Python sorting algorithm summary and examples
This article mainly introduces the relevant information about the summary of python sorting algorithm and detailed examples. Friends who need it can refer to it
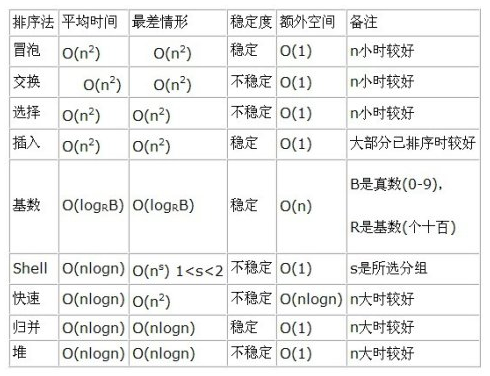
summarizes the common centralized sorting algorithms
Merge sort
Merge sort, also called merge sort, is a typical application of the divide and conquer method. The idea of divide and conquer is to decompose each problem into small problems, solve each small problem, and then merge them.
The specific merge sort is to recursively decompose a set of unordered numbers into sub-items with only one element by n/2, and one element is already sorted. Then merge these ordered sub-elements.
The process of merging is to compare two sorted subsequences, first select the smallest element in the two subsequences, select the smallest subsequence of the two elements, and remove it from the subsequence.
Remove and add to the final result set until the two subsequences are merged.
The code is as follows:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 |
|
Stable, time complexity O(nlog n)
Insertion sort
The code is as follows:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 |
|
Stable, time complexity O(n^2)
To exchange the values of two elements in python, you can write: a, b = b, a. In fact, this is because the left and right sides of the assignment symbol are tuples
(it needs to be emphasized here that in python , tuples are actually delimited by commas "," instead of brackets).
Selection sort
Selection sort is a simple and intuitive sorting algorithm. Here's how it works. First, find the smallest (large) element in the unsorted sequence, and store it at the starting position of the
sorted sequence. Then, continue to find the smallest (large) element from the remaining unsorted elements, and then put it in the sorted sequence. end of sequence. And so on, until all
elements are sorted.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 |
|
Unstable, time complexity O(n^2)
Hill sorting
Hill sorting, also known as descending incremental sorting algorithm, Hill sorting is a non-stable sorting algorithm. This method is also called reducing incremental sorting, because DL. Shell was named after it was proposed in 1959.
First take an integer d1 less than n as the first increment, and divide all the records in the file into d1 groups. All records whose distance is a multiple of d1 are placed in the same group. First sort within each group;
Then, take the second increment d2
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 |
|
Unstable, time complexity average time O(nlogn) Worst time O(n^s)1
Heap Sort(Heap Sort)
The definition of "heap": at the beginning In the "heap" with index 0:
The right child node of node i is at position 2 * i + 24) The parent node of node i is at position floor( (i – 1) / 2) : Note that floor means "Rounding" operation
Characteristics of the heap:
The key value of each node must always be greater than (or less than) its parent node
"Maximum heap":
The root node of the "heap" stores the node with the largest key value. That is, the key value of each node in the "heap" is always greater than its child nodes.
Move up, move down:
When the key value of a node is greater than its parent node, then we have to perform the "move up" operation, that is, we move the node to The position of its parent node, and let its parent node go to its position, and then we continue to judge the node, and do not stop "moving up" until the node is no longer larger than its parent node.
Now let’s take a look at the “move down” operation. When we change the key value of a node to a smaller value, we need to "move it down".
Method:
We first build a maximum heap (time complexity O(n)), and then each time we only need to exchange the root node with the node at the last position, and then replace the last One position is excluded, and then the heap of the root node is adjusted after the exchange (time complexity O(lgn)), that is, the root node is "moved down". The total time complexity of heap sorting is O(nlgn).
