Detailed explanation of MySQL backup and recovery
Mar 01, 2017 pm 01:43 PMMySQL data backup
In mySQL, there are logical backups and physical backups. The biggest advantage of logical backup is that the same method can be used for backup of various storage engines. Physical backup is different, and different storage engines have different backup methods.
Logical backup and recovery
Backup
In MySQL, logical backup uses mysqldump to back up the data in the database as a text file. The backed up file can be viewed and edited. . According to the backup scope, backup can be divided into the following three types of backup.
Back up a specified database or some tables in the database
mysqldump [options] database name [table name] > data.sqlBack up multiple specified databases
mysqldump [options] –database > data.sql database 1 database 2 database 3...Back up all Database
mysqldump [options] –all-database > data.sql
Analysis: [options] During backup, required permission information, etc. There are many options for mysqldump, which can be viewed through mysqldump –help. In order to ensure the consistency of data backup, when the MySQL storage engine is in the north, you need to add the -l parameter, which means to add read locks to all tables. During the backup period, all tables will only be read, not written. But for the InnoDB engine, –single-transaction can be used. Data file backed up by data.sql
Parameters:
l: represents locking all tables
f: represents generating a new daily file
The instance will be xxpt All tables in the database are backed up to the dequan.sql table. The command is as follows:
mysqldump -uroot -p xxpt >dequan.sql 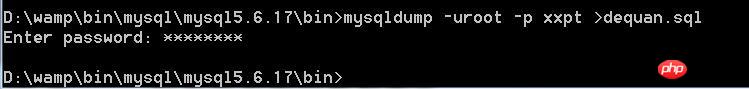
Because I did not specify the backup path above, by default, the backup will be to the current path, so the backup will be to D:\ The wamp\bin\mysql\mysql5.6.17\bin path is under.
Recovery
Full recovery
Mysqldump recovery is also very simple, just execute the backup as input. The results are as follows:
mysql -uroot -p dbname
Incomplete recovery
Incomplete recovery includes point-in-time-based recovery and location-based recovery. The time point and position correspond to the time point and position in the binary log (binlog log). 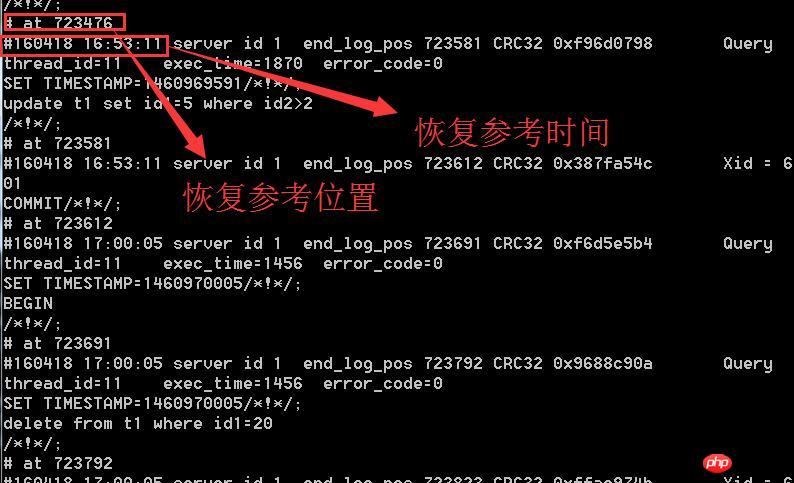
Based on time point
If the data room is set to be wrong between 4:00 pm and before 5:00 pm, it needs to be skipped during recovery. First let's take a look at the binlog log. For example, updating data after 4 pm is wrong and needs to be skipped during recovery. Deleting data after 5 pm is correct and needs to be retained. 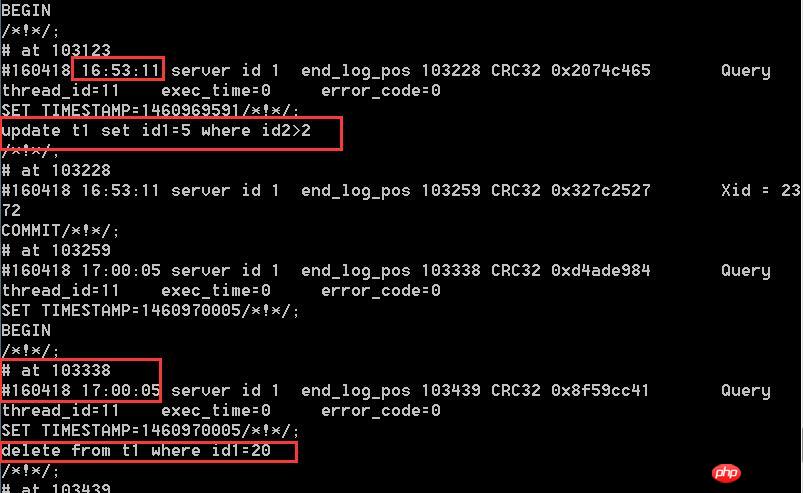
1. Through mysql -uroot -p dbname
Location-based recovery
When using location recovery, we need to first check the binlog log file to determine the location number , and then use the following command to restore:
mysqlbinlog D:\wamp\bin\mysql\mysql5.6.17\data\mybinlog.000012 –stop-position=716406|mysql -uroot -p
Restore the data after 5 points Operation
D:\wamp\bin\mysql\mysql5.6.17\data\mybinlog.000012 –start-position=723613|mysql -uroot -p 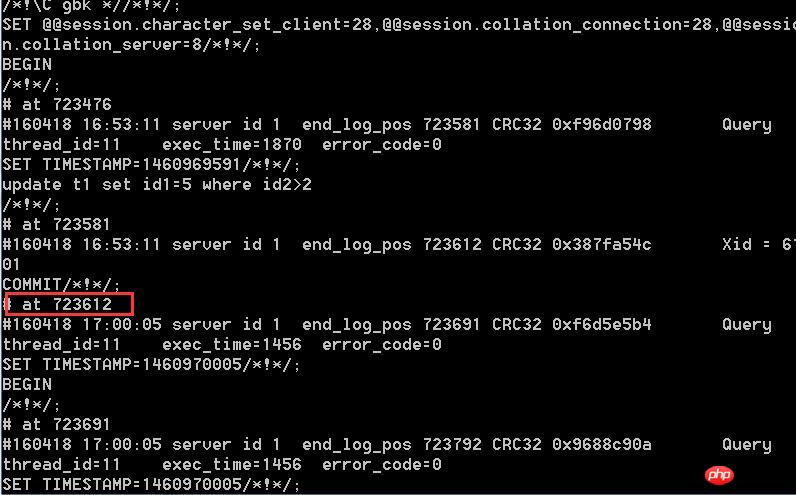
Physical backup and recovery
Physical backup is divided into cold backup and hot backup. Compared with logical backup, its biggest advantage is the fast backup and recovery speed. Because the principle of physical backup is based on file cp.
Cold backup and recovery
Cold backup is actually a method of stopping the database service and copying the data files. This method is suitable for both MyISAM and InnoDB.
Recovery: First stop the Mysql service, restore the MySQL data files at the operating system level, then restart the Mysql service, and use the Mysqlbinlog tool to restore all binlogs since the backup.
Hot backup
The hot backup of different storage engines in mysql is different.
MyISAM Storage Engine
The backup principle of MyISAM storage engine is to add a read lock to the table to be backed up, and then cp the data file to the backup directory. Commonly used methods
Method 1: Use mysqlhotcop
mysqlhotcop db_name [Directory]Method 2: Manually lock the table copy
First Add read locks to all tables in the database, and then cp the data.
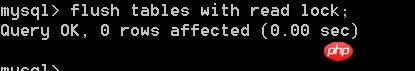
Lock all tables flush tables with read lock;
InnoDB storage engine
Learning···
表的导入与导出
导出
使用SELECT …INTO OUTFILE …+[options]命令实现
关于options参数如下
默认路径为该数据对应的路径下:

