 Backend Development
Backend Development
 C#.Net Tutorial
C#.Net Tutorial
 Detailed introduction to C# container classes, interfaces, and performance
Detailed introduction to C# container classes, interfaces, and performance
Detailed introduction to C# container classes, interfaces, and performance
1 indexer
[]The declared variable must be of fixed length, that is, the length is static; object[] objectArray = new object[10] ;
objectArray is shallow copy, that is, only assign an address value to it in memory. At this time, each item is a null reference;
Application examples
AdjustablePanel[] adjustPanelArrays = new AdjustablePanel[12];
foreach (Control ultraControl in this.Controls)
{ if (ultraControl.GetType() == typeof(UltraGrid) ||
ultraControl.GetType() == typeof(UltraChart) || ultraControl.GetType() == typeof(Panel))
{ //adjustPanelArrays[index]此时为null,因此会出现null引用bug
adjustPanelArrays[index].Controls.Add(ultraControl);
}
}2 Array
Provides Create, Operation, Search and Sort methods of arrays and thus serves as the base class for all arrays in the common language runtime. The length is fixed and cannot be dynamically increased on demand; Array is an abstract class and cannot be created using new Array; GetValue returns the object type.
Array myArray = Array.CreateInstance(typeof(int),3);
myArray.SetValue(1,0);
myArray.SetValue(2,1);
myArray.SetValue(3,2); //GetValue返回的是object类型,需要进行类型提升为int
int val2 = (int)myArray.GetValue(2);3 ArrayList
Implement the IList interface using an array whose size can be dynamically increased on demand, and is for any type.
ArrayList al = new ArrayList();
ArrayList arrayList = new ArrayList();
al.Add("qaz");
al.Add(1);
al.Add(new List<object>());
string str = (string)al[0];
int intval = (int)al[1];
List<object> objs = (List<object>)al[2];Summary
[], The length of Array needs to be known before compilation, it is static, and the type needs to be uniquely determined. Array is an abstract class, and Array is required to create it. CreateInstance();
The length of ArrayList is unknown at compile time, it is dynamic, and the added elements can be of different types.
4 List-APIs
4-1 Introduction
List< T> is a generic class that implements the interface IList< T>, The external interface is displayed by using a dynamically adjusted array internally.
4-2 Add elements
Implement adding an element
Add(obj)
Add elements to the list in batches:
AddRange(objList)
Example:
private List<int> intList = new List<int>(); public void AddApi()
{
intList.Add(10); //添加1个元素
intList.AddRange(new List<int>() { 5, 1, 1, 2, 2, 3 }); //批量添加元素
}Insert an element in the collection at the specified index
void Insert(int index, T item);
void InsertRange(int index, IEnumerable《T》 collection)
4-3 Remove the element
Assume that intList is a List type, and the initial value is {10,5,1,1, 2,2,3}. Execution:
intList.Remove(1);
Remove the first occurrence of a specific object from the intList. After removing element 1, intList = {10,5,1,2,2,3};
Remove a certain range of elements:
intList.RemoveRange(0, 2);
intList = {2,2,3 };
After removing all duplicate elements: intList = {3};
intList.RemoveAll(removeDuplicateElements);
intList.RemoveAll(i =>
{ List<int> elementList = intList.FindAll(r => r.Equals(i)); if (elementList != null && elementList.Count > 1) return true; return false;
});When judging whether an element exists above, such as when removing an element, equality needs to be used Comparators. If type T implements the IEquatable< Let’s look at an example of implementing an interface that is not the default comparator: public class MyObject
{ public int Value { get; set; }
public MyObject(int value)
{ this.Value = value;
}
} //实现接口IEquatable<MyObject>
public class MyObjectCollection : IEquatable<MyObject>
{ private List<MyObject> _myObjects = new List<MyObject>()
{ new MyObject(3),
new MyObject(4),
new MyObject(3),
new MyObject(2),
new MyObject(3)
}; //删除所有重复的元素
public void RemoveDuplicates()
{
_myObjects.RemoveAll(Equals);
} public List<MyObject> MyObjects
{ get
{ return _myObjects;
}
}
public bool Equals(MyObject other)
{
MyObject duplicate = _myObjects.Find(r => r.Value == other.Value);
if (duplicate != null && duplicate!=other)
return true;
return false;
}
}
4-4 Find elements
Determine whether an element is in the List.
bool Contains(obj)
Determines whether it contains elements that match the conditions defined by the specified predicate.
bool Exists(Predicate<T> match)
Search for elements that match the conditions defined by the specified predicate and return the first matching element.
