 Java
Java
 javaTutorial
javaTutorial
 Graphical introduction to the differences between String, StringBuffer and StringBuilder and stack memory allocation in Java
Graphical introduction to the differences between String, StringBuffer and StringBuilder and stack memory allocation in Java
Graphical introduction to the differences between String, StringBuffer and StringBuilder and stack memory allocation in Java
The String class in Java is a very commonly used class, but the least attention is paid to its details, so most interviews will focus on this class. For example, String str = new String("hello"); opens up several memory spaces, the difference between String and StringBuffer, etc. Here is my understanding:
String is a class modified by final and cannot be inherited. StringBuffer is also a class modified by final.
1. JVM memory division
There are mainly 4 pieces of memory in java. These memory spaces are: stack memory space, heap memory space, global data area, and global code area
1. Stack memory space: Save all object names (the address of the referenced heap memory space is saved)
2. Heap memory space: Save the specific content of each object
3. Global data area: Save static type data attributes (global data)
4. Global code area: Save all method definitions
In the JVM, heap memory is the memory space that stores the content of object instantiation (program data). Stack memory stores the name of the object, and its content points to the address of the corresponding heap.
It can also be said that: all object names are stored in stack memory, and the specific contents of the objects are maintained in heap memory. Reference type data must use the new keyword to open up space in heap memory.
2. Memory allocation of Sring
String has a special feature: when constructing a String object, you can use new construction or "hello" direct construction. Of the two methods, it is recommended to use the second one.
1. String a = "hello";
2. String a= new String("hello");
The explanation is as follows:
1: An object reference a is defined in the stack memory, pointing to the memory address of the value "hello" in the heap memory. Finally a memory space was opened up
2: An object reference of a is redefined in the stack memory, first pointing to the memory address of the heap memory with the value "hello", and then pointing to the address of the heap memory with the value of "hello" after new. In the end, two spaces were opened up. The first space has no object references and will be garbage collected by the JVM.
The diagram is as follows:
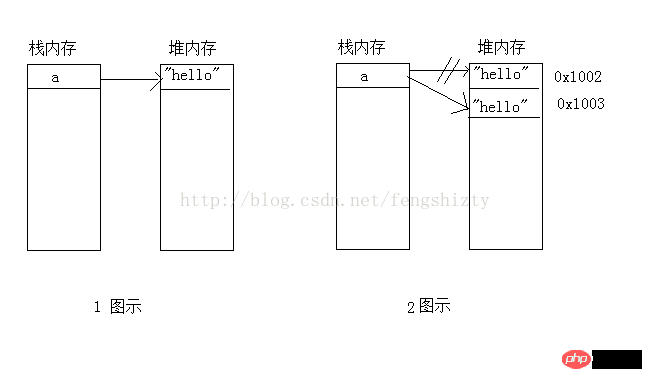
It is not difficult to understand the following codes after understanding the above:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 |
|
##Among them only a==b==d and c=e.
The difference is that StringBuilder is not thread synchronized, so its operation must be more efficient than StringBuffer.
This is what some people will think:
String str = "hello"; Hasn’t it also changed?
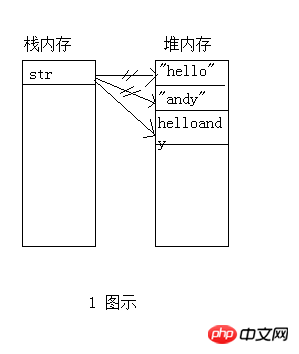
Therefore, when cyclically assigning values to a string, it is best to use StringBuffer (thread-safe) or StringBuilder, which can save memory and improve performance. Remember
.

