 Web Front-end
Web Front-end
 JS Tutorial
JS Tutorial
 An in-depth and simple introduction to the code and text of JavaScript closures (Closure)
An in-depth and simple introduction to the code and text of JavaScript closures (Closure)
An in-depth and simple introduction to the code and text of JavaScript closures (Closure)
Closure (closure) is a very important threshold for mastering Javascript from the beginning to the in-depth. It is a difficulty of the Javascript language and also its characteristic. Many advanced applications It all depends on closure. Write down my study notes below~
Series Directory
Explain JavaScript in a simple and easy way
Explain JavaScript in a simple and easy way This
An in-depth introduction to the prototype chain and inheritance of JavaScript
Closure-everywhere
In front-end programming, the use of closures is very common. We often use closures intentionally or unintentionally, directly or indirectly. Closures can make data transfer more flexible (such as handling some click events)
!function() {
var localData = "localData here";
document.addEventListener('click', //处理点击事件时用到了外部局部变量,比如这里的localData
function(){
console.log(localData);
});
}();Another example is the following example: (Isn’t it very friendly~~)
!function() {
var localData = "localData here";
var url = "http://www.baidu.com/";
$.ajax({
url : url,
success : function() {
// do sth...
console.log(localData);
}
});
}();Let’s look at another example~~this This situation is what we usually call closure
function outer() {
var localVal = 30;
return function(){
return localVal;
}
}
var func = outer();
func(); // 30In this example, calling outer() returns the anonymous function function(). In this anonymous function, you can access the local variable localVal of outer(). When outer() is called After the end, when func() is called again, the local variable localVal of outer() can still be accessed
The concept of closure
Closure, unlike ordinary functions, allows a When a function is called outside the immediate lexical scope, it can still access non-local variables. –Wikipedia
A closure is a function that can read the internal variables of other functions. - Ruan Yifeng
Since in the Javascript language, only sub-functions inside the function can read local variables, closures can be simply understood as "functions defined inside a function".
So, in essence, closure is a bridge that connects the inside of a function with the outside of the function
The purpose of closure
This part is reproduced from this blog post
Closures can be used in many places. It has two greatest uses. One is to read the variables inside the function as mentioned earlier, and the other is to keep the values of these variables in memory.
function f1(){
var n=999;
nAdd=function(){n+=1}
function f2(){
alert(n);
}
return f2;
}
var result=f1();
result(); // 999
nAdd();
result(); // 1000In this code, result is actually the closure f2 function. It was run twice, the first time the value was 999, the second time the value was 1000. This proves that the local variable n in function f1 is always stored in memory and is not automatically cleared after f1 is called.
Why is this so? The reason is that f1 is the parent function of f2, and f2 is assigned to a global variable, which causes f2 to always be in memory, and the existence of f2 depends on f1, so f1 is always in memory and will not be deleted after the call is completed. , recycled by the garbage collection mechanism (garbage collection).
Another thing worth noting in this code is the line "nAdd=function(){n+=1}". First of all, the var keyword is not used before nAdd, so nAdd is a global variable. rather than local variables. Secondly, the value of nAdd is an anonymous function, and the anonymous function itself is also a closure, so nAdd is equivalent to a setter, which can operate on local variables inside the function outside the function.
Closure-Encapsulation
(function() {
var _userId = 23492;
var _typeId = 'item';
var export = {};
function converter(userId) {
return +userId;
}
export.getUserId = function() {
return converter(_userId);
}
export.getTypeId = function() {
return _typeId;
}
window.export = export; //通过此方式输出
}());
export.getUserId(); // 23492
export.getTypeId(); // item
export._userId; // undefined
export._typeId; // undefined
export.converter; // undefinedUsing the characteristics of closure allows us to encapsulate some complex function logic, In this example, the methods on export (getUserId, getTypeId) are called to indirectly access the private variables in the function, but _userId cannot be obtained by calling export._userId directly. This is also a commonly used feature in Node~
Common mistakes: loop closure
In the following case, we Add 3 ps with values aaa, bbb, and ccc. What we want to achieve is to click aaa to output 1, click bbb to output 2, and click ccc to output 3
document.body.innerHTML = "<p id=p1>aaa</p>" + "<p id=p2>bbb</p><p id=p3>ccc</p>";
for (var i = 1; i < 4; i++) {
document.getElementById('p' + i).
addEventListener('click', function() {
alert(i); // all are 4!
});
}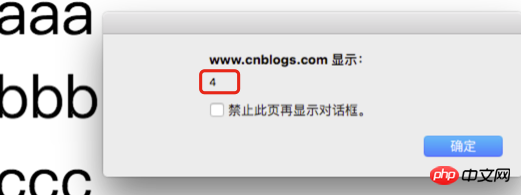
result Clicking aaa, bbb or ccc is all alert(4)~~
The problem is that the value of i is already 4 when the initialization is completed
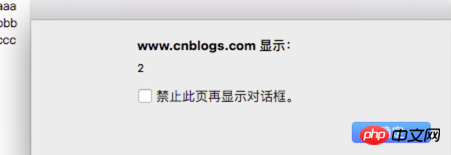
To achieve what we want, click aaa to output 1, click bbb to output 2, and click ccc to output 3. We need to use the closure technique. In each loop, wrap it with an anonymous function that is executed immediately, like this If you do this, the value of alert(i) each time will be taken from i in the closure environment. This i will output 1, 2, and 3 from the assignment i of each loop.