T Find(Predicate<T> match)
Retrieves all elements that match the conditions defined by the specified predicate.
List<T> FindAll(Predicate<T> match)
Search for elements that match the conditions defined by the specified predicate and return the zero-based index of the first matching element
int FindIndex(Predicate<T> match)
Search for elements that match the conditions defined by the specified predicate of elements and returns the zero-based index of the first occurrence in the range of elements from the specified index to the last element.
int FindIndex(int startIndex, Predicate<T> match)
Search for elements that match the conditions defined by the specified predicate and return the zero-based index of the first occurrence in a range of elements starting at the specified index and containing the specified number of elements
int FindIndex(int startIndex, int count, Predicate<T> match)
T FindLast(Predicate<T> match)
int FindLastIndex(Predicate<T> match)
int FindLastIndex(int startIndex, Predicate<T> match)
int FindLastIndex(int startIndex, int count, Predicate<T> match)
Searches the specified object and returns the zero-based index of the first match
int IndexOf(T item)
Searches the specified object and returns the first match in the range of elements from the specified index to the last element The zero-based index of the item
int IndexOf(T item, int index)
int IndexOf(T item, int index, int count)
Searches the specified object and returns the zero-based index of the last matching item.
int LastIndexOf(T item)
int LastIndexOf(T item, int index)
int LastIndexOf(T item, int index, int count)
4-5 Binary Search
Use the default comparator to search for an element in the entire
sortedList and return the zero-based index of the element.
int BinarySearch(T item);
Searches the entire sorted list for an element using the specified comparator and returns the zero-based index of the element.
int BinarySearch(T item, IComparer<T> comparer)
int BinarySearch(int index, int count, T item, IComparer<T> comparer)
4-6 SortingUse the default comparator to sort the elements in the entire List.
void Sort()
Use the specified System.Comparison to sort the elements in the entire List.
void Sort(Comparison<T> comparison)
Use the specified comparator to sort the elements in the List.
void Sort(IComparer<T> comparer)
void Sort(int index, int count, IComparer<T> comparer)
4-7 Performance analysis
| Time complexity | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Insert | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Remove | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| GetAnItem | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sort | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Find | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
4-8 附使用陷阱点:1 list.Min() 和 list.Max() 和 Average()等Linq方法,当list元素个数为0,则会出现“序列不包含任何元素”的异常。 2 object.ToString() 使用前要检测object是否为null。 3 Foreach遍历时,迭代器是不允许增加或删除的。例如: public List<MDevice> GetNormalDevices(List<MDevice> devices)
{
rtnDevices = devices; foreach (var device in devices)
{ var tmpdevices = bslMDevice.GetMDeviceByDeviceCode(device.DeviceCode);
if (!devices[0].IsNormal)
{ //这是非法的,因为移除rtnDevices列表的一个元素,等价于移除devices列表。
rtnDevices.Remove(device);
}
}
