size = os.stat(path).st_size
file_info = 'post|%s|%s' % (file_name, file_size)
sk.sendall(bytes(file_info, 'utf8'))
f = open(path, 'rb')
has_sent = 0
while has_sent != file_size:
data = f.read(1024)
sk.sendall(data)
has_sent += len(data)
f.close()
print("上传成功")socketserver
socketserver模块简化了网络编程服务程序的任务,同时SocketServer模块也是Python标准库中很多服务器框架的基础。
学习它的最好办法是自己浏览一遍它的源码。
首先先看一下如何去运用
import socketserver
class MyServer(socketserver.BaseRequestHandler):
def handle(self):
print("服务端启动")
while True:
conn = self.request
while True:
data = conn.recv(1024)
print(str(data, 'utf8'))
inp = input(">>>>>")
conn.sendall(bytes(inp, 'utf8'))
conn.close()
if __name__ == '__main__':
server = socketserver.ThreadingTCPServer(('127.0.0.1', 8080), MyServer)
server.serve_forever()
serverimport socket
sk = socket.socket()
address = ('127.0.0.1', 8080)
sk.connect(address)
print("客户端启动")
while True:
inp = input(">>>>>")
sk.sendall(bytes(inp, 'utf8'))
if inp == "q":
break
data = sk.recv(1024)
print(str(data, 'utf8'))
sk.close()此代码简单的实现了server端能同时和多个client聊天的功能。
我们在看源码前,首先要明确的是它分了几个类及每个类的功能作用等。
There are five classes in an inheritance diagram, four of which represent
synchronous servers of four types:
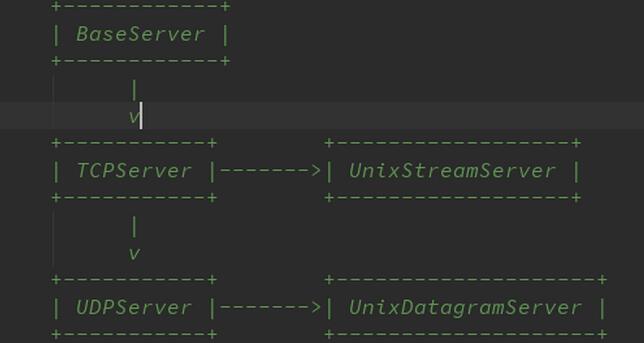
下面的就不一一详细说了,想要了解的更透彻,还是看一遍源码吧。
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支PHP中文网。
更多Socket network programming in python相关文章请关注PHP中文网!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1376
1376
 52
52
 How does PS feathering control the softness of the transition?
Apr 06, 2025 pm 07:33 PM
How does PS feathering control the softness of the transition?
Apr 06, 2025 pm 07:33 PM
The key to feather control is to understand its gradual nature. PS itself does not provide the option to directly control the gradient curve, but you can flexibly adjust the radius and gradient softness by multiple feathering, matching masks, and fine selections to achieve a natural transition effect.
 Do mysql need to pay
Apr 08, 2025 pm 05:36 PM
Do mysql need to pay
Apr 08, 2025 pm 05:36 PM
MySQL has a free community version and a paid enterprise version. The community version can be used and modified for free, but the support is limited and is suitable for applications with low stability requirements and strong technical capabilities. The Enterprise Edition provides comprehensive commercial support for applications that require a stable, reliable, high-performance database and willing to pay for support. Factors considered when choosing a version include application criticality, budgeting, and technical skills. There is no perfect option, only the most suitable option, and you need to choose carefully according to the specific situation.
 How to use mysql after installation
Apr 08, 2025 am 11:48 AM
How to use mysql after installation
Apr 08, 2025 am 11:48 AM
The article introduces the operation of MySQL database. First, you need to install a MySQL client, such as MySQLWorkbench or command line client. 1. Use the mysql-uroot-p command to connect to the server and log in with the root account password; 2. Use CREATEDATABASE to create a database, and USE select a database; 3. Use CREATETABLE to create a table, define fields and data types; 4. Use INSERTINTO to insert data, query data, update data by UPDATE, and delete data by DELETE. Only by mastering these steps, learning to deal with common problems and optimizing database performance can you use MySQL efficiently.