document.body.innerHTML = "<p id=p1>aaa</p>" + "<p id=p2>bbb</p>" + "<p id=p3>ccc</p>";
for (var i = 1; i < 4; i++) {
!function(i){ //②再用这个参数i,到getElementById()中引用
document.getElementById('p' + i).
addEventListener('click', function() {
alert(i); // 1,2,3
});
}(i); //①把遍历的1,2,3的值传到匿名函数里面
}
Thinking Questions
If you can understand the results of the following two pieces of code, you should understand the operating mechanism of closures. (From Teacher Ruan) This question is summarized in seconds~~
Code Fragment One
var name = "The Window";
var object = {
name : "My Object",
getNameFunc : function(){
return function(){
return this.name;
};
}
};
alert(object.getNameFunc()());Code Fragment Two
var name = "The Window";
var object = {
name : "My Object",
getNameFunc : function(){
var that = this;
return function(){
return that.name;
};
}
};
alert(object.getNameFunc()()); The above is an in-depth explanation of JavaScript closures (Closure) Code pictures and texts are introduced in detail. For more related content, please pay attention to the PHP Chinese website (www.php.cn)!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1376
1376
 52
52
 How to implement an online speech recognition system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 pm 02:54 PM
How to implement an online speech recognition system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 pm 02:54 PM
How to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online speech recognition system Introduction: With the continuous development of technology, speech recognition technology has become an important part of the field of artificial intelligence. The online speech recognition system based on WebSocket and JavaScript has the characteristics of low latency, real-time and cross-platform, and has become a widely used solution. This article will introduce how to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online speech recognition system.
 WebSocket and JavaScript: key technologies for implementing real-time monitoring systems
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:30 PM
WebSocket and JavaScript: key technologies for implementing real-time monitoring systems
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:30 PM
WebSocket and JavaScript: Key technologies for realizing real-time monitoring systems Introduction: With the rapid development of Internet technology, real-time monitoring systems have been widely used in various fields. One of the key technologies to achieve real-time monitoring is the combination of WebSocket and JavaScript. This article will introduce the application of WebSocket and JavaScript in real-time monitoring systems, give code examples, and explain their implementation principles in detail. 1. WebSocket technology
 How to implement an online reservation system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 am 09:39 AM
How to implement an online reservation system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 am 09:39 AM
How to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online reservation system. In today's digital era, more and more businesses and services need to provide online reservation functions. It is crucial to implement an efficient and real-time online reservation system. This article will introduce how to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online reservation system, and provide specific code examples. 1. What is WebSocket? WebSocket is a full-duplex method on a single TCP connection.
 How to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 12:09 PM
How to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 12:09 PM
Introduction to how to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system: With the popularity of the Internet and the advancement of technology, more and more restaurants have begun to provide online ordering services. In order to implement a real-time online ordering system, we can use JavaScript and WebSocket technology. WebSocket is a full-duplex communication protocol based on the TCP protocol, which can realize real-time two-way communication between the client and the server. In the real-time online ordering system, when the user selects dishes and places an order
 JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecasting system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecasting system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecast system Introduction: Today, the accuracy of weather forecasts is of great significance to daily life and decision-making. As technology develops, we can provide more accurate and reliable weather forecasts by obtaining weather data in real time. In this article, we will learn how to use JavaScript and WebSocket technology to build an efficient real-time weather forecast system. This article will demonstrate the implementation process through specific code examples. We
 Simple JavaScript Tutorial: How to Get HTTP Status Code
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
Simple JavaScript Tutorial: How to Get HTTP Status Code
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
JavaScript tutorial: How to get HTTP status code, specific code examples are required. Preface: In web development, data interaction with the server is often involved. When communicating with the server, we often need to obtain the returned HTTP status code to determine whether the operation is successful, and perform corresponding processing based on different status codes. This article will teach you how to use JavaScript to obtain HTTP status codes and provide some practical code examples. Using XMLHttpRequest
 How to use insertBefore in javascript
Nov 24, 2023 am 11:56 AM
How to use insertBefore in javascript
Nov 24, 2023 am 11:56 AM
Usage: In JavaScript, the insertBefore() method is used to insert a new node in the DOM tree. This method requires two parameters: the new node to be inserted and the reference node (that is, the node where the new node will be inserted).
 How to get HTTP status code in JavaScript the easy way
Jan 05, 2024 pm 01:37 PM
How to get HTTP status code in JavaScript the easy way
Jan 05, 2024 pm 01:37 PM
Introduction to the method of obtaining HTTP status code in JavaScript: In front-end development, we often need to deal with the interaction with the back-end interface, and HTTP status code is a very important part of it. Understanding and obtaining HTTP status codes helps us better handle the data returned by the interface. This article will introduce how to use JavaScript to obtain HTTP status codes and provide specific code examples. 1. What is HTTP status code? HTTP status code means that when the browser initiates a request to the server, the service



