 Java
Java
 javaTutorial
javaTutorial
 Java network programming from simple to advanced 3. Learn about non-blocking communication in detail with graphic code examples
Java network programming from simple to advanced 3. Learn about non-blocking communication in detail with graphic code examples
Java network programming from simple to advanced 3. Learn about non-blocking communication in detail with graphic code examples
This article introduces in detail the major categories that make up non-blocking communication: Buffer, Channel, Selector, SelectionKey
Non-blocking communication process
ServerSocketChannel obtains ServerSocketChannel through the open method, sets it to non-blocking mode through ServerSocketChannel, and then obtains the socket through ServerSocketChannel, binding Determine the service process listening port. The service started successfully.
Then there is the essence of non-blocking communication. Selector obtains Selector through the static open() method, and then ServerSocketChannel registers the Selection.OP_ACCEPT event to Selector.
Selector will monitor the occurrence of events. Selector monitors the number of SelectionKey objects that have occurred through select(), and returns the corresponding selectionKey object collection through the selectKeys() method. Traverse the collection to obtain the corresponding selectionKey object, obtain the associated ServerSocketChannel object through the channel() method of the object, and obtain the associated Selector object through the selector() method.
Execute the accept() method through the ServerSocketChannel obtained above to obtain the SocketChannel, then set the SocketChannel to non-blocking mode, register the SocketChannel to the Selector created above, and register the
SelectionKey .OP_READ |SelectionKey.OP_WRITEevent.Selector will monitor the corresponding events bound above, and perform read and write operations if the corresponding events are monitored.
Sample code:
The above describes a process of server-side non-blocking communication. The following is implemented through specific code:
/**
* 非阻塞模式
*
*/public class EchoServer2 {
private Selector selector = null;
private ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = null;
private int port = 8001;
private Charset charset = Charset.forName("UTF-8");
public EchoServer2() throws IOException {
selector = Selector.open();
serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open(); //服务器重启的时候,重用端口
serverSocketChannel.socket().setReuseAddress(true); //设置非阻塞模式
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
serverSocketChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(port));
System.out.println("服务器启动成功");
} /**
* 服务方法
*/
public void service() throws IOException {
serverSocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
while (selector.select() > 0) {
Set readyKes = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator it = readyKes.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = null;
try {
key = (SelectionKey) it.next();
it.remove();
if (key.isAcceptable()) {
System.out.println("连接事件");
//连接事件
ServerSocketChannel ssc = (ServerSocketChannel) key.channel();
SocketChannel socketChannel = ssc.accept();
System.out.println("接收到客户连接,来自:" + socketChannel.socket().getInetAddress() + " : " + socketChannel.socket().getPort());
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ |
SelectionKey.OP_WRITE, buffer);
} else if (key.isReadable()) {
//接收数据
receive(key);
} else if (key.isWritable()) {
//发送数据
send(key);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
try {
if (key != null) {
key.cancel();
key.channel().close();
}
}catch (IOException ex){
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
} private void send(SelectionKey key) throws IOException {
ByteBuffer buffer = (ByteBuffer) key.attachment();
SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
buffer.flip(); //把极限设置为位置,把位置设置为0
String data = decode(buffer);
if (data.indexOf("\r\n") == -1) {
return;
}
String outputData = data.substring(0, data.indexOf("\n") + 1);
System.out.println("请求数据:" + outputData);
ByteBuffer outputBuffer = encode("echo:" + outputData);
while (outputBuffer.hasRemaining()) {
channel.write(outputBuffer);
}
ByteBuffer temp = encode(outputData);
buffer.position(temp.limit());
buffer.compact(); if (outputData.equals("bye\r\n")) {
key.cancel();
channel.close();
System.out.println("关闭与客户的连接");
}