}Copy after login 5 SortedList5-1 SortedList简介Sorted表明了它内部实现自动排序,List表明了它有点像List,可以通过index访问集合中的元素。 5-2 内部实现机理一个SortedList对象内部维护了2个数组,以此来存储元素,其中一个数组用来存放键(keys),另一个存放键关联的值(values)。每一个元素都是键值对(key/value pair)。key不能是null,value可以。 5-3 总结API5-3-1 Capacity一个SortedList对象的容量是SortedList能容纳的元素数,这个值是动态变化,自动调整的。如下所示: SortedList mySL = new SortedList();
mySL.Add("Third", "!");
mySL.Add("Second", "World");
mySL.Add("First", "Hello");
Console.WriteLine( "mySL" );
Console.WriteLine( " Capacity: {0}", mySL.Capacity );Copy after login 此时Capacity: 16 如果添加到mySL中的元素增多,相应的Capacity会相应的自动变大。 5-3-2 访问元素通过index访问SortedList对象要想通过index访问,需要使用构造函数SortedList() 或 SortedList(IComparer icompared)。 SortedList sortedList = new SortedList(); sortedList.Add(3,"gz"); sortedList.Add(9, "lhx"); sortedList.Add(3, "gz");object getByIndex = sortedList.GetByIndex(2); Copy after login 通过key访问SortedList对象要想通过key访问,需要使用带有TKey,TValue的泛型构造函数。 SortedList<int,string> sortedList = new SortedList<int,string>(); sortedList.Add(3,"gz"); sortedList.Add(9, "lhx");object getByIndex = sortedList[3]; Copy after login 5-3-3排序SortedList有一种默认的比较顺序,比如下面的代码: SortedList<int,string> sortedList = new SortedList<int,string>(); sortedList.Add(9,"gz"); sortedList.Add(3, "lhx"); Copy after login Copy after login 结果是 sortedList中第一个对是3,”lhx” 如果不想按照默认的排序顺序,需要自己在构造时定制一种排序顺序,如下面的代码: 实现排序接口新建一个私有排序类,实现接口IComparer private class ImplementICompare: IComparer<int>
{ public int Compare(int x, int y)
{ return x < y ? 1 : -1;
}
}Copy after login 构造SortedListImplementICompare impleCompare = new ImplementICompare(); SortedList<int, string> sortedList = new SortedList<int, string>(impleCompare); sortedList.Add(9,"gz"); sortedList.Add(3, "lhx"); Copy after login 按照键从大到小的顺序排序,结果是 sortedList中第一个对是9,”gz” 5-3-4 添加元素用add接口实现添加某个元素到集合中,不允许重复添加相同键。 SortedList<int,string> sortedList = new SortedList<int,string>(); sortedList.Add(9,"gz"); sortedList.Add(3, "lhx"); Copy after login Copy after login 5-3-5 移除元素移除集合中指定元素Remove(object removedElement);指定index处移除元素RemoveAt(int index)。 Remove(object)SortedList mySL = new SortedList(); mySL.Add( "3c", "dog" ); mySL.Add( "2c", "over" ); mySL.Add( "3a", "the" ); mySL.Add( "3b", "lazy" ); mySL.Remove( "3b" ); //sucessful to remove Copy after login SortedList<int, string> sortedList = new SortedList<int, string>(); sortedList.Add(9,"gz"); sortedList.Add(3, "lhx");bool removedFlag = sortedList.Remove(3); //true Copy after login ImplementICompare impleCompare = new ImplementICompare(); SortedList<int, string> sortedList = new SortedList<int, string>(impleCompare); sortedList.Add(9,"gz"); sortedList.Add(3, "lhx");bool removedFlag = sortedList.Remove(3); //false Copy after login 这是需要注意的一个地方,构造器带有impleCompare实现了排序接口时,好像不能移除某个元素,需要待确认。 RemoveAt(int index)SortedList sorted = new SortedList(); sorted.Add(9, "gz"); sorted.Add(3, "lhx"); sortedList.RemoveAt(1); //在排序后的位置移除,sortedList的一个对的键 为3,第二个对的键为9,因此移除了9这个键值对 Copy after login 5-4 性能一个SortedList的操作相比Hashtable对象是要慢些的,由于它实现了排序功能。但是,SortedList提供了访问的方便性,由于既可以通过index,也可以通过key去访问元素。 6 .net容器相关接口
7 Interface UML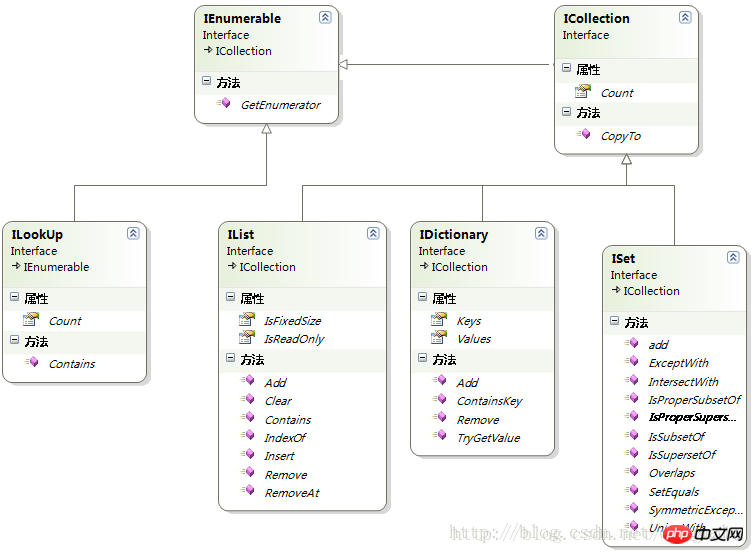 8 Time complexity of each container
Statement of this Website
The content of this article is voluntarily contributed by netizens, and the copyright belongs to the original author. This site does not assume corresponding legal responsibility. If you find any content suspected of plagiarism or infringement, please contact admin@php.cn

Hot AI Tools
Undresser.AI UndressAI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos 
AI Clothes RemoverOnline AI tool for removing clothes from photos. 