 How to set up PS feathering?
Apr 06, 2025 pm 07:36 PM
How to set up PS feathering?
Apr 06, 2025 pm 07:36 PM
PS feathering is an image edge blur effect, which is achieved by weighted average of pixels in the edge area. Setting the feather radius can control the degree of blur, and the larger the value, the more blurred it is. Flexible adjustment of the radius can optimize the effect according to images and needs. For example, using a smaller radius to maintain details when processing character photos, and using a larger radius to create a hazy feeling when processing art works. However, it should be noted that too large the radius can easily lose edge details, and too small the effect will not be obvious. The feathering effect is affected by the image resolution and needs to be adjusted according to image understanding and effect grasp.
 How to optimize database performance after mysql installation
Apr 08, 2025 am 11:36 AM
How to optimize database performance after mysql installation
Apr 08, 2025 am 11:36 AM
MySQL performance optimization needs to start from three aspects: installation configuration, indexing and query optimization, monitoring and tuning. 1. After installation, you need to adjust the my.cnf file according to the server configuration, such as the innodb_buffer_pool_size parameter, and close query_cache_size; 2. Create a suitable index to avoid excessive indexes, and optimize query statements, such as using the EXPLAIN command to analyze the execution plan; 3. Use MySQL's own monitoring tool (SHOWPROCESSLIST, SHOWSTATUS) to monitor the database health, and regularly back up and organize the database. Only by continuously optimizing these steps can the performance of MySQL database be improved.
 MySQL download file is damaged and cannot be installed. Repair solution
Apr 08, 2025 am 11:21 AM
MySQL download file is damaged and cannot be installed. Repair solution
Apr 08, 2025 am 11:21 AM
MySQL download file is corrupt, what should I do? Alas, if you download MySQL, you can encounter file corruption. It’s really not easy these days! This article will talk about how to solve this problem so that everyone can avoid detours. After reading it, you can not only repair the damaged MySQL installation package, but also have a deeper understanding of the download and installation process to avoid getting stuck in the future. Let’s first talk about why downloading files is damaged. There are many reasons for this. Network problems are the culprit. Interruption in the download process and instability in the network may lead to file corruption. There is also the problem with the download source itself. The server file itself is broken, and of course it is also broken when you download it. In addition, excessive "passionate" scanning of some antivirus software may also cause file corruption. Diagnostic problem: Determine if the file is really corrupt
 MySQL can't be installed after downloading
Apr 08, 2025 am 11:24 AM
MySQL can't be installed after downloading
Apr 08, 2025 am 11:24 AM
The main reasons for MySQL installation failure are: 1. Permission issues, you need to run as an administrator or use the sudo command; 2. Dependencies are missing, and you need to install relevant development packages; 3. Port conflicts, you need to close the program that occupies port 3306 or modify the configuration file; 4. The installation package is corrupt, you need to download and verify the integrity; 5. The environment variable is incorrectly configured, and the environment variables must be correctly configured according to the operating system. Solve these problems and carefully check each step to successfully install MySQL.
 How to optimize MySQL performance for high-load applications?
Apr 08, 2025 pm 06:03 PM
How to optimize MySQL performance for high-load applications?
Apr 08, 2025 pm 06:03 PM
MySQL database performance optimization guide In resource-intensive applications, MySQL database plays a crucial role and is responsible for managing massive transactions. However, as the scale of application expands, database performance bottlenecks often become a constraint. This article will explore a series of effective MySQL performance optimization strategies to ensure that your application remains efficient and responsive under high loads. We will combine actual cases to explain in-depth key technologies such as indexing, query optimization, database design and caching. 1. Database architecture design and optimized database architecture is the cornerstone of MySQL performance optimization. Here are some core principles: Selecting the right data type and selecting the smallest data type that meets the needs can not only save storage space, but also improve data processing speed.