} private String decode(ByteBuffer buffer) {
CharBuffer charBuffer = charset.decode(buffer); return charBuffer.toString();
} private ByteBuffer encode(String s) { return charset.encode(s);
} private void receive(SelectionKey key) throws IOException {
ByteBuffer buffer = (ByteBuffer) key.attachment();
SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
ByteBuffer readBuff = ByteBuffer.allocate(32);
socketChannel.read(readBuff);
readBuff.flip();
buffer.limit(buffer.capacity());
buffer.put(readBuff);
} public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { new EchoServer2().service();
}
}/**
* 创建非阻塞客户端
*
*/public class EchoClient2 {
private SocketChannel socketChannel; private int port = 8001; private Selector selector; private ByteBuffer sendBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); private ByteBuffer receiveBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); private Charset charset = Charset.forName("UTF-8"); public EchoClient2() throws IOException {
socketChannel = SocketChannel.open();
InetSocketAddress inetSocketAddress = new InetSocketAddress(InetAddress.getLocalHost(), port);
socketChannel.connect(inetSocketAddress);//
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);//设置为非阻塞模式
System.out.println("与服务器连接成功");
selector = Selector.open();
} public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { final EchoClient2 client = new EchoClient2();
Thread receiver = new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override
public void run() {
client.receiveFromUser();
}
});
receiver.start();
client.talk();
} private void receiveFromUser() { try {
System.out.println("请输入数据:");
BufferedReader localReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String msg = null; while ((msg = localReader.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.println("用户输入的数据:" + msg); synchronized (sendBuffer) {
sendBuffer.put(encode(msg + "\r\n"));
} if (msg.equalsIgnoreCase("bye")) { break;
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} private ByteBuffer encode(String s) { return charset.encode(s);
} private void talk() throws IOException {
socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ | SelectionKey.OP_WRITE); while (selector.select() > 0) {
Set<SelectionKey> keys = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator<SelectionKey> it = keys.iterator(); while (it.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = null; try {
key = it.next();
it.remove(); if (key.isReadable()) { //System.out.println("读事件");
//读事件
receive(key);
} if (key.isWritable()) { // System.out.println("写事件");
//写事件
send(key);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace(); if (key != null) {
key.cancel();
key.channel().close();
}
}
}
}
} private void send(SelectionKey key) throws IOException {
SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel) key.channel(); synchronized (sendBuffer) {
sendBuffer.flip();//把极限设为位置,把位置设为零
channel.write(sendBuffer);
sendBuffer.compact();//删除已经发送的数据。
}
} private void receive(SelectionKey key) throws IOException {
SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
channel.read(receiveBuffer);
receiveBuffer.flip();//将limit的值设置为position的值,将position的值设置为0
String receiveData = decode(receiveBuffer); if (receiveData.indexOf("\n") == -1) { return;
}
String outputData = receiveData.substring(0, receiveData.indexOf("\n") + 1);
System.out.println("响应数据:" + outputData); if (outputData.equalsIgnoreCase("echo:bye\r\n")) {
key.cancel();
socketChannel.close();
;
System.out.println("关闭与服务器的连接");
selector.close();
System.exit(0);
}
ByteBuffer temp = encode(outputData);
receiveBuffer.position(temp.limit());
receiveBuffer.compact();//删除已经打印的数据
} private String decode(ByteBuffer receiveBuffer) {
CharBuffer buffer = charset.decode(receiveBuffer); return buffer.toString();
}
}How to implement non-blocking communication
Buffer
Channel
Selector
Buffer
Function: Reduce the number of physical reads and writes, and reduce the number of memory creation and destruction. Buffer attributes: capacity (maximum capacity), limit (actual capacity), position (current position). PS: Other places are translated into capacity (capacity), limit (limit), position (position). I personally think it is better to understand it when translated into the above. Why use the following method? You can understand it through analysis and diagrams. Of course it is best to express it most clearly in English.