使用mysqldump
mysqldump -u username -T targetDir dbname tableName[options]
比如:
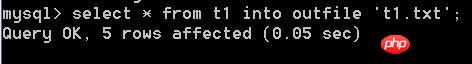
mysqldump -uroot -p -T D:/wamp/bin/mysql/mysql5.6.17/ xxpt t1
生成了两个文件,如下图:
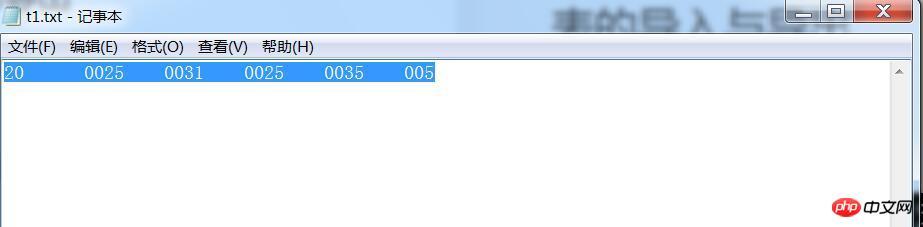
t1.txt中保存中数据信息,t1.sql文件内容如下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 |
|
导入
方法一:
load data infile
eg:
load data infile ‘D:/wamp/bin/mysql/mysql5.6.17/t1.txt’ into table t1; 
方法二:使用mysqlinport
以上就是MySQL的备份与恢复详解的内容,更多相关内容请关注PHP中文网(www.php.cn)!

Hot Article

Hot tools Tags

Hot Article

Hot Article Tags

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 PHP's big data structure processing skills
May 08, 2024 am 10:24 AM
PHP's big data structure processing skills
May 08, 2024 am 10:24 AM
PHP's big data structure processing skills
 How to optimize MySQL query performance in PHP?
Jun 03, 2024 pm 08:11 PM
How to optimize MySQL query performance in PHP?
Jun 03, 2024 pm 08:11 PM
How to optimize MySQL query performance in PHP?
 How to use MySQL backup and restore in PHP?
Jun 03, 2024 pm 12:19 PM
How to use MySQL backup and restore in PHP?
Jun 03, 2024 pm 12:19 PM
How to use MySQL backup and restore in PHP?
 What are the application scenarios of Java enumeration types in databases?
May 05, 2024 am 09:06 AM
What are the application scenarios of Java enumeration types in databases?
May 05, 2024 am 09:06 AM
What are the application scenarios of Java enumeration types in databases?
 How to insert data into a MySQL table using PHP?
Jun 02, 2024 pm 02:26 PM
How to insert data into a MySQL table using PHP?
Jun 02, 2024 pm 02:26 PM
How to insert data into a MySQL table using PHP?
 How to fix mysql_native_password not loaded errors on MySQL 8.4
Dec 09, 2024 am 11:42 AM
How to fix mysql_native_password not loaded errors on MySQL 8.4
Dec 09, 2024 am 11:42 AM
How to fix mysql_native_password not loaded errors on MySQL 8.4
 How to use MySQL stored procedures in PHP?
Jun 02, 2024 pm 02:13 PM
How to use MySQL stored procedures in PHP?
Jun 02, 2024 pm 02:13 PM
How to use MySQL stored procedures in PHP?
 How to create a MySQL table using PHP?
Jun 04, 2024 pm 01:57 PM
How to create a MySQL table using PHP?
Jun 04, 2024 pm 01:57 PM
How to create a MySQL table using PHP?