
I feel like this title is too big
In fact, date objects are not commonly used, and there don’t seem to be many applications
But we need to understand some basic usage
Date date object is the native js constructor
Unlike arrays, objects, etc., it has no corresponding constant form
Creating a date object is very simple
var date = new Date();
Date() can take parameters (string), specify the date and time like this
console.log(new Date("2016/1/1"));Without parameters, the current date and time are used
Date() is mainly used to obtain the current Timestamp (number of milliseconds since January 1, 1970)
This value can be obtained through the getTime method of the date object
Let’s take a look at the commonly used methods of obtaining date objects
getFullYear() Get the year
getMonth() Get the month
The thing to note is not to use getYear(), because it returns the year difference from 1900, and no one uses it
There is also the getMonth() method The returned month starts from zero, that is, 0 to 11, representing January to December.
The range of getDay() is 0 to 6, 0 represents Sunday.
Let’s practice encapsulating a function to print the current date information.
Look at the table, today is 18:45 on November 6, 2016
function getCurrentDate(){ var date = new Date();
console.log('年份:' + date.getFullYear(),
'月份:' + (date.getMonth() + 1),
'天数:' + date.getDate(),
'小时:' + date.getHours(),
'分钟:' + date.getMinutes(),
'秒数:' + date.getSeconds());
}
getCurrentDate();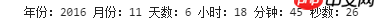
The definition given by w3c: returns January 1, 1970 The number of milliseconds from midnight to the specified date (string)
Use this way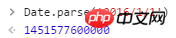
It is nothing more than getting the current date, Performance test
To get the current date, just instantiate a date object directly, and then call the method
function loop(){
for(var i = 0; i < 1000; i++){
console.log(1);
}
}var timeStart = new Date().getTime();
loop();var timeEnd = new Date().getTime();
console.log('程序运行时间:' + (timeEnd - timeStart)); Or you can use the method I used in the JavaScript single-threaded underlying principle
Or you can use the method I used in the JavaScript single-threaded underlying principle
function loop(){
for(var i = 0; i < 1000; i++){
console.log(1);
}
}var timeStart = +new Date();
loop();var timeEnd = +new Date();
console.log('程序运行时间:' + (timeEnd - timeStart));The plus sign is equivalent to the implicit conversion of the instantiated date object into a number
That is, calling the valueOf() overridden by the Date object
function loop(){
for(var i = 0; i < 1000; i++){
console.log(1);
}
}var timeStart = Date.now();
loop();var timeEnd = Date.now();
console.log('程序运行时间:' + (timeEnd - timeStart));if(!Date.now){ Date.now = function(){
return new Date().getTime();
}
}