The relationship between the three attributes is: capacity≥limit≥position≥0
The graphic relationship is as follows: 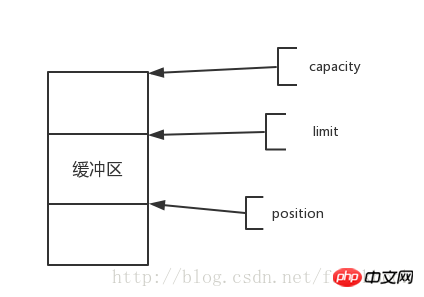
Buffer class structure:
java.nio.ByteBuffer class It is an abstract class and cannot be instantiated. However, 8 specific implementation classes are provided, of which the most basic buffer is ByteBuffer, which stores data units in bytes. 
Commonly used methods:
clear(): Set limit to capacity, and then set the position to 0
flip(): Set limit to position, and then set position to 0.
rewind(): Do not change the limit and set the position to 0.
allocate(): Create a buffer, the method parameter specifies the buffer size
compact(): Copies the bytes (if any) between the buffer's current position and the limit to the beginning of the buffer.
Test the above method:
Test the clear() method
@Test
public void testClear() { //创建一个10chars大小的缓冲区,默认情况下limit和capacity是相等的
CharBuffer buffer = CharBuffer.allocate(10);
System.out.println("创建默认情况");
printBufferInfo(buffer);
buffer.limit(8);//修改limit的值
System.out.println("修改limit后");
printBufferInfo(buffer); // clear():把limit设置为capacity,再把位置设为0
buffer.clear();
System.out.println("执行clear()方法后");
printBufferInfo(buffer);
}The execution results are as follows: 
Test the flip() method:
@Test
public void testFlip() {
CharBuffer buffer = CharBuffer.allocate(10);
System.out.println("创建默认情况");
printBufferInfo(buffer); //put的方法会修改position的值
buffer.put('H');
buffer.put('E');
buffer.put('L');
buffer.put('L');
buffer.put('O');
System.out.println("调用put方法后:");
printBufferInfo(buffer); //flip():把limit设置为position,再把位置设置为0。
buffer.flip();
System.out.println("调用flip方法后:");
printBufferInfo(buffer);
}The execution results are as follows: 
Test the rewind() method
@Test
public void testRewind() {
CharBuffer buffer = CharBuffer.allocate(10);
System.out.println("创建默认情况");
printBufferInfo(buffer); //put的方法会修改position的值
buffer.put('H');
buffer.put('E');
buffer.put('L');
buffer.put('L');
buffer.put('O');
buffer.limit(8);
System.out.println("调用put、limit方法后:");
printBufferInfo(buffer); //rewind():不改变limit,把位置设为0。
buffer.rewind();
System.out.println("调用rewind方法后:");
printBufferInfo(buffer);
}The execution results are as follows: 
Test compact() method
@Test
public void testCompact(){
CharBuffer buffer = CharBuffer.allocate(10);
System.out.println("创建默认情况");
printBufferInfo(buffer); //put的方法会修改position的值
buffer.put('H');
buffer.put('E');
buffer.put('L');
buffer.put('L');
buffer.put('O');
buffer.limit(8);//修改limit的值
System.out.println("调用put和limit方法后:");
printBufferInfo(buffer);
System.out.println("调用compact方法后:"); //将缓冲区的当前位置和界限之间的字节(如果有)复制到缓冲区的开始处。
buffer.compact();
printBufferInfo(buffer);
}
This This is the function of this method introduced in the JDK:
Copy the bytes (if any) between the current position of the buffer and the limit to the beginning of the buffer. That is, copy the byte at index p = position() to index 0, copy the byte at index p + 1 to index 1, and so on until the byte at index limit() - 1 is copied to Index n = limit() - 1 - p. Then set the buffer's position to n+1 and its bounds to its capacity. If the tag is already defined, it is discarded.