The code is as follows:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 |
|
is unstable and the time complexity is O( nlog n)
Quick sort
The quick sort algorithm, like the merge sort algorithm, is also based on the divide and conquer model. The three steps of the divide-and-conquer process of quick sorting the subarray A[p…r] are:
Decomposition: Divide the array A[p…r] into A[p…q-1] and A[ q+1…r], where every element in A[p…q-1] is less than or equal to A[q] and every element in A[q+1…r] is greater than or equal to A[q ];
Solution: Sort the subarrays A[p...q-1] and A[q+1...r] by recursively calling quick sort;
Merge: Because the two subarrays Arrays are sorted in-place, so no additional operations are required.
For the beginning of each iteration of partition partition, x=A[r], for any array subscript k, there are:
1) If p≤k≤i, then A[ k]≤x.
2) If i+1≤k≤j-1, then A[k]>x.
3) If k=r, then A[k]=x.
The code is as follows:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 |
|
Unstable, the best time complexity is O(nlogn) and the worst time is O(n^2)
Let’s talk about sequences in python:
Lists, tuples and strings It's all sequences, but what are sequences and why are they so special? The two main features of sequences are the indexing operator and the slicing operator. The index operator allows us to grab a specific item from a sequence. The slice operator allows us to obtain a slice of the sequence, that is, a part of the sequence, such as: a = ['aa','bb','cc'], print a[0] is an index operation, print a[0:2] for slicing operations.
I hope to master the knowledge of Python algorithm sorting through this article. Thank you for your support of this site!
For more articles related to python sorting algorithm summary and examples, please pay attention to the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1377
1377
 52
52
 How to solve the permissions problem encountered when viewing Python version in Linux terminal?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 05:09 PM
How to solve the permissions problem encountered when viewing Python version in Linux terminal?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 05:09 PM
Solution to permission issues when viewing Python version in Linux terminal When you try to view Python version in Linux terminal, enter python...
 How to efficiently copy the entire column of one DataFrame into another DataFrame with different structures in Python?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 11:15 PM
How to efficiently copy the entire column of one DataFrame into another DataFrame with different structures in Python?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 11:15 PM
When using Python's pandas library, how to copy whole columns between two DataFrames with different structures is a common problem. Suppose we have two Dats...
 How to dynamically create an object through a string and call its methods in Python?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 11:18 PM
How to dynamically create an object through a string and call its methods in Python?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 11:18 PM
In Python, how to dynamically create an object through a string and call its methods? This is a common programming requirement, especially if it needs to be configured or run...
 How to teach computer novice programming basics in project and problem-driven methods within 10 hours?
Apr 02, 2025 am 07:18 AM
How to teach computer novice programming basics in project and problem-driven methods within 10 hours?
Apr 02, 2025 am 07:18 AM
How to teach computer novice programming basics within 10 hours? If you only have 10 hours to teach computer novice some programming knowledge, what would you choose to teach...
 How does Uvicorn continuously listen for HTTP requests without serving_forever()?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 10:51 PM
How does Uvicorn continuously listen for HTTP requests without serving_forever()?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 10:51 PM
How does Uvicorn continuously listen for HTTP requests? Uvicorn is a lightweight web server based on ASGI. One of its core functions is to listen for HTTP requests and proceed...
 What are some popular Python libraries and their uses?
Mar 21, 2025 pm 06:46 PM
What are some popular Python libraries and their uses?
Mar 21, 2025 pm 06:46 PM
The article discusses popular Python libraries like NumPy, Pandas, Matplotlib, Scikit-learn, TensorFlow, Django, Flask, and Requests, detailing their uses in scientific computing, data analysis, visualization, machine learning, web development, and H
 How to handle comma-separated list query parameters in FastAPI?
Apr 02, 2025 am 06:51 AM
How to handle comma-separated list query parameters in FastAPI?
Apr 02, 2025 am 06:51 AM
Fastapi ...
 How to avoid being detected by the browser when using Fiddler Everywhere for man-in-the-middle reading?
Apr 02, 2025 am 07:15 AM
How to avoid being detected by the browser when using Fiddler Everywhere for man-in-the-middle reading?
Apr 02, 2025 am 07:15 AM
How to avoid being detected when using FiddlerEverywhere for man-in-the-middle readings When you use FiddlerEverywhere...