Undress AI ToolUndress images for free 
Clothoff.ioAI clothes remover 
AI Hentai GeneratorGenerate AI Hentai for free. 
Hot Article
Assassin's Creed Shadows: Seashell Riddle Solution
3 weeks ago
By DDD
What's New in Windows 11 KB5054979 & How to Fix Update Issues
2 weeks ago
By DDD
Where to find the Crane Control Keycard in Atomfall
3 weeks ago
By DDD
Saving in R.E.P.O. Explained (And Save Files)
1 months ago
By 尊渡假赌尊渡假赌尊渡假赌

Hot Tools
Notepad++7.3.1Easy-to-use and free code editor 
SublimeText3 Chinese versionChinese version, very easy to use 
Zend Studio 13.0.1Powerful PHP integrated development environment 
Dreamweaver CS6Visual web development tools 
SublimeText3 Mac versionGod-level code editing software (SublimeText3) 
Hot Topics
CakePHP Tutorial
 1386
1386
 52
52
 Active Directory with C#
Sep 03, 2024 pm 03:33 PM
Active Directory with C#
Sep 03, 2024 pm 03:33 PM
Guide to Active Directory with C#. Here we discuss the introduction and how Active Directory works in C# along with the syntax and example.  C# Serialization
Sep 03, 2024 pm 03:30 PM
C# Serialization
Sep 03, 2024 pm 03:30 PM
Guide to C# Serialization. Here we discuss the introduction, steps of C# serialization object, working, and example respectively.  Random Number Generator in C#
Sep 03, 2024 pm 03:34 PM
Random Number Generator in C#
Sep 03, 2024 pm 03:34 PM
Guide to Random Number Generator in C#. Here we discuss how Random Number Generator work, concept of pseudo-random and secure numbers.  C# Data Grid View
Sep 03, 2024 pm 03:32 PM
C# Data Grid View
Sep 03, 2024 pm 03:32 PM
Guide to C# Data Grid View. Here we discuss the examples of how a data grid view can be loaded and exported from the SQL database or an excel file.  Patterns in C#
Sep 03, 2024 pm 03:33 PM
Patterns in C#
Sep 03, 2024 pm 03:33 PM
Guide to Patterns in C#. Here we discuss the introduction and top 3 types of Patterns in C# along with its examples and code implementation.  Prime Numbers in C#
Sep 03, 2024 pm 03:35 PM
Prime Numbers in C#
Sep 03, 2024 pm 03:35 PM
Guide to Prime Numbers in C#. Here we discuss the introduction and examples of prime numbers in c# along with code implementation.  Factorial in C#
Sep 03, 2024 pm 03:34 PM
Factorial in C#
Sep 03, 2024 pm 03:34 PM
Guide to Factorial in C#. Here we discuss the introduction to factorial in c# along with different examples and code implementation.  The difference between multithreading and asynchronous c#
Apr 03, 2025 pm 02:57 PM
The difference between multithreading and asynchronous c#
Apr 03, 2025 pm 02:57 PM
The difference between multithreading and asynchronous is that multithreading executes multiple threads at the same time, while asynchronously performs operations without blocking the current thread. Multithreading is used for compute-intensive tasks, while asynchronously is used for user interaction. The advantage of multi-threading is to improve computing performance, while the advantage of asynchronous is to not block UI threads. Choosing multithreading or asynchronous depends on the nature of the task: Computation-intensive tasks use multithreading, tasks that interact with external resources and need to keep UI responsiveness use asynchronous. 
|