The official statement is too difficult to understand:
将缓冲区的当前位置和界限之间的字节(如果有)复制到缓冲区的开始处。并将limit(实际容量)设置为 capacity(最大容量)。执行compact()方法前,limit的值是:8,position的值是:5。按照上面描述的执行完compact()后,position的值计算方式是:n+1;n=limit-1-p;所有n=8-1-5=2,最后position的值为:2+1=3。和程序运行的结果一致。
可以在这种情况:从缓冲区写入数据之后调用此方法,以防写入不完整。
buf.clear(); // Prepare buffer for use
while (in.read(buf) >= 0 || buf.position != 0) {
buf.flip();
out.write(buf);
buf.compact(); // In case of partial write
}如果out.write()方法没有将缓存中的数据读取完,这个时候的position位置指向的是剩余数据的位置。达到防止写入不完整。
通道
作用: 连接缓冲区与数据源或数据目的地。
常用类:
Channel
接口有下面两个子接口ReadableByteChannel和WritableByteChannel和一个抽象实现类SelectableChannel。
在ReadableByteChannel接口中申明了read(ByteBuffer
dst)方法。在WritableByteChannel接口中申明了write(ByteBuffer[]
srcs):方法。SelectableChannel抽象类中主要方法,configureBlocking(boolean
block)、register();方法。 ByteChannel
接口继承了ReadableChannel和WritableChannel。所以ByteChannel具有读和写的功能。ServerSocketChannel继承了SelectableChannel类抽象类,所以SocketChannel具有设置是否是阻塞模式、向selector注册事件功能。
SocketChannel也继承了SelectableChannel类还实现ByteChannel接口,所以SocketChannel具有设置是否是阻塞模式、向selector注册事件、从缓冲区读写数据的功能。
通过类图展现: 
Selector类:
作用:只要ServerSocketChannel及SocketChannel向Selector注册了特定的事件,Selector就会监听这些事件的发生。
流程:
Selector通过静态的open()方法创建一个Selector对象,SelectableChannel类向Selector注册了特定的事件。Selector就会监控这些事件发生,Selector通过select()监控已发生的SelectionKey对象的数目,通过selectKeys()方法返回对应的selectionKey对象集合。遍历该集合得到相应的selectionKey对象,通过该对象的channel()方法获取关联的SelectableChannel对象,
通过selector()方法就可以获取关联的Selector对象。
Note:
当Selector的select()方法还有一个重载方式:select(long timeout)。并且该方法采用阻塞的工作方式,如果相关事件的selectionKey对象的数目一个也没有,就进入阻塞状态。知道出现以下情况之一,才从select()方法中返回。
至少有一个SelectionKey的相关事件已经发生。
其他线程调用了Selector的wakeup()方法,导致执行select()方法的线程立即返回。
当前执行的select()方法的线程被中断。
超出了等待时间。仅限调用select(long timeout)方法时出现。如果没有设置超时时间,则永远不会超时。
Selector类有两个非常重要的方法: 静态方法open(),这是Selector的静态工厂方法,创建一个Selector对象。
selectedKeys()方法返回被Selector捕获的SelectionKey的集合。
SelectionKey类
作用:
ServerSocketChannel或SocketChannel通过register()方法向Selector注册事件时,register()方法会创建一个SelectionKey对象,该对象是用来跟踪注册事件的句柄。在SelectionKey对象的有效期间,Selector会一直监控与SelectionKey对象相关的事件,如果事件发生,就会把SelectionKey对象添加到Selected-keys集合中。SelectionKey中定义的事件: 定义了4种事件:
1、SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT:接收连接就绪事件,表示服务器监听到了客户连接,服务器可以接收这个连接了。常量值为16.
2、SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT:连接就绪事件,表示客户与服务器的连接已经建立成功。常量值为8.
3、SelectionKey.OP_READ:读就绪事件,表示通道中已经有了可读数据可以执行读操作。常量值为1.
4、SelectionKey.OP_WRITE:写就绪事件,表示已经可以向通道写数据了。常量值为4.Common methods:
channel() method: Returns the SelectedChannel associated with it (including ServerSocketChannel and SocketChannel).
selector() method: Returns the Selector object associated with it.