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1376
1376
 52
52
 Convert basic data types to strings using Java's String.valueOf() function
Jul 24, 2023 pm 07:55 PM
Convert basic data types to strings using Java's String.valueOf() function
Jul 24, 2023 pm 07:55 PM
Convert basic data types to strings using Java's String.valueOf() function In Java development, when we need to convert basic data types to strings, a common method is to use the valueOf() function of the String class. This function can accept parameters of basic data types and return the corresponding string representation. In this article, we will explore how to use the String.valueOf() function for basic data type conversions and provide some code examples to
 How to convert char array to string
Jun 09, 2023 am 10:04 AM
How to convert char array to string
Jun 09, 2023 am 10:04 AM
Method of converting char array to string: It can be achieved by assignment. Use {char a[]=" abc d\0efg ";string s=a;} syntax to let the char array directly assign a value to string, and execute the code to complete the conversion.
 Convert string to StringBuilder in Java
Sep 02, 2023 pm 03:57 PM
Convert string to StringBuilder in Java
Sep 02, 2023 pm 03:57 PM
The append() method of StringBuilder class accepts a String value and adds it to the current object. Convert string value to StringBuilder object - Get string value. Append using the append() method to get the string into the StringBuilder. Example In the following Java program, we are converting an array of strings into a single StringBuilder object. Real-time demonstration publicclassStringToStringBuilder{ publicstaticvoidmain(Stringargs[]){&a
 Use the delete() method of the StringBuilder class in Java to delete part of the content in the string
Jul 26, 2023 pm 08:43 PM
Use the delete() method of the StringBuilder class in Java to delete part of the content in the string
Jul 26, 2023 pm 08:43 PM
Use the delete() method of the StringBuilder class in Java to delete part of the content in a string. The String class is a commonly used string processing class in Java. It has many commonly used methods for string operations. However, in some cases, we need to frequently modify strings, and the immutability of the String class will lead to frequent creation of new string objects, thus affecting performance. To solve this problem, Java provides the StringBuilder class, which
 What are the methods to clear stringbuilder?
Oct 12, 2023 pm 04:57 PM
What are the methods to clear stringbuilder?
Oct 12, 2023 pm 04:57 PM
The methods to clear stringbuilder are: 1. Use the setLength(0) method to clear the StringBuilder object; 2. Use the delete(0, length) method to clear the StringBuilder object; 3. Use the replace(0, length, "") method to clear the StringBuilder object; 4. , Use new StringBuilder() to re-create a new StringBuilder object.
 Use Java's String.replace() function to replace characters (strings) in a string
Jul 25, 2023 pm 05:16 PM
Use Java's String.replace() function to replace characters (strings) in a string
Jul 25, 2023 pm 05:16 PM
Replace characters (strings) in a string using Java's String.replace() function In Java, strings are immutable objects, which means that once a string object is created, its value cannot be modified. However, you may encounter situations where you need to replace certain characters or strings in a string. At this time, we can use the replace() method in Java's String class to implement string replacement. The replace() method of String class has two types:
 Use java's StringBuilder.replace() function to replace a specified range of characters
Jul 24, 2023 pm 06:12 PM
Use java's StringBuilder.replace() function to replace a specified range of characters
Jul 24, 2023 pm 06:12 PM
Use java's StringBuilder.replace() function to replace a specified range of characters. In Java, the StringBuilder class provides the replace() method, which can be used to replace a specified range of characters in a string. The syntax of this method is as follows: publicStringBuilderreplace(intstart,intend,Stringstr) The above method is used to replace the index star from
 Interpretation of Java documentation: Detailed introduction to the substring() method of the StringBuilder class
Nov 03, 2023 pm 04:31 PM
Interpretation of Java documentation: Detailed introduction to the substring() method of the StringBuilder class
Nov 03, 2023 pm 04:31 PM
Interpretation of Java documentation: Detailed introduction to the substring() method of the StringBuilder class Introduction: In Java programming, string processing is one of the most common operations. Java provides a series of classes and methods for string processing, among which the StringBuilder class is a commonly used choice for frequent string operations. In the StringBuilder class, the substring() method is a very useful method for intercepting substrings of strings. This article will