The relationship between them is as follows:
The above is the detailed explanation of the graphic and text code examples of non-blocking communication from Java network programming to understanding non-blocking communication, and more related content Please pay attention to the PHP Chinese website (www.php.cn)!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
In this article, we have kept the most asked Java Spring Interview Questions with their detailed answers. So that you can crack the interview.
 Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8 introduces the Stream API, providing a powerful and expressive way to process data collections. However, a common question when using Stream is: How to break or return from a forEach operation? Traditional loops allow for early interruption or return, but Stream's forEach method does not directly support this method. This article will explain the reasons and explore alternative methods for implementing premature termination in Stream processing systems. Further reading: Java Stream API improvements Understand Stream forEach The forEach method is a terminal operation that performs one operation on each element in the Stream. Its design intention is
 How to convert XML to PDF on your phone?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
How to convert XML to PDF on your phone?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
It is not easy to convert XML to PDF directly on your phone, but it can be achieved with the help of cloud services. It is recommended to use a lightweight mobile app to upload XML files and receive generated PDFs, and convert them with cloud APIs. Cloud APIs use serverless computing services, and choosing the right platform is crucial. Complexity, error handling, security, and optimization strategies need to be considered when handling XML parsing and PDF generation. The entire process requires the front-end app and the back-end API to work together, and it requires some understanding of a variety of technologies.
 Java Program to Find the Volume of Capsule
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Java Program to Find the Volume of Capsule
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Capsules are three-dimensional geometric figures, composed of a cylinder and a hemisphere at both ends. The volume of the capsule can be calculated by adding the volume of the cylinder and the volume of the hemisphere at both ends. This tutorial will discuss how to calculate the volume of a given capsule in Java using different methods. Capsule volume formula The formula for capsule volume is as follows: Capsule volume = Cylindrical volume Volume Two hemisphere volume in, r: The radius of the hemisphere. h: The height of the cylinder (excluding the hemisphere). Example 1 enter Radius = 5 units Height = 10 units Output Volume = 1570.8 cubic units explain Calculate volume using formula: Volume = π × r2 × h (4
 PHP vs. Python: Understanding the Differences
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:15 AM
PHP vs. Python: Understanding the Differences
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:15 AM
PHP and Python each have their own advantages, and the choice should be based on project requirements. 1.PHP is suitable for web development, with simple syntax and high execution efficiency. 2. Python is suitable for data science and machine learning, with concise syntax and rich libraries.
 Create the Future: Java Programming for Absolute Beginners
Oct 13, 2024 pm 01:32 PM
Create the Future: Java Programming for Absolute Beginners
Oct 13, 2024 pm 01:32 PM
Java is a popular programming language that can be learned by both beginners and experienced developers. This tutorial starts with basic concepts and progresses through advanced topics. After installing the Java Development Kit, you can practice programming by creating a simple "Hello, World!" program. After you understand the code, use the command prompt to compile and run the program, and "Hello, World!" will be output on the console. Learning Java starts your programming journey, and as your mastery deepens, you can create more complex applications.
 How to Run Your First Spring Boot Application in Spring Tool Suite?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:11 PM
How to Run Your First Spring Boot Application in Spring Tool Suite?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:11 PM
Spring Boot simplifies the creation of robust, scalable, and production-ready Java applications, revolutionizing Java development. Its "convention over configuration" approach, inherent to the Spring ecosystem, minimizes manual setup, allo
 PHP: A Key Language for Web Development
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:08 AM
PHP: A Key Language for Web Development
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:08 AM
PHP is a scripting language widely used on the server side, especially suitable for web development. 1.PHP can embed HTML, process HTTP requests and responses, and supports a variety of databases. 2.PHP is used to generate dynamic web content, process form data, access databases, etc., with strong community support and open source resources. 3. PHP is an interpreted language, and the execution process includes lexical analysis, grammatical analysis, compilation and execution. 4.PHP can be combined with MySQL for advanced applications such as user registration systems. 5. When debugging PHP, you can use functions such as error_reporting() and var_dump(). 6. Optimize PHP code to use caching mechanisms, optimize database queries and use built-in functions. 7






